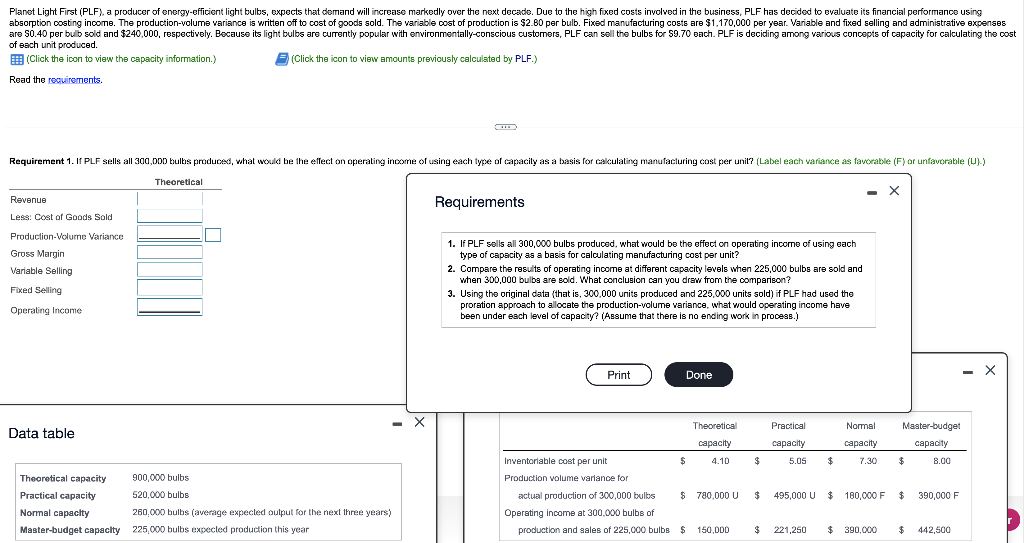
Planet Light First (PLF), a producer of energy-efficient light bulbs, expects that demand will increase markedly over the next decade. Due to the high fixed costs involved in the business, PLF has decided to evaluate its financial performance using absorption costing income. The production-volume variance is written off to cost of goods sold. The variable cost of production is $2.80 per bulb. Fixed manufacturing costs are $1,170,000 per year. Variable and fixed selling and administrative expenses are 50.40 per bulb sold and $240,000, respectively. Because its light bulbs are currently popular with environmentally-conscious customers, PLF can sell the bulbs for 59.70 each. PLF is deciding among various concepts of capacity for calculating the cost of each unit produced. (Click the icon to view the capacity information.) (Click the icon to view amounts previously calculated by PLF.) Read the requirements. Requirement 1. If PLF sells all 300,000 bulbis produced, what would be the effect on operating income of using each type of capacity as a basis for calculating manufacturing cost per unit? (Label each variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).) Theoretical - X Revenue Requirements Less: Cost of Goods Sold Production-Volume Variance Gross Margin Variable Selling 1. If PLF sells all 300,000 bulbs produced, what would be the effect on operating income of using each type of capacity as a basis for calculating manufacturing cost per unit? 2. Compare the results of operating income at different capacity levels when 225,000 bulbs are sold and when 300,000 bulbs are sold. What conclusion can you draw from the comparison? 3. Using the original data (that is, 300,000 units produced and 225,000 units sold) if PLF had used the proration approach to allocate the production-volume variance, what would operating income have been under each level of capacity? (Assume that there is no ending work in process.) Fixed Selling Operating Income Print Done - X Normal Data table Practical capacity Master-budget capacity capacity 5.05 $ 7.30 $ 8.00 Theoretical capacity Inventoriable cost per unit $ 4.10 Production volume variance for actual production of 300,000 bulbs $ 780,000 U Operating income at 300.000 bulbs of production and sales of 225,000 bulbs S 150,0DD $ 495,000 U $ 180,000 F $ Theoretical capacity 900,000 bulbs Practical capacity 520.000 bulbs Normal capacity 260.000 bulbs (average expected output for the next three years) Master-budget capacity 225,000 bulbs expected production this year 390,000 F r $ 221,250 $ 390,000 $ 442,500







