please answer all of the questions posted below. Please include all calculations made on excel and how it would look in the end. Appreciate all the help!
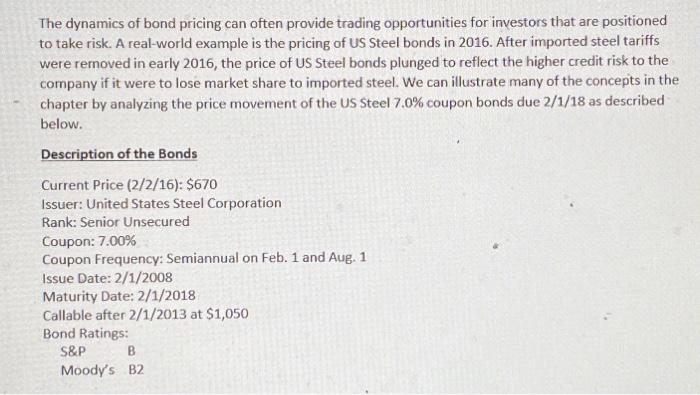
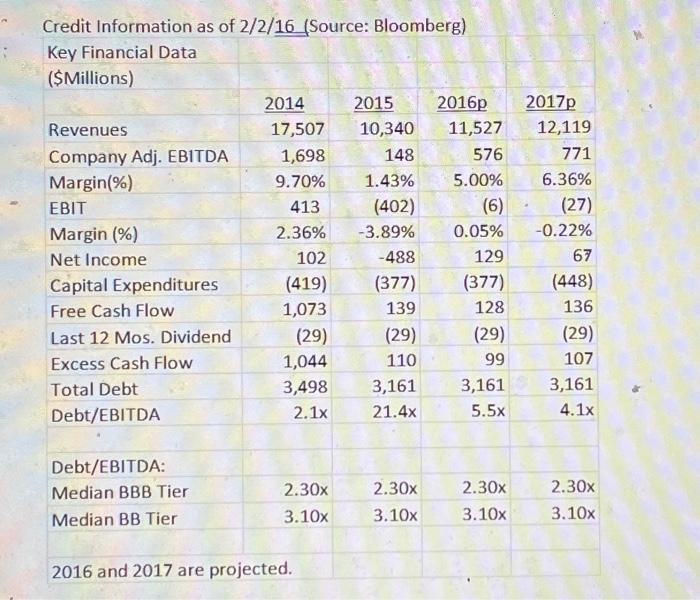
The dynamics of bond pricing can often provide trading opportunities for investors that are positioned to take risk. A real-world example is the pricing of US Steel bonds in 2016. After imported steel tariffs were removed in early 2016, the price of US Steel bonds plunged to reflect the higher credit risk to the company if it were to lose market share to imported steel. We can illustrate many of the concepts in the chapter by analyzing the price movement of the US Steel 7.0% coupon bonds due 2/1/18 as described below. Description of the Bonds Current Price (2/2/16):$670 Issuer: United States Steel Corporation Rank: Senior Unsecured Coupon: 7.00% Coupon Frequency: Semiannual on Feb. 1 and Aug. 1 Issue Date: 2/1/2008 Maturity Date: 2/1/2018 Callable after 2/1/2013 at $1,050 Bond Ratings: S&PMoodysBB2 Credit Information as of 2/2/16 (Source: Bloomberg) You may show your calculations on an Excel spreadsheet and answer the non-computational parts of questions on a Word document. Alternatively, you can put the written responses in a text box in Excel. 1) (5 points) Based on the above information, what is the bond's annualized yield to maturity as of 2/2/16 ? Show your calculations on an attached Excel spreadsheet. 2) (10 points) Evaluate the financial condition of US Steel as of the beginning of 2016 from the information in the table. Note that the metrics for calendar years 2016 and 2017 are projected. Review the financial analysis in Chapter 2 and the credit rating descriptions in Chapter 6. Identify the weaknesses that support the current B credit rating by Standard \& Poor's. Note: Free cash flow is defined as Cash Flow from Operating Activities (the top third of the Statement of Cash Flows) less capital expenditures. It measures the cash flow available to return to the company's investors, both bondholders and stockholders. Debt/EBITDA measures how many years EBITDA (a proxy for cash flow) it takes to pay off the debt. The lower the ratio the stronger the financial condition of the company. Mention specific ratio and line items in your analysis. 3) a) (10 points) Given the junk bond status of US Steel, the yield to maturity calculation may be too optimistic. Assume that there is a 50% probability that the bonds will return $800 at maturity and a 50% probability that the bonds will return full par value. Calculate the average expected price of the bond based on the debt cost of capital from the table below. Then calculate the bond's expected return based on the average expected price. Be sure to show your calculations. b) (5 points) Explain why the expected return on the US Steel bond does not equal the bond's yield to maturity. c) (5 points) Under what macroeconomic conditions would the credit spread between AAArated bonds and B-rated bonds widen? 4) During the early summer of 2016 the import tariffs on foreign steel were reinstated, allowing domestic steel producers to raise their prices. As a result of this policy change, the US Steel 7.0% bonds maturing on 2/1/18 rose to $912 on 8/2/16. a) (5 points) Assuming that the bonds pay the full par value on maturity, what is the yield to maturity on 8/2/16 ? Show your calculations on an Excel Spreadsheet. b) ( 5 points) What is the bond's annualized return from 2/2/16 to 8/2/16 in terms of an effective annual rate (EAR)? Show your calculations. 5) (5 points) Without showing any calculations why would the price of a US Steel bond maturing in 18 months have a higher price than another senior unsecured us Steel bond of equal credit rating maturing in 10 years? Explain in terms of bond pricing and credit risk