Question: Please answer all parts SHOWING ALL STEPS CLEARLY EXPLAINING THE CONCEPTS and make sure all are 100% correct solutions and do NOT use calculus (integration,
Please answer all parts SHOWING ALL STEPS CLEARLY EXPLAINING THE CONCEPTS and make sure all are 100% correct solutions and do NOT use calculus (integration, Cross product, etc.) to solve any of them. Thank you!

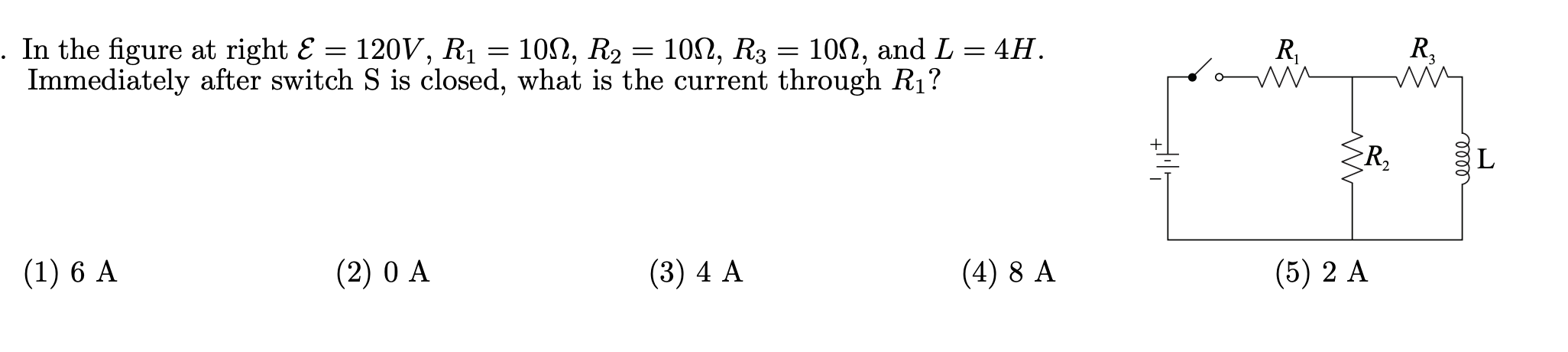

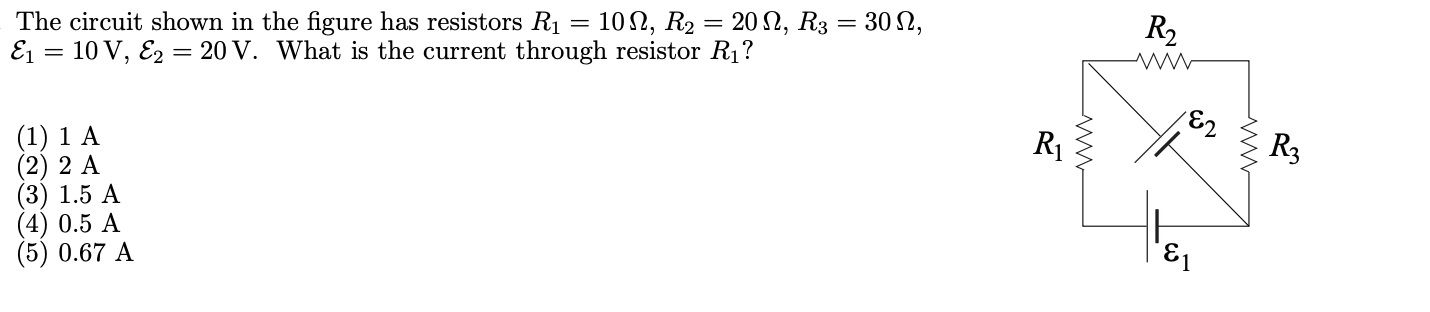

. A negatively charged particle enters a region of uniform magnetic eld pointing in the +z-direction. If it experiences a magnetic force in the wdirecti0n, then its velocity must be pointing: (1) +3! (2) y (3) +93 (4) $ (5) Z In the figure at right & = 120V, R1 = 1002, R2 = 1002, R3 = 100, and L = 4H. R Immediately after switch S is closed, what is the current through R1? R2 L (1) 6 A (2) 0 A (3) 4 A (4) 8 A (5) 2 A. An 8.0 mH inductor and a 3.5 Q resistor are wired in series to a 35 V ideal battery. A switch in the circuit is closed at time 0, at which time the current is 0. At a time 2.4 msec after the switch is thrown the potential difference across the inductor is: (1) 12.2 V (2) 19.2 V (3) 4.4 V (4) 22.8 V (5) 35.0 V The circuit shown in the gure has resistors R1 = 10 Q, R2 = 20 9, R3 = 30 Q, 51 = 10 V, 52 = 20 V. What is the current through resistor R1? (1) 1 A (2) 2 A (3) 1.5 A (4) 0.5 A (5) 0.67 A 31 , A voltmeter has an internal resistance R = 1 M9 and is designed to measure difference of potentials up to 10 V. A student needs to measure a difference of potentials that can be as large as 50 V. The student vaguely recalls that this can be done by adding a resistor to the voltmeter and asks for your guidance: What should be the value of the additional resistor? Should it be connected in series with or parallel to the voltmeter? (1) 4.0 M9, series (2) 5.0 MG, series (3) 0.17 M52, parallel (4) 0.20 MQ, parallel (5) Cannot be done (the max voltage rating of a voltmeter can only be decreased.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


