 Please answer all parts, thank you in advance! If you are having trouble viewing the question, try CTRL+Scroll to zoom on the image and you will see it!
Please answer all parts, thank you in advance! If you are having trouble viewing the question, try CTRL+Scroll to zoom on the image and you will see it!
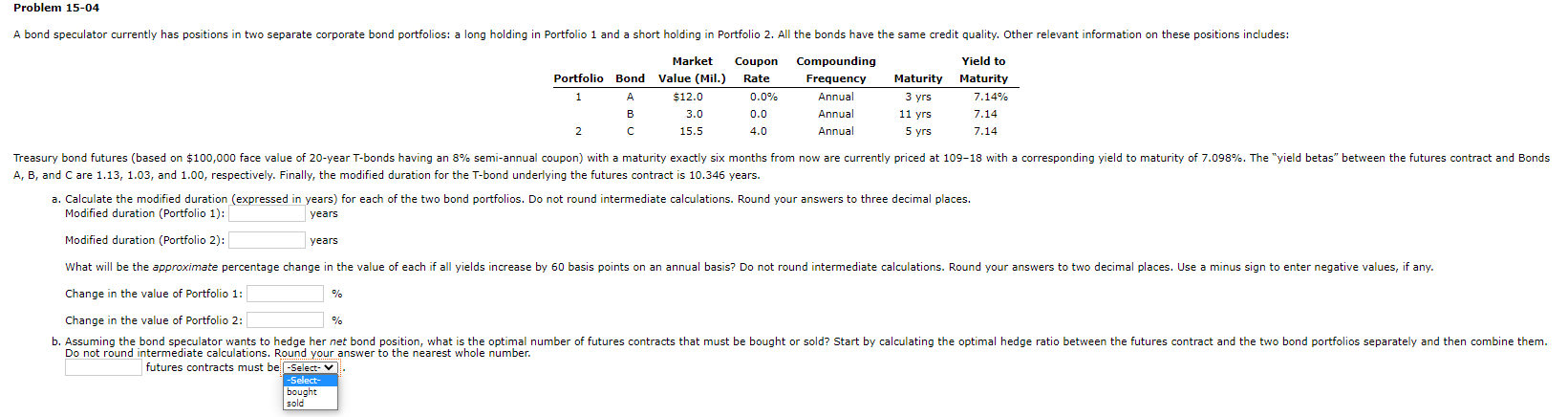
Problem 15-04 A bond speculator currently has positions in two separate corporate bond portfolios: a long holding in Portfolio 1 and a short holding in Portfolio 2. All the bonds have the same credit quality. Other relevant information on these positions includes: Market Coupon Compounding Yield to Portfolio Bond Value (Mil.) Rate Frequency Maturity Maturity 1 A $12.0 0.0% Annual 3 yrs 7.14% B 3.0 0.0 Annual 11 yrs 7.14 2 15.5 4.0 Annual 5 yrs 7.14 Treasury bond futures (based on $100,000 face value of 20-year T-bonds having an 8% semi-annual coupon) with a maturity exactly six months from now are currently priced at 109-18 with a corresponding yield to maturity of 7.098%. The "yield betas" between the futures contract and Bonds A, B, and C are 1.13, 1.03, and 1.00, respectively. Finally, the modified duration for the T-bond underlying the futures contract is 10.346 years. a. Calculate the modified duration (expressed in years) for each of the two bond portfolios. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to three decimal places. Modified duration (Portfolio 1): years Modified duration (Portfolio 2): years What will be the approximate percentage change in the value of each if all yields increase by 60 basis points on an annual basis? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Use a minus sign to enter negative values, if any. Change in the value of Portfolio 1: Change in the value of Portfolio 2: b. Assuming the bond speculator wants to hedge her net bond position, what is the optimal number of futures contracts that must be bought or sold? Start by calculating the optimal hedge ratio between the futures contract and the two bond portfolios separately and then combine them. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest whole number. futures contracts must be -Select- V. -Select- bought sold Problem 15-04 A bond speculator currently has positions in two separate corporate bond portfolios: a long holding in Portfolio 1 and a short holding in Portfolio 2. All the bonds have the same credit quality. Other relevant information on these positions includes: Market Coupon Compounding Yield to Portfolio Bond Value (Mil.) Rate Frequency Maturity Maturity 1 A $12.0 0.0% Annual 3 yrs 7.14% B 3.0 0.0 Annual 11 yrs 7.14 2 15.5 4.0 Annual 5 yrs 7.14 Treasury bond futures (based on $100,000 face value of 20-year T-bonds having an 8% semi-annual coupon) with a maturity exactly six months from now are currently priced at 109-18 with a corresponding yield to maturity of 7.098%. The "yield betas" between the futures contract and Bonds A, B, and C are 1.13, 1.03, and 1.00, respectively. Finally, the modified duration for the T-bond underlying the futures contract is 10.346 years. a. Calculate the modified duration (expressed in years) for each of the two bond portfolios. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to three decimal places. Modified duration (Portfolio 1): years Modified duration (Portfolio 2): years What will be the approximate percentage change in the value of each if all yields increase by 60 basis points on an annual basis? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Use a minus sign to enter negative values, if any. Change in the value of Portfolio 1: Change in the value of Portfolio 2: b. Assuming the bond speculator wants to hedge her net bond position, what is the optimal number of futures contracts that must be bought or sold? Start by calculating the optimal hedge ratio between the futures contract and the two bond portfolios separately and then combine them. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest whole number. futures contracts must be -Select- V. -Select- bought sold
 Please answer all parts, thank you in advance! If you are having trouble viewing the question, try CTRL+Scroll to zoom on the image and you will see it!
Please answer all parts, thank you in advance! If you are having trouble viewing the question, try CTRL+Scroll to zoom on the image and you will see it!





