please answer all sections
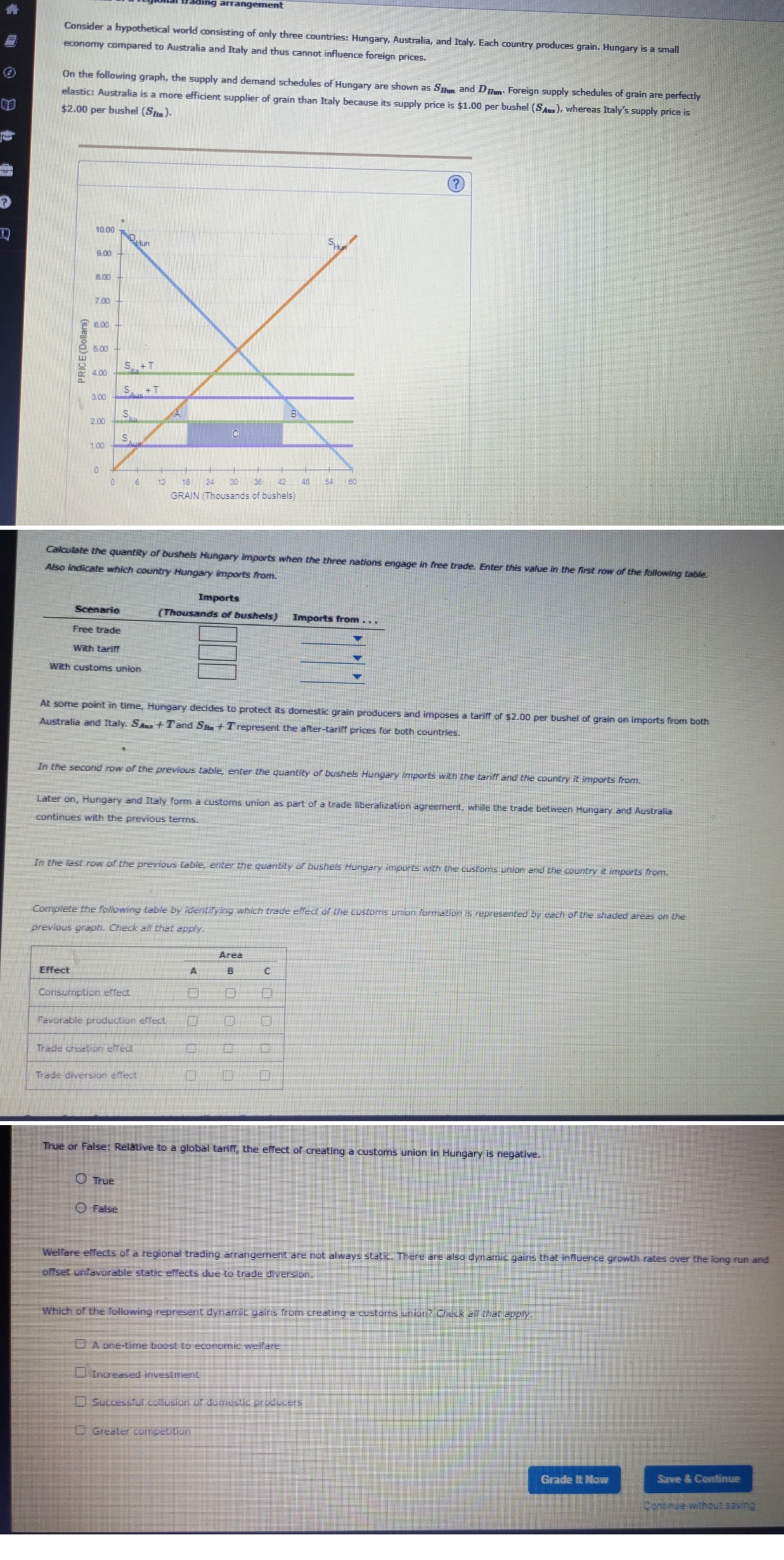
Consider a hypothetical world consisting of only three countries: Hungary, Australia, and Italy. Each country produces grain. Hungary is a small economy compared to Australia and Italy and thus cannot influence foreign prices. On the following graph, the supply and demand schedules of Hungary are shown as $fun and D Hun. Foreign supply schedules of grain are perfectly elastic: Australia is a more efficient supplier of grain than Italy because its supply price is $1.00 per bushel (SAm.), whereas Italy's supply price is $2.00 per bushel (Site). ? 10.00 ur SH 9.00 8.00 7,00 6.00 e 4 00 S. +T S +T 3:00 S 200 S 100 0 12 18 24 30 42 48 54 GRAIN (Thousands of bushels) Calculate the quantity of bushels Hungary imports when the three nations engage in free trade. Enter this value in the first row of the following table. Also indicate which country Hungary imports from Imports Scenario (Thousands of bushels) Imports from . . . Free trade With tariff With customs union At some point in time, Hungary decides to protect its domestic grain producers and imposes a tariff of $2.00 per bushel of grain on imports from both Australia and Italy. SAm + Tand Sme + T represent the after-tariff prices for both countries. In the second row of the previous table, enter the quantity of bushels Hungary imports with the tariff and the country it imports from. Later on, Hungary and Italy form a customs union as part of a trade liberalization agreement, while the trade between Hungary and Australia continues with the previous terms. In the last row of the previous table, enter the quantity of bushels Hungary imports with the customs union and the country it imports from. Complete the following table by identifying which trade effect of the customs union formation is represented by each of the shaded areas on the previous graph. Check all that apply. Area Effect A B Consumption effect Favorable production effect Trade creation effect Trade diversion effect True or False: Relative to a global tariff, the effect of creating a customs union in Hungary is negative. True O False Welfare effects of a regional trading arrangement are not always stalk. There are also dynamic gains that influence growth rates over the long run and offset unfavorable static effects due to trade diversion. Which of the following represent dynamic gains from creating a customs union? Check all that apply. O A one-time boost to economic welfare D Increased investment [) Successful collusion of domestic producers Greater competition Grade It Now Save & Continue Continue without saving