Question: Please answer all the questions properly all the relevant in is provided. Pls try your best! im Counting on u! Thank uuuuu :) Please write



![A flying saucer moving initially at 20 m/s[E] accelerates to 50 m/s[W]](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/66739402d0318_56266739402b3ff7.jpg)



Please answer all the questions properly all the relevant in is provided. Pls try your best! im Counting on u! Thank uuuuu :)



![m[W] of its owner, and then secondly to a position 12.6 m[E]](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/667394065aefe_5666673940635a20.jpg)


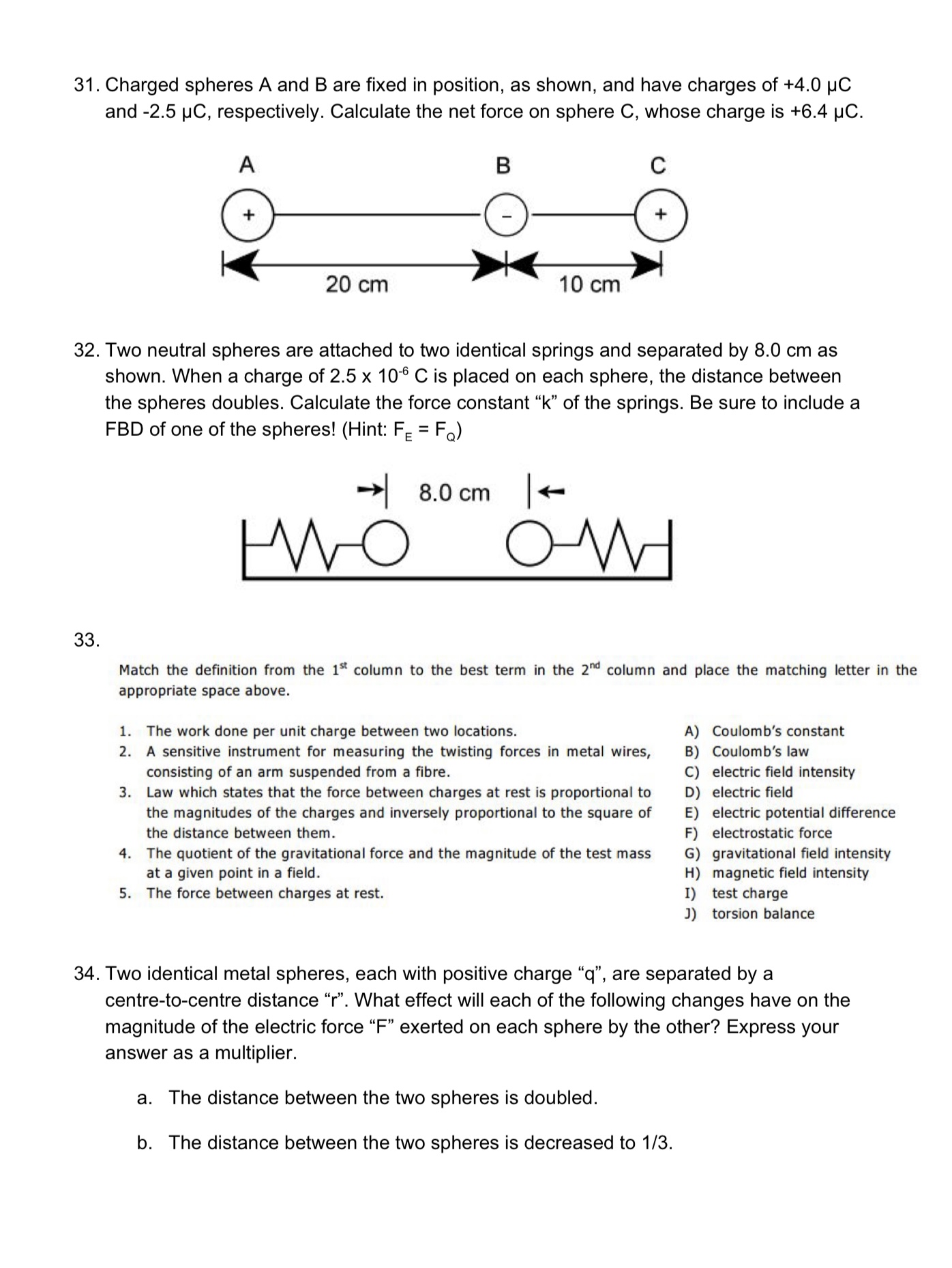


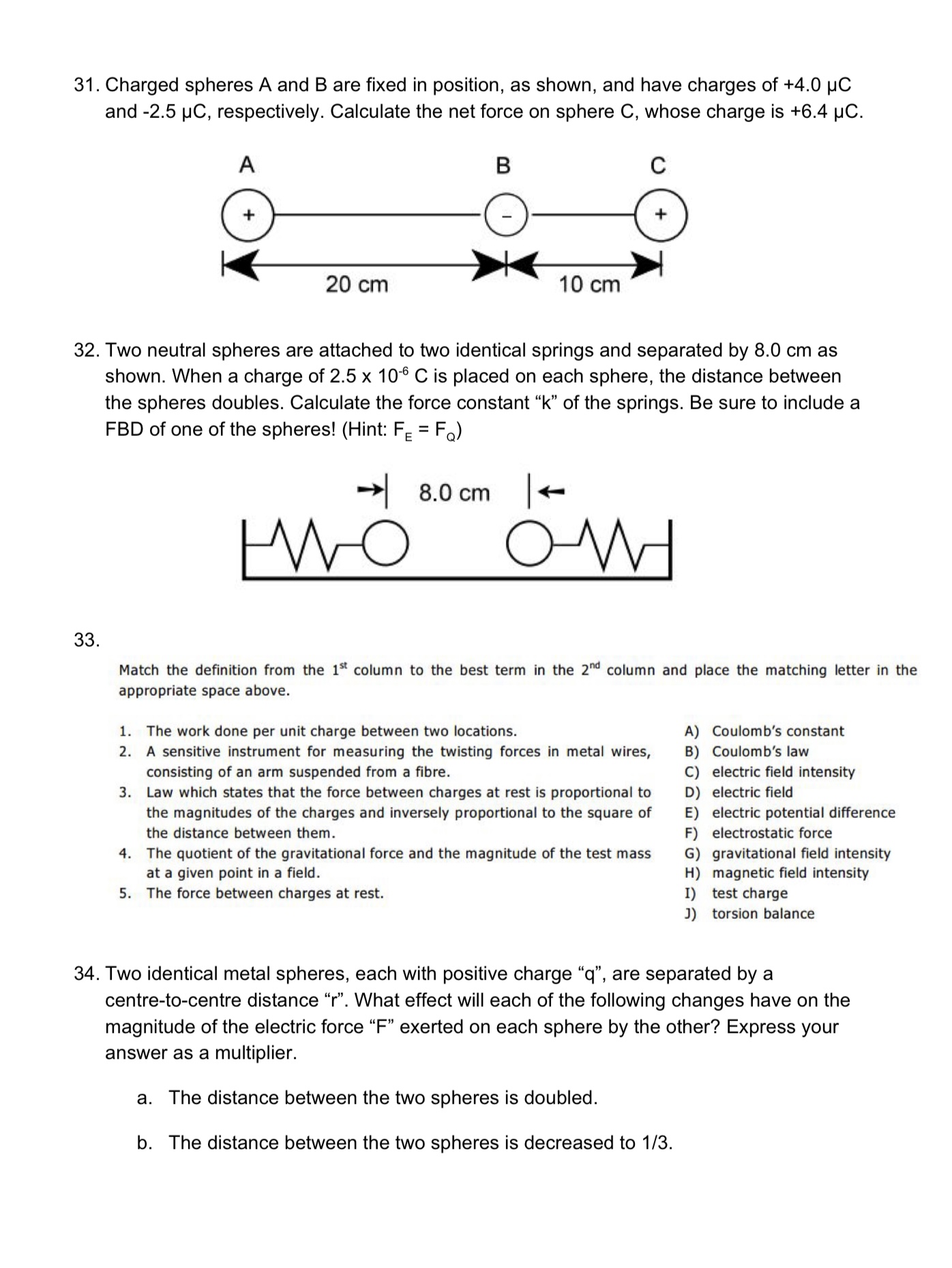
Please write your answers (showing all steps) neatly and clearly. This assignment has 50 questions and should take you 2 hours to complete. 1. A flying saucer moving initially at 20 m/s[E] accelerates to 50 m/s[W] in 3.8 s. Find the saucer's average acceleration during the time interval. 2. R.R. Hood is travelling to visit her grandmother. First, she travels at an average speed of 12 km/h for 10 km. Then she travels at 8.0 km/h for another 1.25 h. Calculate her average speed for the entire trip to grandma's house? (Don't worry about the return trip - she catches a ride with B.B. Wolf) 3. A dog, initially sitting next to its owner, runs first to a position 2.8 m[W] of its owner, and then secondly to a position 12.6 m[E] of its owner. a. Draw a diagram showing the (i) position vectors and (ii) resultant displacement vector in this situation. b. Determine the dog's total distance and total displacement. 4. Match the definition from the 15 column to the best term in the 2 column and place the matching letter in the appropriate space on your answer sheet. 1. Total displacement of an object per unit time A acceleration 2. The area under this graph is used to construct the corresponding position-time acceleration-time graph graph. displacement distance 3. Quantity that has magnitude, but no direction. position-tin 4. Total length of path travelled by an object as it moves from one position to scalar quantity another speed 5. The slope of this graph is used to construct the corresponding velocity-time vector quantity velocity graph. velocity-time graph 5. A store clerk pushes a parcel along a counter with a force of 17.7 N[W]. The parcel has a mass of 2.5 kg. The kinetic friction acting on the parcel is 6.5 N[E]. a. Draw a FBD of the parcel as it is being pushed. Be sure to label your forces appropriately and to include values. b. Calculate the net force acting on the parcel. c. Calculate the acceleration of the parcel. d. Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction between the parcel and the counter.6. Two crates, of mass 12.0 kg and 20.0 kg, respectively, are pushed across a smooth (ie no friction) floor together, the 12 kg crate in front of the 20 kg crate. Their acceleration is 3.50 mlsz. a. Calculate the force applied to push the crates. Don't forget to include a FBD. b. Calculate the action-reaction force between the two crates. Don't forget to include FBD(s). 7. A child's wagon experiences a frictional force of 63 N whenever it is in motion, regardless of the load it is carrying. An applied horizontal force of 128 N causes the wagon to accelerate at 5.0 mlsz. The same applied force, with a child on the wagon, causes it to accelerate at 1.0 m/sz. a. What is the mass of the sled? Don't for get to include a FBD. b. What is the mass of the child? Don't forget include a FBD. 8. Match the denition from the 15' column to the best term in the 2\"\" column and place the matching letter in the appropriate space on your answer sheet. 1. Quantity of matter in an object. A) 2. Force that opposes the motion between two objects in contact. 8) 3. Ratio of the magnitude of friction to the magnitude of the normal force. C) 4. Force exerted by string, ropes, fibres, and cables. 0) 5. Vector sum of all the forces acting on an object. E} F) G) H) I) J} coefcient of friction force of gravity free-body diagram friction force inertia mass net force normal force tension force weight 9. Assume that for each pulse, a human heart accelerates 2.1 X 10'2 kg of blood from 0.18 m/s2 to 0.28 m/s2 during a time interval of 0.10 5. Calculate the magnitude of: a. the acceleration of the blood b. the net force needed to cause that acceleration 10. An astronaut on the surface of Mars finds that a rock accelerates at 3.6 mls2 when it is dropped. The astronaut also 2 finds that a force scale reads 260 N when the astronaut steps on it. a. What is the astronaut's mass as determined on the surface of Mars? b. What would the force scale read if the astronaut stepped on it on Earth? 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. A sled, 14.0 kg in mass, is being towed over ice by a rope that makes an angle of 30.0\" with the horizontal. A force of 236 N acts along the rope. The frictional force is 100 N. Draw a FBD of the situation. Be sure to label your forces appropriately and to include their values. A skier weighing 300 N (is F = 300 N) hasjust begun descending a 20 slope. The coefcient of kinetic friction is 0.20. Draw a FBD of the situation. Be sure to label your 9 forces appropriately and to include their values. A girl pushes a snow shovel weighing 30 N at a uniform velocity across a sidewalk. The handle of the shovel is inclined at 40 to the horizontal and she pushes along the handle with a force of 150 N. a. Draw a FBD of the situation. Be sure to label your forces appropriately and applied to include values. b. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction? A 8.0 kg mass on a frictionless table is accelerated by a 2.0 kg mass hanging from the table as shown. a. Draw a FBD for each mass. Be sure to label your forces appropriately and to include values (if possible). b. Calculate the acceleration of the blocks. c. Calculate the tension in the rope. A cougar is crouched on the branch of a tree that is 3.82 m above the ground. He sees an unsuspecting rabbit on the ground, sitting 4.12 m from the spot directly below the branch on which he is crouched. Hejumps horizontally and lands on the rabbit. a. How long was the cougar in flight? b. What was the initial velocity of the cougar? A beam of electrons (mass = 9.11 x 103'1 kg) is caused to move in a circular path of radius 3.00 m at a velocity of 2.00 x 107 m/s. a. Find the (i) centripetal acceleration and (ii) centripetal force acting on one electron. b. What type of force supplies the centripetal force? 17. While hiking in the wilderness, you come to the top of a cliff that is 80.0 m high. You throw a stone from the cliff, giving it an initial velocity of 27 m/s at 55 above the horizontal. a. What are the horizontal and vertical components of the initial velocity? b. How long was the stone in flight? c. How far from the base of the cliff does the stone land? 18. A car exiting a freeway enters an icy curve (ie no friction) with a radius of curvature of 175 m is banked at 12. a. Draw a FBD of the situation. Be sure to label your forces appropriately and to include values (if possible). b. At what speed (in kmi'h) must a car travel to ensure that it does not leave the road? 19. If the coefcient of friction between your running shoes and the gym floor is 0.90, what is the smallest circle (radius) that you could run at 6.2 m/s without slipping? Be sure to include a FBD to help you analyze this problem! 20. Match the denition from the I'Icolumn to the best term in the 2"\" column and place the matching letter in the appropriate space on your answer sheet. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Law which states that the applied force is directly proportional to the amount A) conservative force of extension or compression of a spring. B) elastic potential energy Material that does not return precisely to its original form after the applied C) gravitational potentiaienergy force is removed. D) Hooke's law Form of energy that accumulates when an elastic object is bent, stretched, or E) kinetic energy compressed. F) non-conservative force Force that does work on an object in such a way that the amount of work G) plastic done is dependent on the path taken. H) restoring force Form of energy possessed by an object due to its motion. 1) spring constant J) work 21. The force-deformation graph for a non-Hooke's Law spring is shown below. a. How much work must be done to Fm compress the spring 0.16 m? 3.0 . _ 6.0 b. How much potential energy Is stored in the Spring at this compression? 4'0 .~...a~o..a..a....'~t.'.i.a.~..'n. : xfm) 0.54 abs o.i2 one c. What speed would a 1.0 kg mass acquire if it were placed next to this compressed spring, on a smooth, horizontal surface, and then released? 22. A 4.0 kg cart moving at 5.0 m/s[R] collides head-on with a 2.0 kg cart moving at 4.0 m/s[L]. Their collision is cushioned by a linear elastic spring between them. a. What is the total energy of the system before the collision? b. At minimum separation, what is the velocity of each cart? (Hint: @ min. sep. v1' = V2' : len ) c. Calculate the total kinetic energy at minimum separation. d. If the force constant of the spring is 900 Mm, what is its maximum compression during the collision? 23. A bullet's speed may be determined by firing it into a sandbag pendulum, and measuring the vertical height to which the pendulum rises, as shown. (The bullet stays in the sandbag) M = 10.00 kg a. What is the change in gravitational potential energy of the sandbag and bullet during the swing? b. What is the velocity of the sandbag-bullet combination at the start of the swing? c. What is the original velocity of the bullet? d. Explain why the collision between the bullet and the sandbag is inelastic? 24. Determine the momentum of the following objects: a. an electron of mass 9.11 x 10'31 kg travelling north at 6.45 x 106 mfs b. a 4.0 X 105 kg jet travelling south at 755 kmlh 25. What impulse is exerted in each case? a. a force of 35 N[W] on a dynamics cart for 2.3 s b. the Earth pulling down on a 16 kg rock during the 4.0 s it takes to fall from a cliff 26. A student practises his batting at a local batting cage. a. A 0.350 kg baseball is travelling at 46 mls toward the batter. After the batter hits the ball, the ball is travelling at 62 m/s in the opposite direction. What is the impulse of the interaction? b. If the duration of the interaction is 25 ms, what is the average force exerted on the ball by the batter? 27. A 80 kg girl running at 3.5 mlsjumps onto a sled that has a mass of 10 kg and that is moving in the opposite direction to the girl, at 2.0 m/s. What will be the final velocity of the girl and the sled, assuming that she manages to hang on, that the sled is on level snow and that there is no friction? 28. A 125 kg astronaut pushes off from his 2500 kg space capsule, quickly acquiring a constant velocity of 4.0 m/s. (Assume that both the astronaut and spacecraft are at rest to begin with.) a. What is the velocity of the space capsule, after he pushes off? b. If he is tethered to the space capsule by a 20 m line, what time will elapse before the line becomes taut? (Hint: think relative velocities!) 29. Two charged spheres, 3.0 cm apart, repel each other with a force of 2.4 x 10'5 N. Determine the magnitude and sign of the charge on each, if one has twice the charge (of the same sign) as the other. 30. Match the definition from the 1St column to the best term in the 2"" column and place the matching letter in the appropriate space on your answer sheet. U'I-hLAJINJl-l Car design that can expand the duration of a crash. A) closed system System which can exchange both matter and energy with its surroundings. B) conservation of momentum Collision in which kinetic energy is not conserved. C) crumple zone System which can exchange energy with its surroundings but not matter. D) elastic collision Product of an object's mass and its velocity. E) impulse F) inelastic collision G) isolated system H) momentum I) open system J) recoil 31. Charged spheres A and B are fixed in position, as shown, and have charges of +4.0 p0 and -2.5 pC, respectively. Calculate the net force on sphere C, whose charge is +6.4 uC. 900 |(2)|
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Certainly Lets take it step by step 1 Average Acceleration Given Initial velocity vi 20 ms E Final velocity vf 50 ms W Time interval t 38 s First we n... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


