Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please answer every parts of the question. Thanks The Haber-Bosch reaction converts nitrogen (N) and hydrogen (H) gas into ammonia (NH3) at high temperature and
Please answer every parts of the question. Thanks
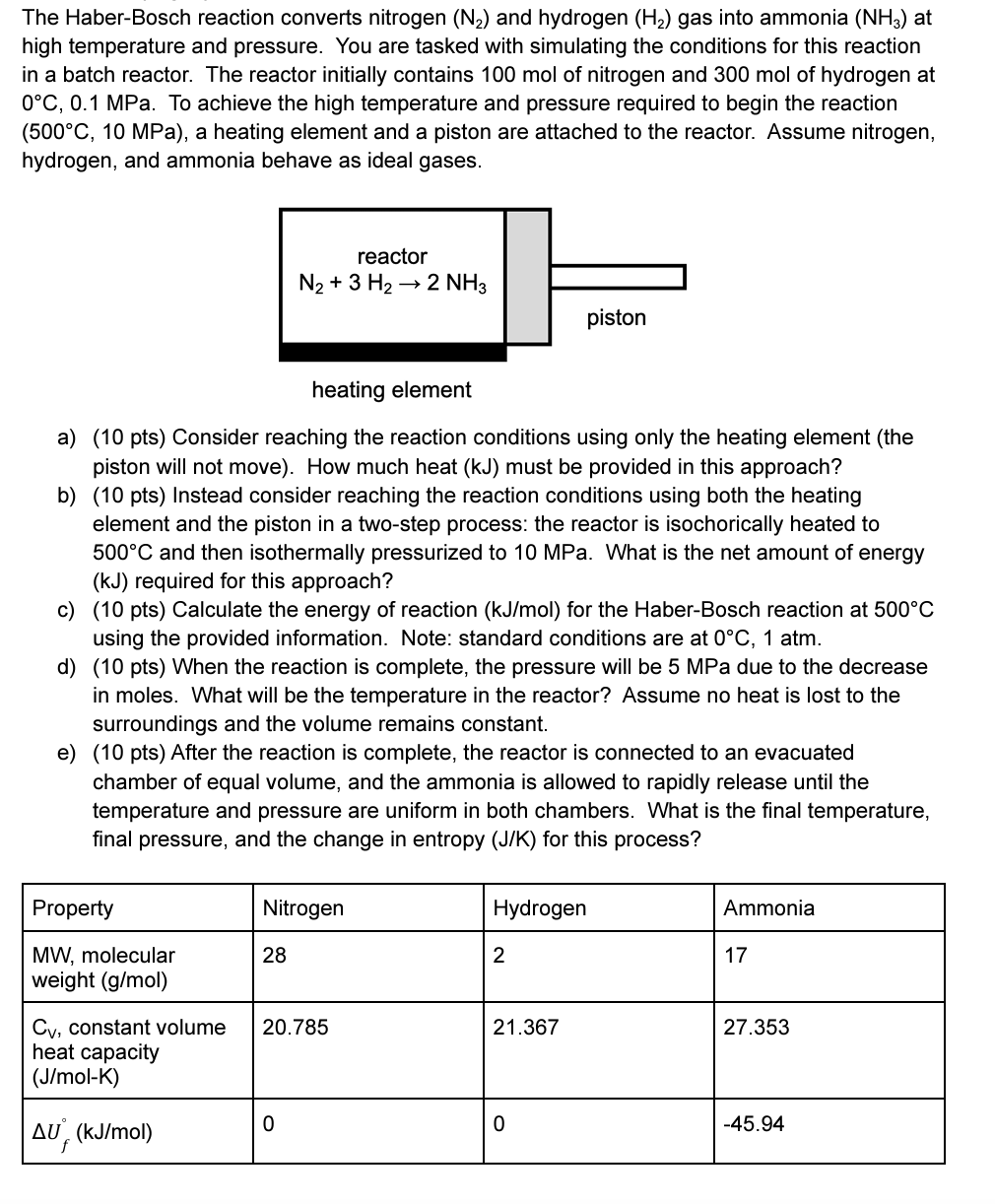
The Haber-Bosch reaction converts nitrogen (N) and hydrogen (H) gas into ammonia (NH3) at high temperature and pressure. You are tasked with simulating the conditions for this reaction in a batch reactor. The reactor initially contains 100 mol of nitrogen and 300 mol of hydrogen at 0C, 0.1 MPa. To achieve the high temperature and pressure required to begin the reaction (500C, 10 MPa), a heating element and a piston are attached to the reactor. Assume nitrogen, hydrogen, and ammonia behave as ideal gases. heating element a) (10 pts) Consider reaching the reaction conditions using only the heating element (the piston will not move). How much heat (kJ) must be provided in this approach? b) (10 pts) Instead consider reaching the reaction conditions using both the heating element and the piston in a two-step process: the reactor is isochorically heated to 500C and then isothermally pressurized to 10 MPa. What is the net amount of energy (kJ) required for this approach? c) (10 pts) Calculate the energy of reaction (kJ/mol) for the Haber-Bosch reaction at 500C using the provided information. Note: standard conditions are at 0C, 1 atm. Property MW, molecular weight (g/mol) d) (10 pts) When the reaction is complete, the pressure will be 5 MPa due to the decrease in moles. What will be the temperature in the reactor? Assume no heat is lost to the surroundings and the volume remains constant. e) (10 pts) After the reaction is complete, the reactor is connected to an evacuated chamber of equal volume, and the ammonia is allowed to rapidly release until the temperature and pressure are uniform in both chambers. What is the final temperature, final pressure, and the change in entropy (J/K) for this process? reactor N + 3 H 2 NH3 AU (kJ/mol) Nitrogen 28 Cv, constant volume 20.785 heat capacity (J/mol-K) 0 Hydrogen 2 piston 21.367 0 Ammonia 17 27.353 -45.94
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.46 Rating (143 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
A a Consider reaching the reaction conditions using only the heating element the piston will not move How much heat kJ must be provided in this approach In order to reach the reaction conditions of 50...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


