Please answer question 2 , I will give you a thumb

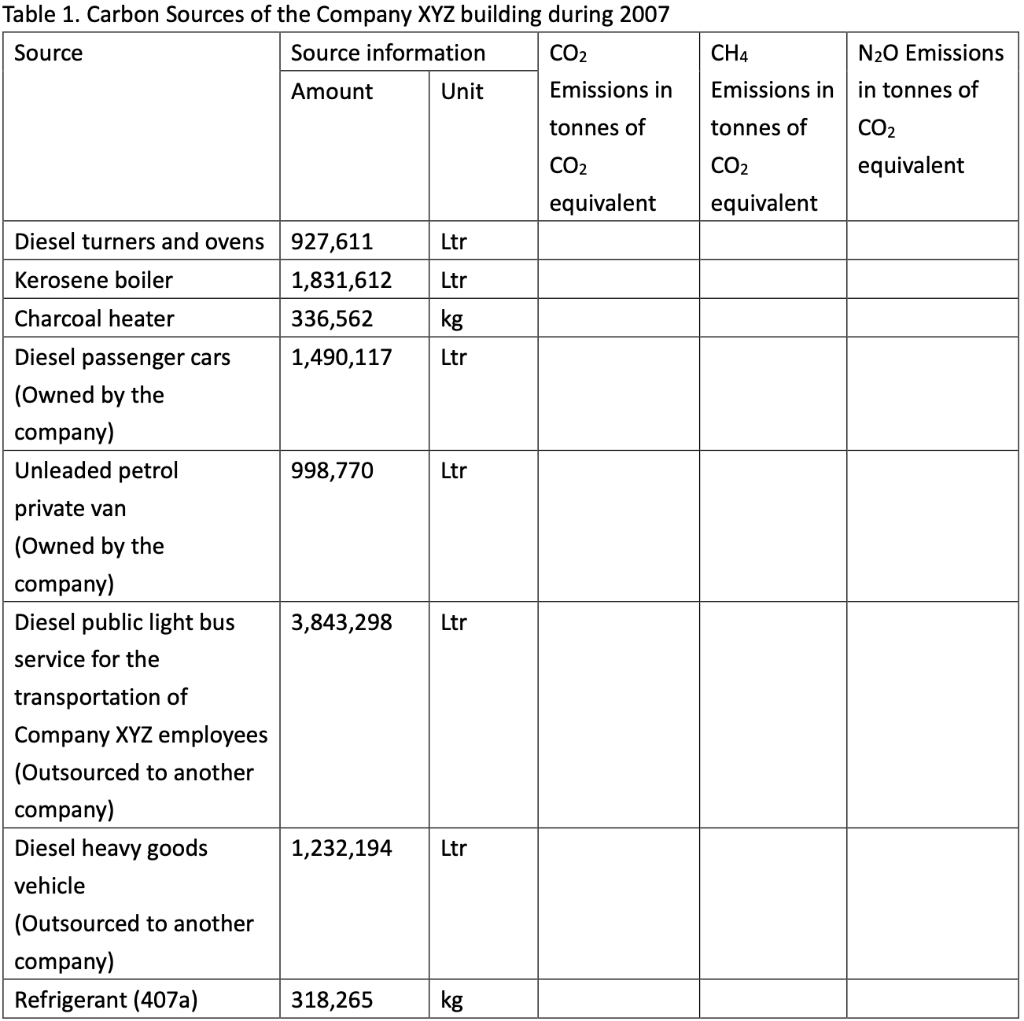
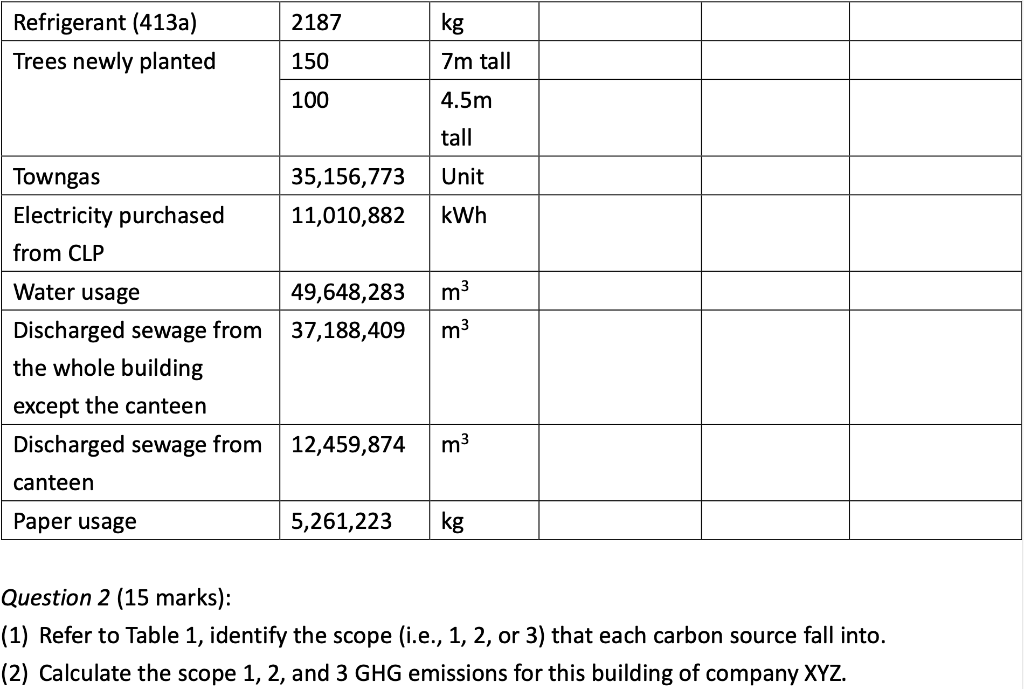
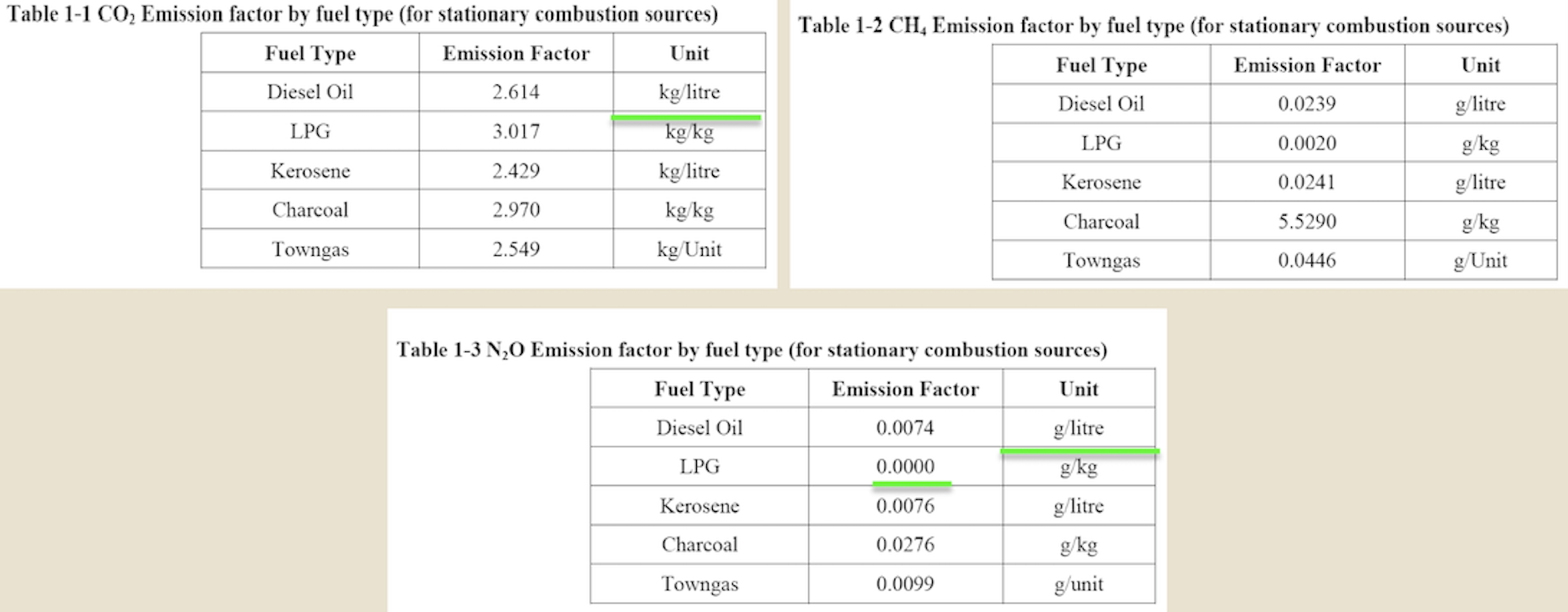

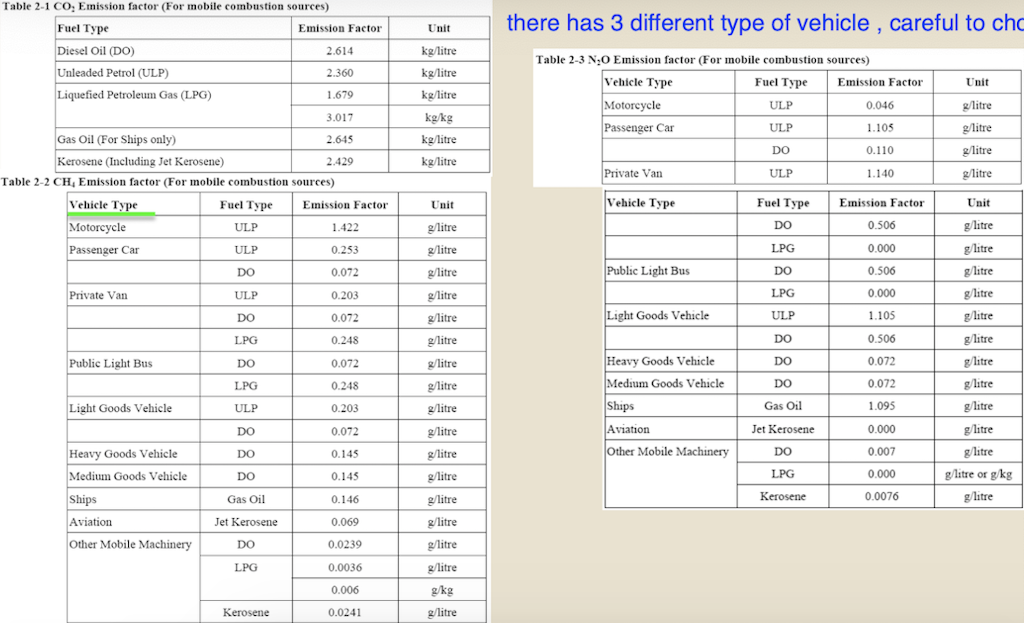
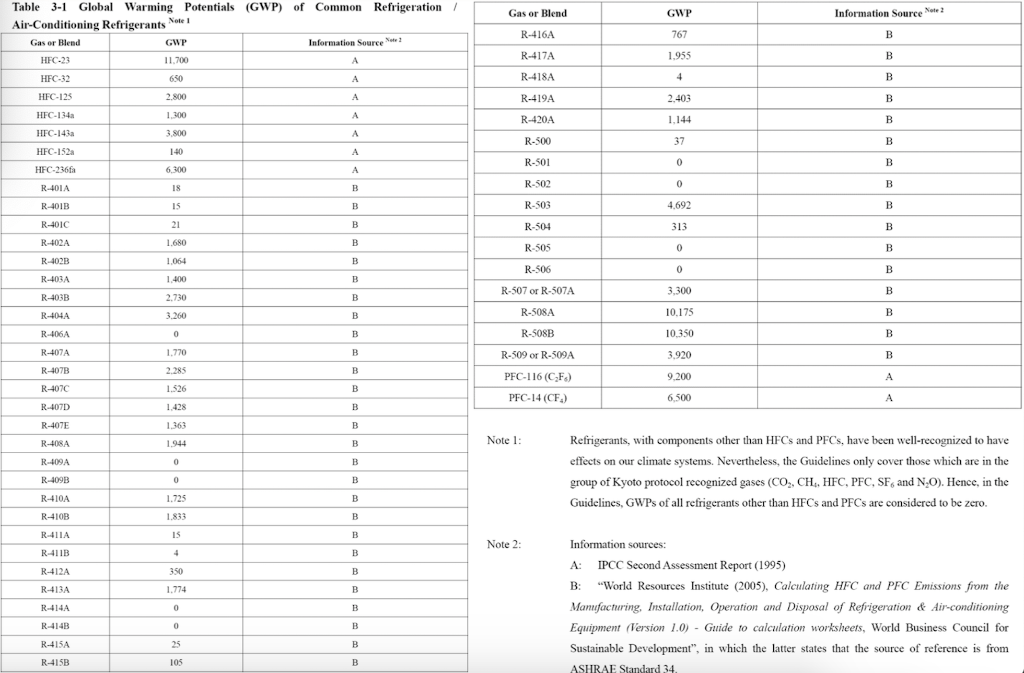
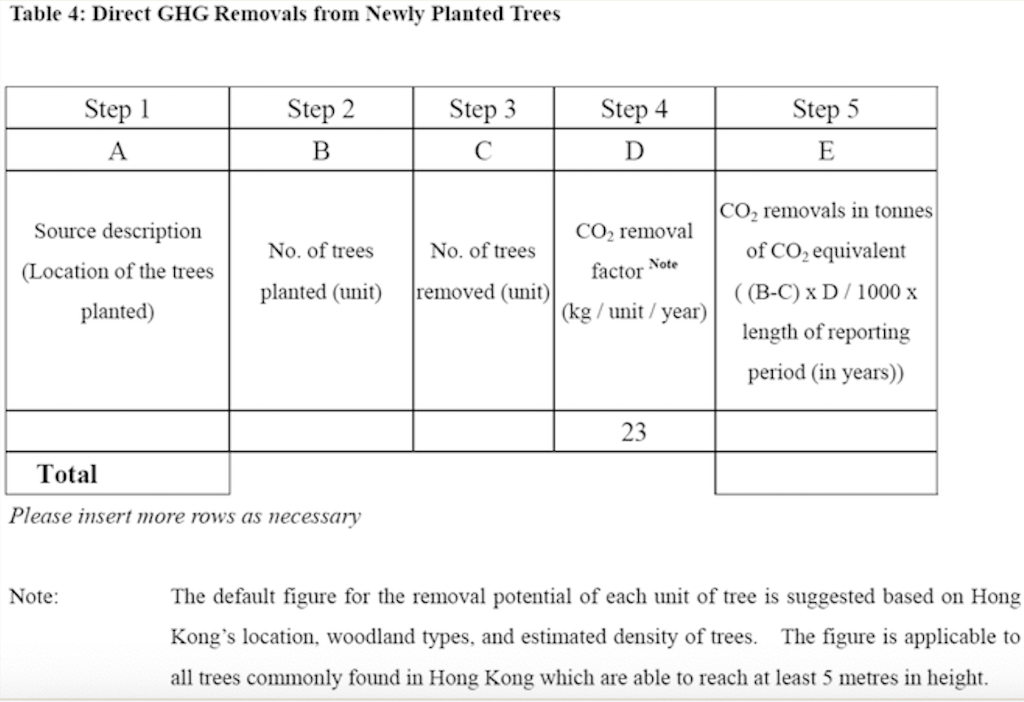
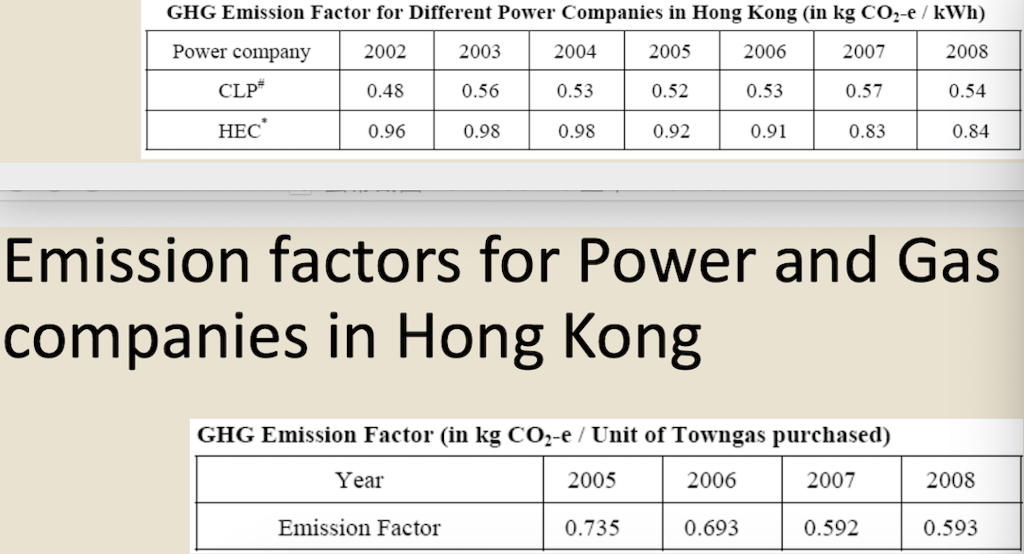
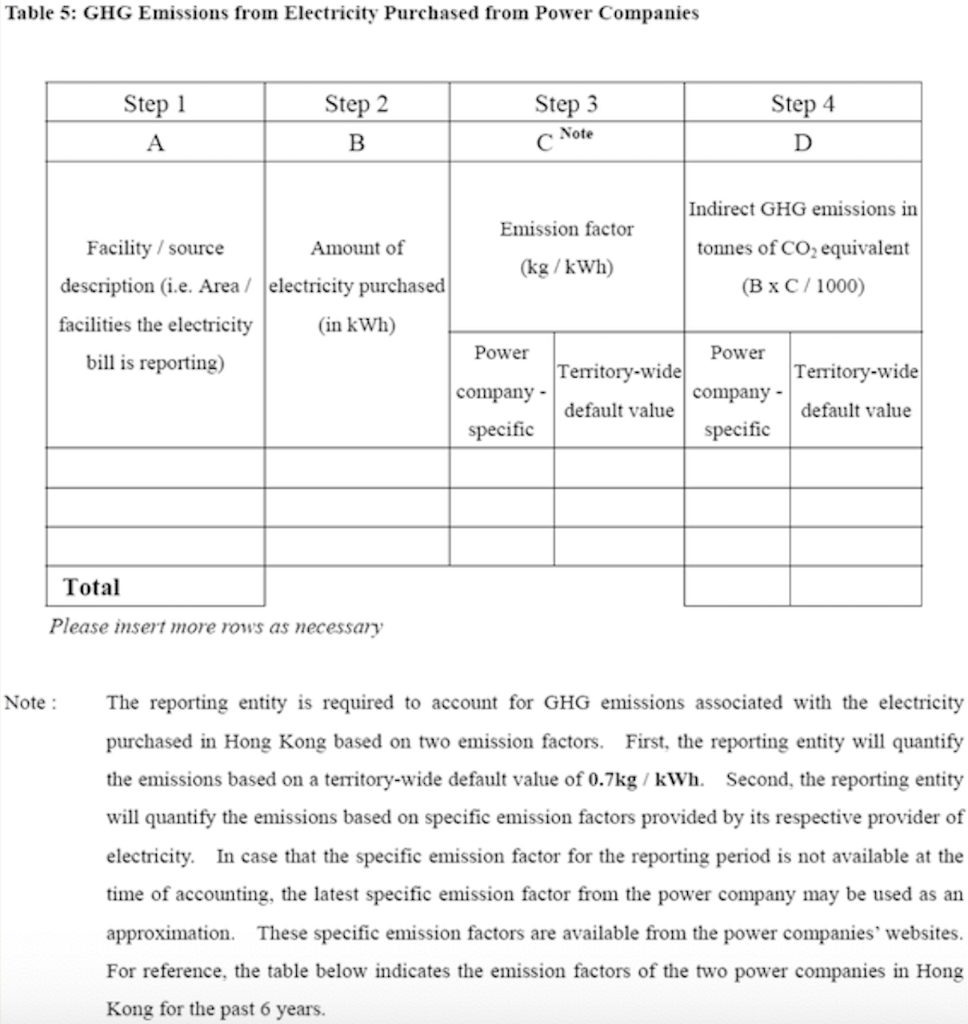
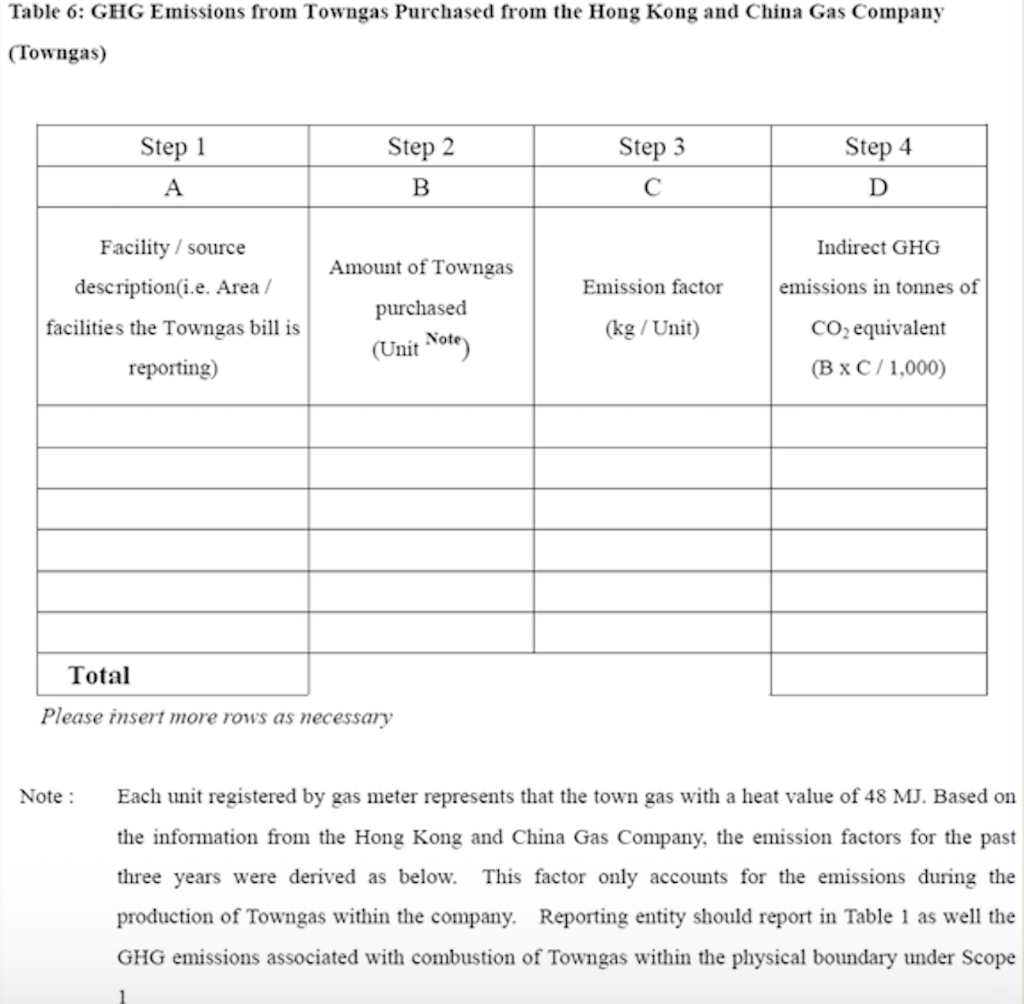

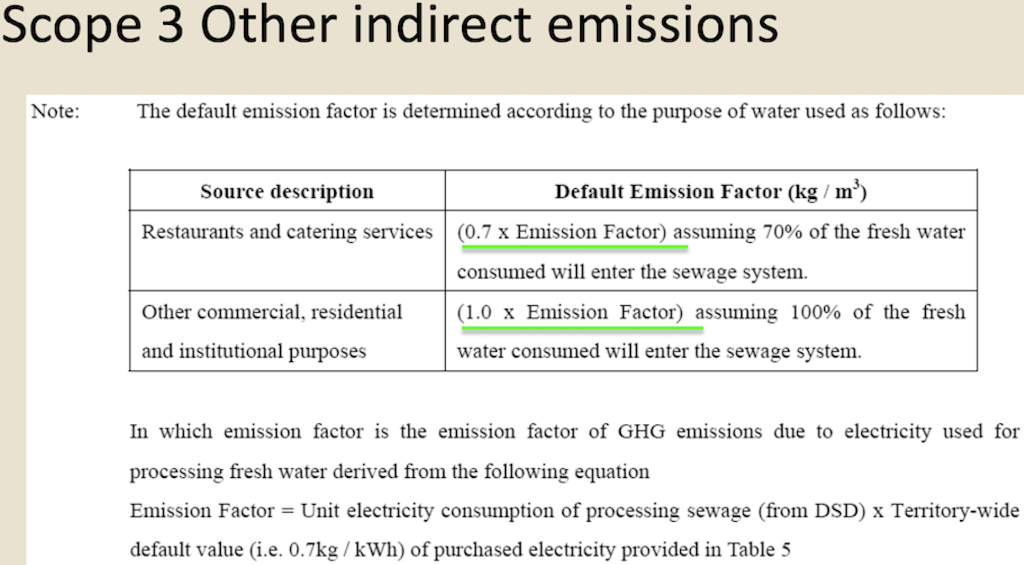
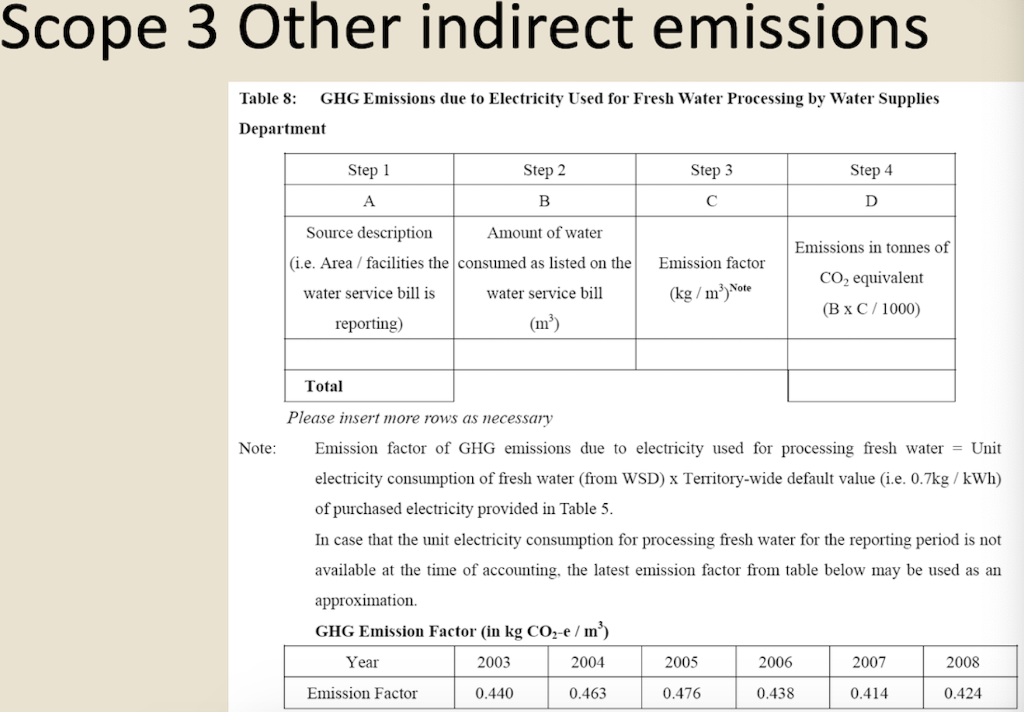
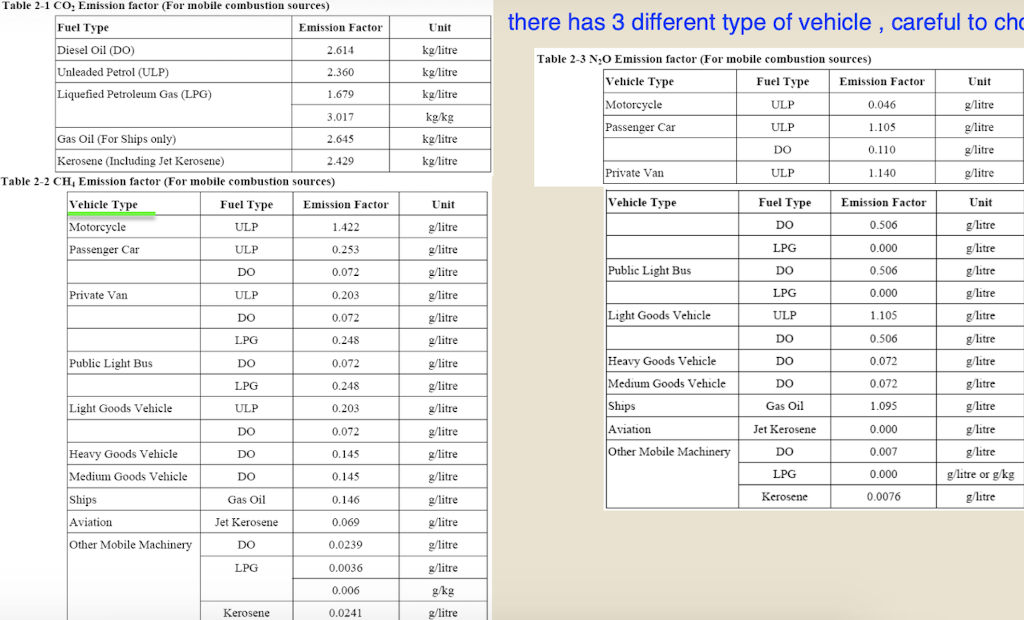
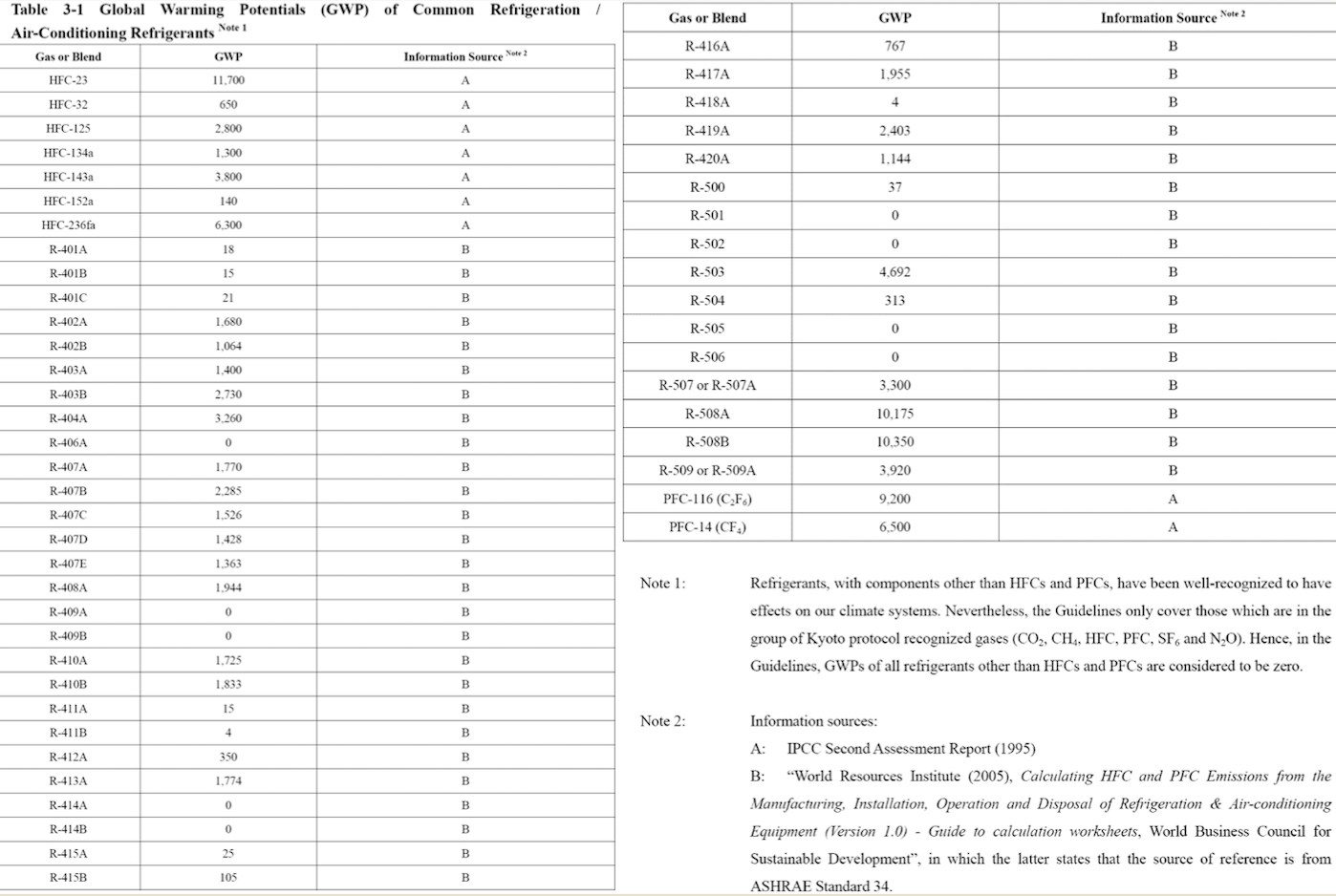
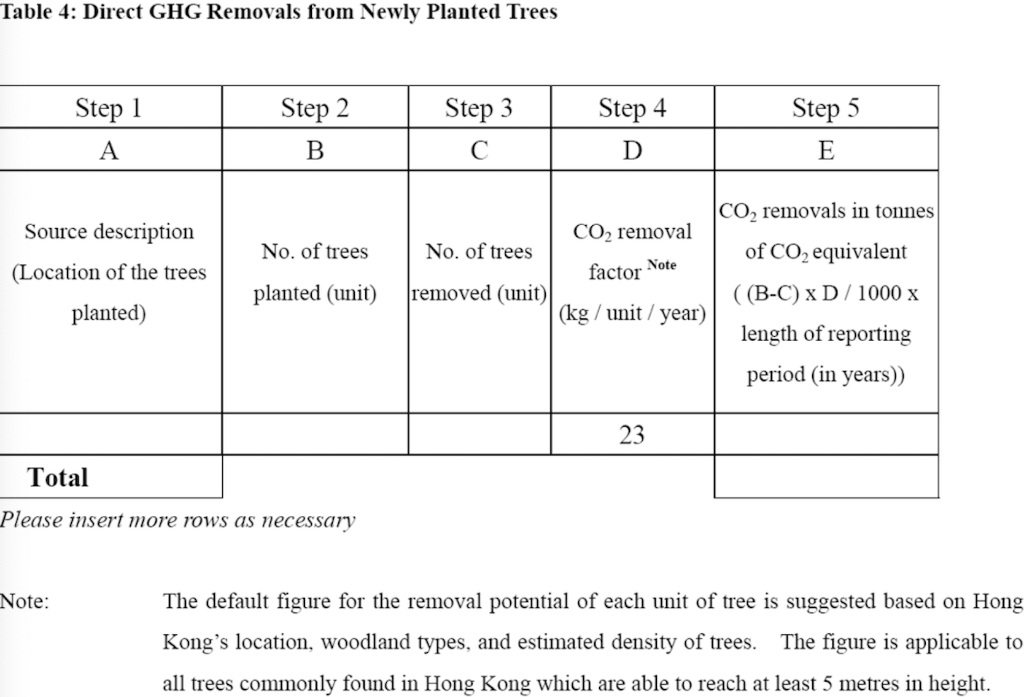
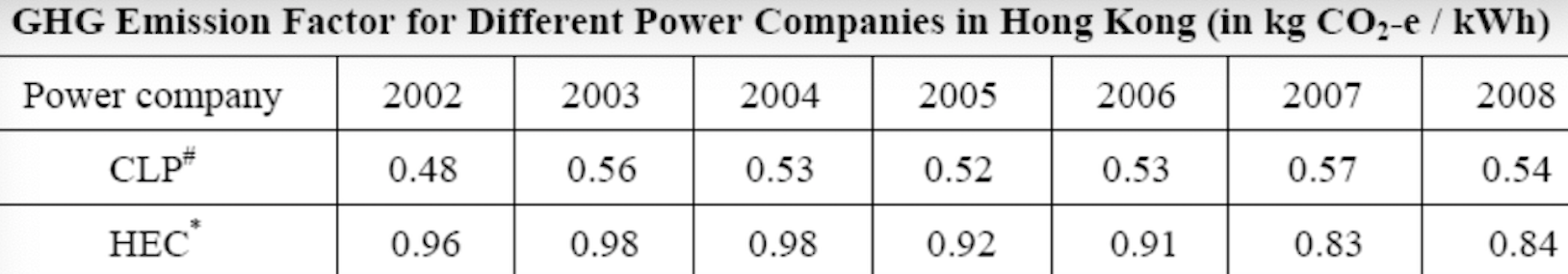
Question 1 (50 marks): Table 1 contains the fuel use data for company XYZ in a building in Hong Kong during 2007. Please help this company to calculate the greenhouse gas emissions for CO2, CH4, and N20. Put N.A. if the cell value is not available. For calculation, please use the emission factors as shown during lecture 5 (slide 46-77), and the global warming potential for CH4 and N20 is 21 and 310, respectively. Table 1. Carbon Sources of the Company XYZ building during 2007 Source Source information CO2 Amount Unit Emissions in tonnes of CH4 N20 Emissions Emissions in in tonnes of tonnes of CO2 CO2 equivalent equivalent CO2 equivalent Diesel turners and ovens Ltr Kerosene boiler Ltr 927,611 1,831,612 336,562 1,490,117 Charcoal heater kg Ltr 998,770 Ltr 3,843,298 Ltr Diesel passenger cars (Owned by the company) Unleaded petrol private van (Owned by the company) Diesel public light bus service for the transportation of Company XYZ employees (Outsourced to another company) Diesel heavy goods vehicle (Outsourced to another company) Refrigerant (407a) 1,232,194 Ltr 318,265 kg 2187 kg Refrigerant (413a) Trees newly planted 150 7m tall 100 4.5m tall Unit Towngas Electricity purchased from CLP 35,156,773 11,010,882 kWh Water usage m? 49,648,283 37,188,409 m3 Discharged sewage from the whole building except the canteen Discharged sewage from 12,459,874 m3 canteen Paper usage 5,261,223 kg Question 2 (15 marks): (1) Refer to Table 1, identify the scope (i.e., 1, 2, or 3) that each carbon source fall into. (2) Calculate the scope 1, 2, and 3 GHG emissions for this building of company XYZ. Table 1-2 CH, Emission factor by fuel type (for stationary combustion sources) Fuel Type Emission Factor Unit Diesel Oil 0.0239 g/litre Table 1-1 CO, Emission factor by fuel type (for stationary combustion sources) Fuel Type Emission Factor Unit Diesel Oil 2.614 kg/litre LPG 3.017 kg/kg Kerosene 2.429 kg/litre Charcoal 2.970 kg/kg Towngas 2.549 kg Unit LPG 0.0020 g/kg Kerosene 0.0241 g/litre Charcoal 5.5290 g/kg g/Unit Towngas 0.0446 Table 1-3 N20 Emission factor by fuel type (for stationary combustion sources) Fuel Type Emission Factor Unit Diesel Oil 0.0074 glitre LPG 0.0000 Kerosene 0.0076 g/kg glitre g/kg g/unit Charcoal 0.0276 Towngas 0.0099 (iii) HFC and PFC Emissions for refrigeration/ Air-conditioning OE = { (C, + C;- Co-Ce); x GWP; = where: OE = Emissions from operation of equipment due to release of refrigerantj (in CO2-equivalent) C = Refrigerant inventory at beginning of the reporting period (in storage, not equipment) (kg) total amount of refrigeration C = Refrigerant added to the inventory during the reporting period (kg) Ca = Refrigerant disposed of through environmentally responsible means (e.g., collected by contractor for recycling) during the reporting period (kg) know to be use or in storage Ce = Refrigerant inventory at end of the reporting period (in storage, not equipment) (kg) GWP=100-year global warming potential of the refrigerant j. Global Warming Potential (GWP) of the corresponding refrigerant can be obtained using Table 3-1. Fuel Type Unit Table 2-1 CO, Emission factor (For mobile combustion sources) Emission Factor Diesel Oil (DO) 2.614 Unleaded Petrol (ULP) 2.360 Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) 1.679 kg/litre kg/litre kg/litre Unit there has 3 different type of vehicle , careful to cho 9 Table 2-3 N90 Emission factor (For mobile combustion sources) ) Vehicle Type Fuel Type Emission Factor Motorcycle g/litre Passenger Car ULP g/litre a/litre Private Van g/litre ULP 0.046 3.017 1.105 kg/kg kg/litre kg/litre DO 0.110 ULP 1.140 Unit Vehicle Type Fuel Type Einission Factor Unit Gas Oil (For Ships only) 2.6-45 Kerosene (Including Jet Kerosene) 2.429 Table 2-2 CH, Emission factor (For mobile combustion sources) Vehicle Type Fuel Type Emission Factor Motorcycle ULP 1.422 Passenger Car ULP 0.253 DO 0.072 Private Van ULP 0.203 DO 0.072 DO 0.506 LPG 0.000 Public Light Bus DO 0.506 g/litre g/litre a a/litre g/litre g/litre g/litre e/litre LPG 0.000 Light Goods Vehicle 1.105 g/litre glitre glitre g/litre glitre g/litre glitre g/litre glitre g/litre LPG ULP DO DO 0.248 0.506 Public Light Bus DO 0.072 0.072 0.248 Heavy Goods Vehicle Medium Goods Vehicle LPG DO 0.072 Light Goods Vehicle ULP 0.203 Gas Oil 1.095 DO 0.072 Ships Aviation Other Mobile Machinery 0.000 DO 0.145 g/litre g/litre g/litre g/litre g/litre g/litre a/litre 0.007 Jet Kerosene DO LPG Kerosene DO Heavy Goods Vehicle Medium Goods Vehicle Ships Aviation Other Mobile Machinery 0.145 0.000 g/litre glitre or gkg g/litre Gas Oil 0.146 0.0076 Jet Kerosene 0.069 DO 0.0239 g/litre LPG 0.0036 g/litre 0.006 g/kg g/litre Kerosene 0.0241 Gas or Blend GWP Information Source Note: R-416A 767 B Table 3-1 Global Warming Potentials (GWP) of Common Refrigeration/ Air-Conditioning Refrigerants Note Gas or Blend GWP Information Source Note: HFC-23 11.700 HFC-32 650 R-417A 1.955 B A R-418A 4 B HFC-125 2.800 A R-419A 2.403 B B HFC-134 1.300 A R-420A 1.144 B B 3.800 A HFC-1433 HFC-152 R-500 37 B 1-40 A R-501 0 B B 6.300 A HFC-236 R-401A 18 R-502 B 0 B R-4013 IS B R-503 4,692 B R-401C 21 B R-504 313 B B R-402A 1.680 B R-505 0 B R-402B 1.064 B R-506 0 B R-403A 1.400 B R-507 or R-507A 3,300 B R-403B 2.730 B R-404A 3.260 B B R-508A 10.175 B R-406A 0 0 B B R-SO8B 10.350 B 1.770 B R-509 or R-509A 3.920 B R-407A R-4073 2.285 B B 9.200 A . R-407C 1.526 B PFC-116 (CF) PFC-14 (CF) 6.500 R-407D 1.428 B 1.363 B R-407E R-408A 1.944 Note 1: B R-409A 0 B Refrigerants, with components other than HFCs and PFCs, have been well-recognized to have effects on our climate systems. Nevertheless, the Guidelines only cover those which are in the group of Kyoto protocol recognized gases (CO, CH, HFC, PFC, SF, and N.0). Hence, in the Guidelines, GWPs of all refrigerants other than HFCs and PFCs are considered to be zero. R-409B 0 0 E R-410A 1.725 B R-410B 1.833 B R-411A IS B Note 2: R-4113 4 B R-412A 350 B 1.774 B R-413A R-414A Information sources: : A: IPCC Second Assessment Report (1995) B: "World Resources Institute (2005), Calculating HFC and PFC Emissions from the Manufacturing, Installation, Operation and Disposal of Refrigeration & Air-conditioning Equipment (Version 1.0) - Guide to calculation worksheets, World Business Council for Sustainable Development", in which the latter states that the source of reference is from 0 E R-4143 0 0 B 25 B R-415A R-415B 105 B ASHRAE Standard 34 Table 4: Direct GHG Removals from Newly Planted Trees Step 1 Step 2 B Step 3 Step 4 D Step 5 E A No. of trees Source description (Location of the trees planted) factor Note planted (unit) CO2 removals in tonnes CO2 removal No. of trees of CO2 equivalent removed (unit) ((B-C) x D/1000 x (kg/unit/year) length of reporting period in years)) 23 Total Please insert more rows as necessary Note: The default figure for the removal potential of each unit of tree is suggested based on Hong Kong's location, woodland types, and estimated density of trees. The figure is applicable to all trees commonly found in Hong Kong which are able to reach at least 5 metres in height. GHG Emission Factor for Different Power Companies in Hong Kong (in kg CO2-e / kWh) Power company 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 0.48 0.56 0.53 0.52 0.53 0.57 0.54 CLP HEC 0.96 0.98 0.98 0.92 0.91 0.83 0.84 Emission factors for Power and Gas companies in Hong Kong GHG Emission Factor (in kg CO2-e / Unit of Towngas purchased) Year 2005 2006 2007 2008 Emission Factor 0.735 0.693 0.592 0.593 Table 5: GHG Emissions from Electricity Purchased from Power Companies Step 1 A Step 2 B Step 3 Note Step 4 D Emission factor Indirect GHG emissions in tonnes of CO2 equivalent (B x C/1000) (kg/kWh) Facility / source Amount of description (i.e. Area / electricity purchased facilities the electricity (in kWh) bill is reporting) Power Territory-wide company - Power Territory-wide company - default value specific default value specific Total Please insert more rows as necessary Note : The reporting entity is required to account for GHG emissions associated with the electricity purchased in Hong Kong based on two emission factors. First, the reporting entity will quantify the emissions based on a territory-wide default value of 0.7kg / kWh. Second, the reporting entity will quantify the emissions based on specific emission factors provided by its respective provider of electricity. In case that the specific emission factor for the reporting period is not available at the time of accounting, the latest specific emission factor from the power company may be used as an approximation. These specific emission factors are available from the power companies' websites. For reference, the table below indicates the emission factors of the two power companies in Hong Kong for the past 6 years. Table 6: GHG Emissions from Towngas Purchased from the Hong Kong and China Gas Company (Towngas) Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Step 1 A B D Indirect GHG Amount of Towngas Emission factor emissions in tonnes of Facility / source description(i.e. Area facilities the Towngas bill is reporting) purchased (kg/Unit) (Unit Note) CO2 equivalent (BxC71,000) Total Please insert more rows as necessary Note : Each unit registered by gas meter represents that the town gas with a heat value of 48 MJ. Based on the information from the Hong Kong and China Gas Company, the emission factors for the past three years were derived as below. This factor only accounts for the emissions during the production of Towngas within the company. Reporting entity should report in Table 1 as well the GHG emissions associated with combustion of Towngas within the physical boundary under Scope Scope 3 Other indirect emissions It is assumed in the Guidelines that all paper (i.e., paper which is stored or purchased within the organization boundary) will eventually be disposed at landfills unless collected and recycled The equation for calculating emissions for operating process can be summarized as follows: E = (Ps + P;-P,- Pe) x Emission Factor (estimated at 4.8 kg CO2e / kg) = where E = Emissions from paper waste disposed at landfills P = Paper inventory at the beginning of the reporting period (in storage) (kg) P:= Paper added to the inventory during the reporting period (kg) P, = Paper collected for recycling purpose (kg) Pe= Paper inventory at the end of the reporting period (in storage) (kg) Scope 3 Other indirect emissions Note: The default emission factor is determined according to the purpose of water used as follows: Source description Default Emission Factor (kg/m) Restaurants and catering services (0.7 x Emission Factor) assuming 70% of the fresh water consumed will enter the sewage system. Other commercial, residential (1.0 x Emission Factor) assuming 100% of the fresh and institutional purposes water consumed will enter the sewage system. In which emission factor is the emission factor of GHG emissions due to electricity used for processing fresh water derived from the following equation Emission Factor = Unit electricity consumption of processing sewage (from DSD) x Territory-wide default value (i.e. 0.7kg /kWh) of purchased electricity provided in Table 5 Scope 3 Other indirect emissions Table 8: GHG Emissions due to Electricity Used for Fresh Water Processing by Water Supplies Department Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 A B D Emission factor Source description Amount of water (i.e. Area / facilities the consumed as listed on the water service bill is water service bill reporting) (m) Emissions in tonnes of CO, equivalent (kg/m) Note (BxC/ 1000) Total Please insert more rows as necessary Note: Emission factor of GHG emissions due to electricity used for processing fresh water = Unit electricity consumption of fresh water (from WSD) x Territory-wide default value (i.e. 0.7kg /kWh) of purchased electricity provided in Table 5. In case that the unit electricity consumption for processing fresh water for the reporting period is not available at the time of accounting, the latest emission factor from table below may be used as an approximation. GHG Emission Factor (in kg CO2-e/m) Year 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 Emission Factor 0.440 0.463 0.476 0.438 0.414 0.424 Unit there has 3 different type of vehicle , careful to cho 0 kg/litre kg/litre kg/litre Unit Table 2-3 N,O Emission factor (For mobile combustion sources) Vehicle Type Fuel Type Emission Factor Motorcycle ULP 0.046 Passenger Car ULP 1.105 DO 0.110 g/litre g/litre kg/kg kg/litre kg/litre g/litre Table 2-1 CO, Emission factor (For mobile combustion sources) Fuel Type Emission Factor Diesel Oil (DO) 2.614 Unleaded Petrol (ULP) 2.360 Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) 1.679 3.017 Gas Oil (For Ships only) 2.645 Kerosene (Including Jet Kerosene) 2.429 Table 2-2 CH, Emission factor (For mobile combustion sources) Vehicle Type Fuel Type Emission Factor Motorcycle ULP 1.422 Passenger Car ULP 0.253 DO 0.072 Private Van ULP 0.203 DO 0.072 Private Van ULP 1.140 g/litre Unit Vehicle Type Fuel Type Einission Factor Unit DO 0.506 g/litre LPG 0.000 g/litre g/litre g/litre g/litre g/litre glitre Public Light Bus DO 0.506 LPG 0.000 glitre g/litre Light Goods Vehicle ULP 1.105 g/litre g/litre LPG 0.248 DO 0.506 glitre Public Light Bus DO 0.072 DO 0.072 glitre Heavy Goods Vehicle Medium Goods Vehicle LPG 0.248 g/litre g/litre / g/litre DO 0.072 Light Goods Vehicle ULP 0.203 Ships Gas Oil 1.095 glitre g/litre g/litre DO 0.072 Aviation 0.000 Jet Kerosene DO DO 0.145 Other Mobile Machinery 0.007 DO 0.145 LPG 0.000 Heavy Goods Vehicle Medium Goods Vehicle Ships Aviation Other Mobile Machinery g/litre g/litre or gkg g/litre Gas Oil 0.146 Kerosene 0.0076 g/litre /litre g/litre g/litre g/litre g/litre g/litre g g/kg 0.069 Jet Kerosene DO 0.0239 LPG 0.0036 0.006 Kerosene 0.0241 g/litre Gas or Blend GWP Information Source Note 2 R-416A 767 Table 3-1 Global Warming Potentials (GWP) of Common Refrigeration/ Air-Conditioning Refrigerants Note 1 Gas or Blend GWP Information Source Note: HFC-23 - 11.700 A HFC-32 650 B B B R-417A 1.955 A R-418A 4 B B HFC-125 2.800 R-419A 2.403 B 1.300 A A R-420A 1.144 B HFC-134a HFC-143a 3.800 A R-500 37 B HFC-152a 140 R-501 0 B B HFC-236fa 6.300 A R-401A R-502 18 B 0 B R-401B 15 B R-503 4,692 R-401C 21 B R-504 313 B R-402A 1.680 B B R-505 0 B R-402B 1.064 B R-506 0 B R-403A 1.400 B R-507 or R-507A 3,300 B B R-403B 2.730 B R-404A 3.260 B R-508A 10.175 B R-406A 0 B R-508B 10.350 B R-407A 1.770 B R-509 or R-509A 3.920 B R-407B 2.285 B 9.200 A R-407C 1.526 B PFC-116 (CF) PFC-14 (CF) ) 6,500 A A R-407D 1.428 B R-407E 1.363 B R-408A Note 1: 1.944 B R-409A 0 B Refrigerants, with components other than HFCs and PFCs, have been well-recognized to have effects on our climate systems. Nevertheless, the Guidelines only cover those which are in the group of Kyoto protocol recognized gases (CO2, CH., HFC, PFC, SF, and N,O). Hence, in the Guidelines, GWPs of all refrigerants other than HFCs and PFCs are considered to be zero. R-409B 0 B R-410A 1.725 B R-410B 1.833 B B R-411A 15 B 2: Note 2: R-411B 4 B R-412A 350 B R-413A 1.774 B R-414A 0 B Information sources: A: IPCC Second Assessment Report (1995) B: World Resources Institute (2005), Calculating HFC and PFC Emissions from the Manufacturing, Installation, Operation and Disposal of Refrigeration & Air-conditioning Equipment (Version 1.0) - Guide to calculation worksheets, World Business Council for Sustainable Development, in which the latter states that the source of reference is from ASHRAE Standard 34. R-414B 0 B R-415A 25 B R-415B 105 B Table 4: Direct GHG Removals from Newly Planted Trees Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 E A B D No. of trees Source description (Location of the trees planted) planted (unit) CO, removals in tonnes CO2 removal No. of trees of CO2 equivalent factor Note removed (unit) ((B-C) x D/ 1000 x (kg/unit/ /year) length of reporting period (in years)) 23 Total Please insert more rows as necessary Note: The default figure for the removal potential of each unit of tree is suggested based on Hong Kong's location, woodland types, and estimated density of trees. The figure is applicable to all trees commonly found in Hong Kong which are able to reach at least 5 metres in height. GHG Emission Factor for Different Power Companies in Hong Kong (in kg CO2-e/kWh) Power company 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 CLP 0.48 0.56 0.53 0.52 0.53 0.57 0.54 HEC 0.96 0.98 0.98 0.92 0.91 0.83 0.84
























