
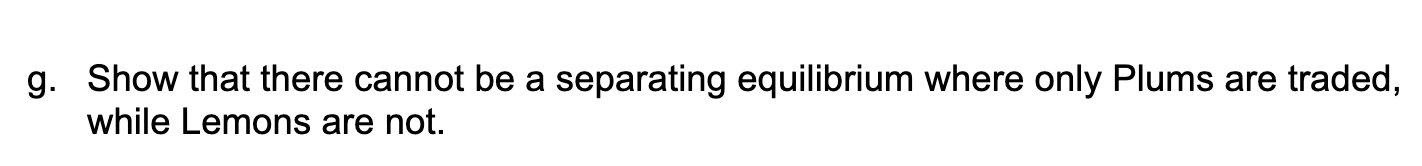 please answer the question about the separating equilibrium perfect bayesian equilibrium, part f and g
please answer the question about the separating equilibrium perfect bayesian equilibrium, part f and g
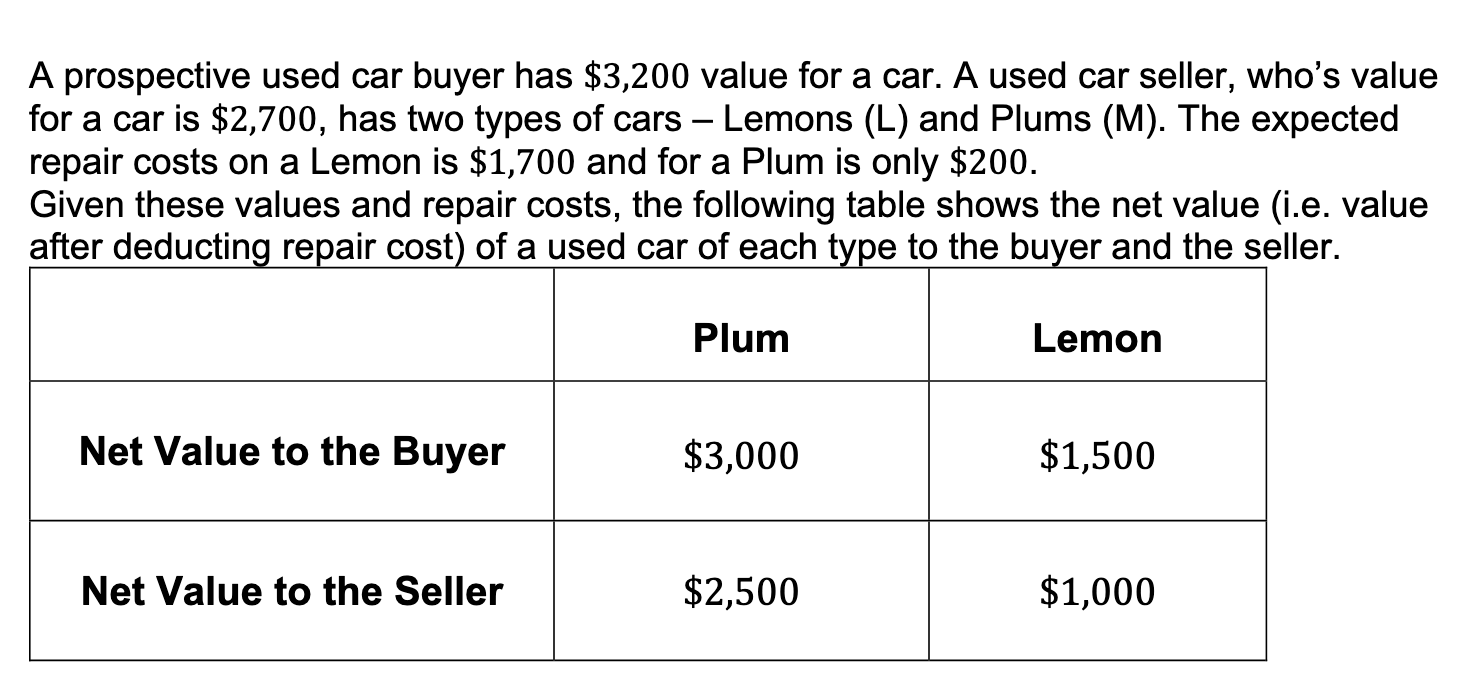
A prospective used car buyer has $3,200 value for a car. A used car seller, who's value for a car is $2,700, has two types of cars Lemons (L) and Plums (M). The expected repair costs on a Lemon is $1,700 and for a Plum is only $200. Given these values and repair costs, the following table shows the net value (i.e. value after deducting repair cost) of a used car of each type to the buyer and the seller. Plum Lemon Net Value to the Buyer $3,000 $1,500 Net Value to the Seller $2,500 $1,000 a. Suppose the buyer could distinguish between a Lemon and Plum, would a Plum be traded between the buyer and seller at some price? What about a Lemon? If yes, what is the range of prices that the seller could charge for the trade to occur? Suppose the buyer cannot tell a Lemon from a Plum, but she knows that half the cars in the dealership are Lemons and the remaining half are Plums. Thus, the prior probabilities are 1 1 0 = Pr[Lemon] 1 - 0 = Pr[Plum] 2' 2 Consider a pooling strategy for the seller, where she always sells both types of cars. b. What is the buyer's updated belief conditional on the seller offering a car for sale? = c. Given the buyers updated beliefs, what is the highest price that the buyer will be willing to pay for a car? d. Given the highest price that the buyer is willing to pay (determined in part c), is a best response for the seller to offer both types of cars up for sale? e. Based on your answers to a) to d), is there a pooling PBE where both types of cars are sold? f. Show that there is a separating equilibrium that is a PBE where only Lemons are traded, while Plums are not. (Adverse Selection). Describe the PBE completely as a pair of strategies chosen by the seller and buyer and the buyer's conditional belief about the car type, q. a g. Show that there cannot be a separating equilibrium where only Plums are traded, while Lemons are not. A prospective used car buyer has $3,200 value for a car. A used car seller, who's value for a car is $2,700, has two types of cars Lemons (L) and Plums (M). The expected repair costs on a Lemon is $1,700 and for a Plum is only $200. Given these values and repair costs, the following table shows the net value (i.e. value after deducting repair cost) of a used car of each type to the buyer and the seller. Plum Lemon Net Value to the Buyer $3,000 $1,500 Net Value to the Seller $2,500 $1,000 a. Suppose the buyer could distinguish between a Lemon and Plum, would a Plum be traded between the buyer and seller at some price? What about a Lemon? If yes, what is the range of prices that the seller could charge for the trade to occur? Suppose the buyer cannot tell a Lemon from a Plum, but she knows that half the cars in the dealership are Lemons and the remaining half are Plums. Thus, the prior probabilities are 1 1 0 = Pr[Lemon] 1 - 0 = Pr[Plum] 2' 2 Consider a pooling strategy for the seller, where she always sells both types of cars. b. What is the buyer's updated belief conditional on the seller offering a car for sale? = c. Given the buyers updated beliefs, what is the highest price that the buyer will be willing to pay for a car? d. Given the highest price that the buyer is willing to pay (determined in part c), is a best response for the seller to offer both types of cars up for sale? e. Based on your answers to a) to d), is there a pooling PBE where both types of cars are sold? f. Show that there is a separating equilibrium that is a PBE where only Lemons are traded, while Plums are not. (Adverse Selection). Describe the PBE completely as a pair of strategies chosen by the seller and buyer and the buyer's conditional belief about the car type, q. a g. Show that there cannot be a separating equilibrium where only Plums are traded, while Lemons are not


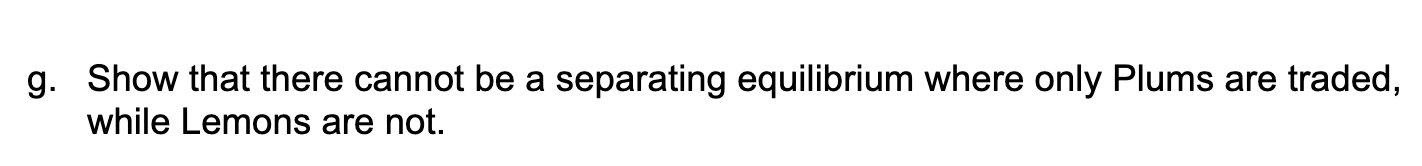 please answer the question about the separating equilibrium perfect bayesian equilibrium, part f and g
please answer the question about the separating equilibrium perfect bayesian equilibrium, part f and g





