Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please answer the question asap! Need an answer! Randomized Wages ( 20 points) Consider a standard principal-agent model. The set of possible outputs is Y=
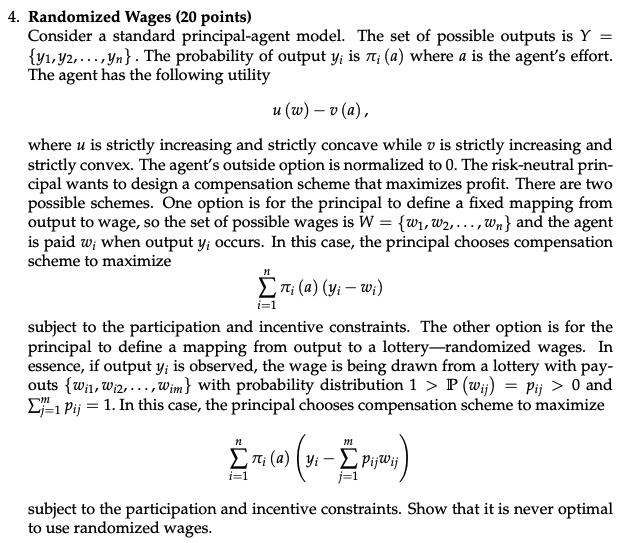
Please answer the question asap! Need an answer!
Randomized Wages ( 20 points) Consider a standard principal-agent model. The set of possible outputs is Y= {y1,y2,,yn}. The probability of output yi is i(a) where a is the agent's effort. The agent has the following utility u(w)v(a), where u is strictly increasing and strictly concave while v is strictly increasing and strictly convex. The agent's outside option is normalized to 0 . The risk-neutral principal wants to design a compensation scheme that maximizes profit. There are two possible schemes. One option is for the principal to define a fixed mapping from output to wage, so the set of possible wages is W={w1,w2,,wn} and the agent is paid wi when output yi occurs. In this case, the principal chooses compensation scheme to maximize i=1ni(a)(yiwi) subject to the participation and incentive constraints. The other option is for the principal to define a mapping from output to a lottery-randomized wages. In essence, if output yi is observed, the wage is being drawn from a lottery with payouts {wi1,wi2,,wim} with probability distribution 1>P(wij)=pij>0 and j=1mpij=1. In this case, the principal chooses compensation scheme to maximize i=1ni(a)(yij=1mpijwij) subject to the participation and incentive constraints. Show that it is never optimal to use randomized wages. Randomized Wages ( 20 points) Consider a standard principal-agent model. The set of possible outputs is Y= {y1,y2,,yn}. The probability of output yi is i(a) where a is the agent's effort. The agent has the following utility u(w)v(a), where u is strictly increasing and strictly concave while v is strictly increasing and strictly convex. The agent's outside option is normalized to 0 . The risk-neutral principal wants to design a compensation scheme that maximizes profit. There are two possible schemes. One option is for the principal to define a fixed mapping from output to wage, so the set of possible wages is W={w1,w2,,wn} and the agent is paid wi when output yi occurs. In this case, the principal chooses compensation scheme to maximize i=1ni(a)(yiwi) subject to the participation and incentive constraints. The other option is for the principal to define a mapping from output to a lottery-randomized wages. In essence, if output yi is observed, the wage is being drawn from a lottery with payouts {wi1,wi2,,wim} with probability distribution 1>P(wij)=pij>0 and j=1mpij=1. In this case, the principal chooses compensation scheme to maximize i=1ni(a)(yij=1mpijwij) subject to the participation and incentive constraints. Show that it is never optimal to use randomized wagesStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


