please answer the questions
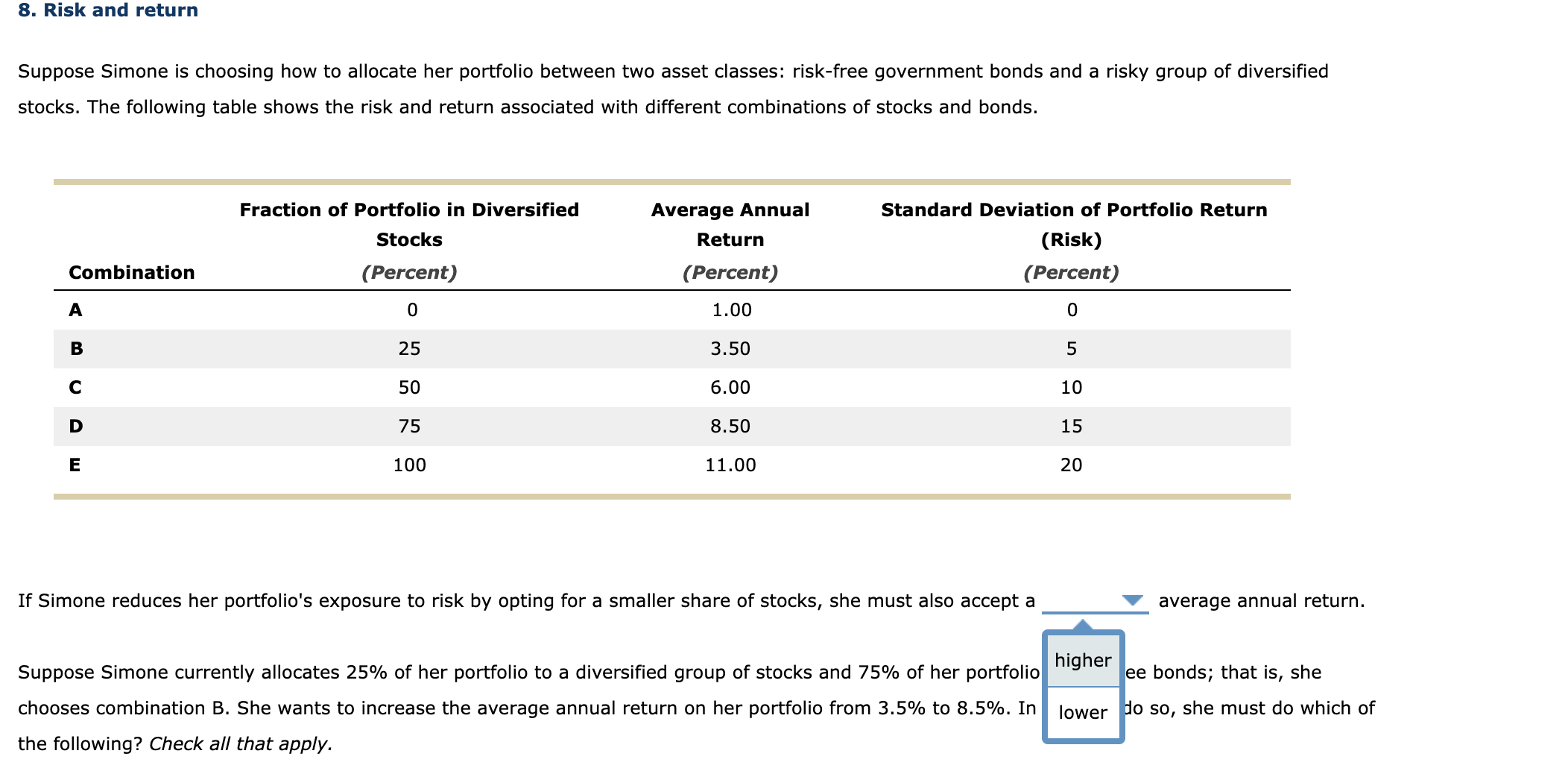
8. Risk and return Suppose Simone is choosing how to allocate her portfolio between two asset classes: risk-free government bonds and a risky group of diversied stocks. The following table shows the risk and return associated with different combinations of stocks and bonds. Fraction of Portfolio in Diversified Average Annual Standard Deviation of Portfolio Return Stocks Return (Risk) Combination (Percent) (Percent) (Percent) A 0 1.00 0 B 25 3.50 5 C 50 6.00 10 D 75 8.50 15 E 100 11.00 20 If Simone reduces her portfolio's exposure to risk by opting for a smaller share of stocks, she must also accept a V average annual return. Suppose Simone currently allocates 25% of her portfolio to a diversified group of stocks and 75% of her portfolio ee bonds; that is, she chooses combination B. She wants to increase the average annual return on her portfolio from 3.5% to 8.5%. In no so, she must do which of the following? Check all that apply. Suppose Simone currently allocates 25% of her portfolio to a diversified group of stocks and 75% of her portfolio to risk-free bonds; that is, she chooses combination B. She wants to increase the average annual return on her portfolio from 3.5% to 8.5%. In order to do so, she must do which of the following? Check all that apply. Accept more risk _ Sell some of her bonds and use the proceeds to purchase stocks Sell some of her stocks and use the proceeds to purchase bonds Sell some of her stocks and place the proceeds in a savings account The table uses the standard deviation of the ortfolio's return as a measure of risk. A normal random variable, such as a portfolio's return, stays p within two standard deviations of its average approximately 95% of the time. Suppose Simone modifies her portfolio to contain 75% diversied stocks and 25% risk-free government bonds; that is, she chooses combination D. The average annual return for this type of portfolio is 8.5%, but given the standard deviation of 15%, the returns will typically (about 95% of the time) vary from a gain of V to a loss of V . The table uses the standa n of the portfolio's return as a measure of risk. A normal random variable, such as a portfolio's return, stays within two standard devia average approximately 95% of the time. Suppose Simone modifies lio to contain 75% diversied stocks and 25% risk-free government bonds; that is, she chooses combination D. The average annual retur pe of portfolio is 8.5%, but given the standard deviation of 15%, the returns will typically (about 95% of the time) vary from a gain of v to a loss of v . L] Sell some 01' her stocks and place the proceeds in a savings account The table uses the standard deviation of the portfoli s a measure of risk. A normal random variable, such as a portfolio's return, stays within two standard deviations of its average appro % of the time. Suppose Simone modifies her portfolio to contain 7' ed stocks and 25% risk-free government bonds; that is, she chooses combination D. The average annual return for this type of portfolio i t given the standard deviation of 15%, the returns will typically (about 95% of the time) vary from a gain of V to a loss of V