Question: Please answer these following questions and try to answer fast if you can thanks! Question 1 The table below shows Nominal GDP, Real GDP, the
Please answer these following questions and try to answer fast if you can thanks!
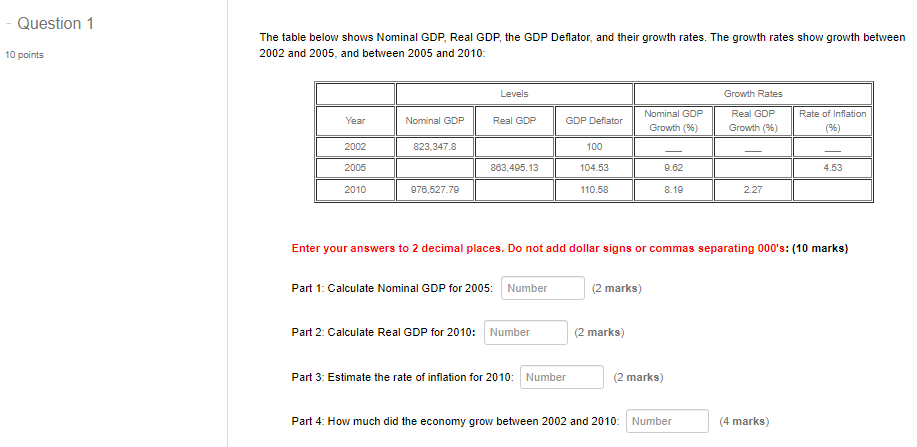
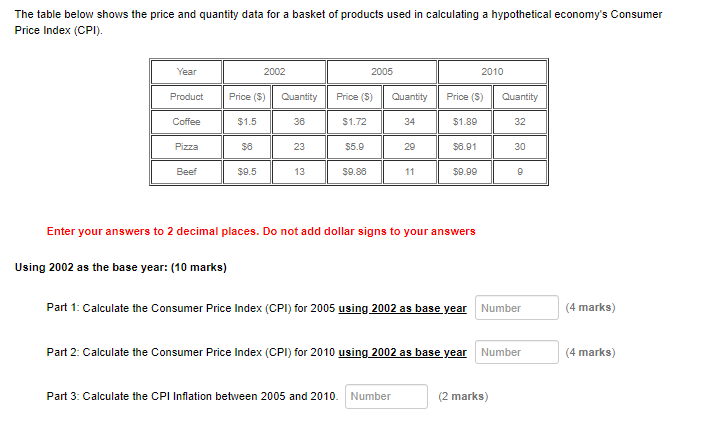
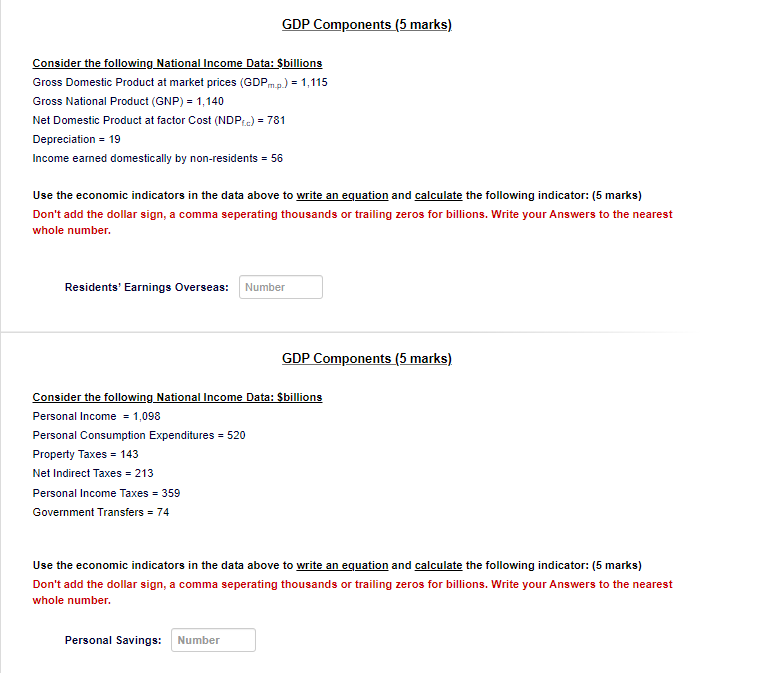
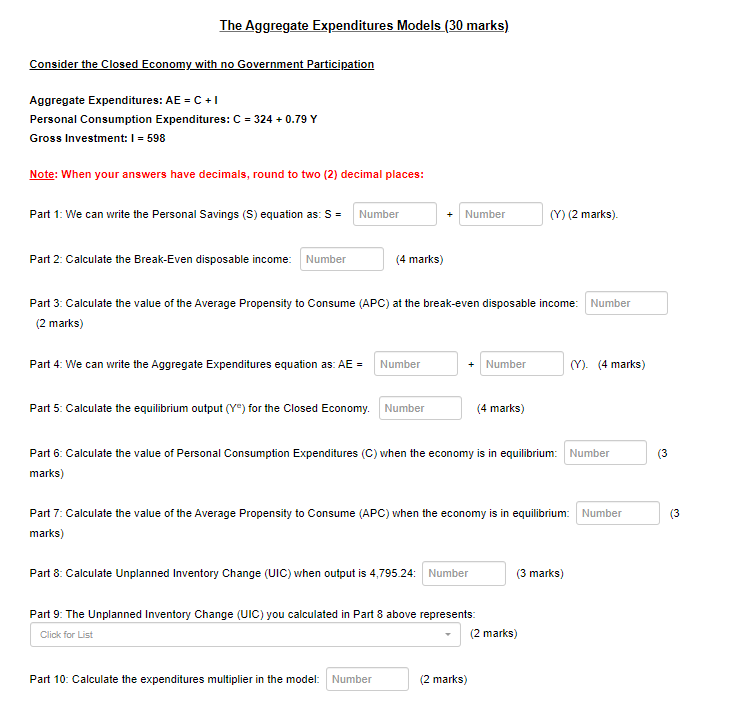
Question 1 The table below shows Nominal GDP, Real GDP, the GDP Deflator, and their growth rates. The growth rates show growth between 10 points 2002 and 2005, and between 2005 and 2010: Levels Growth Rates Nominal GDP Year Nominal GDP Real GDP Real GDP GDP Deflator Rate of Inflation Growth (9%) Growth (96) (96) 2002 823.347.8 100 2005 863,495.13 104.53 9.62 4.53 2010 976,527.79 110.58 8.19 2.27 Enter your answers to 2 decimal places. Do not add dollar signs or commas separating 000's: (10 marks) Part 1: Calculate Nominal GDP for 2005: Number (2 marks) Part 2: Calculate Real GDP for 2010: Number (2 marks) Part 3: Estimate the rate of inflation for 2010: Number (2 marks) Part 4: How much did the economy grow between 2002 and 2010: Number (4 marks)The table below shows the price and quantity data for a basket of products used in calculating a hypothetical economy's Consumer Price Index (CPI). Year 2002 2005 2010 Product Price ($) Quantity Price ($) Quantity Price ($) Quantity Coffee $1.5 38 $1.72 34 $1.89 32 Pizza 36 23 $5.9 29 $6.01 30 Beef $0.5 13 59.86 11 $0.09 9 Enter your answers to 2 decimal places. Do not add dollar signs to your answers Using 2002 as the base year: (10 marks) Part 1: Calculate the Consumer Price Index (CPI) for 2005 using 2002 as base year Number (4 marks) Part 2: Calculate the Consumer Price Index (CPI) for 2010 using 2002 as base year Number (4 marks) Part 3: Calculate the CPI Inflation between 2005 and 2010. Number (2 marks)GDP Components (5 marks) Consider the following National Income Data: $billions Gross Domestic Product at market prices (GDPm ( ) = 1,115 Gross National Product (GNP) = 1,140 Net Domestic Product at factor Cost (NDP() = 781 Depreciation = 19 Income earned domestically by non-residents = 56 Use the economic indicators in the data above to write an equation and calculate the following indicator: (5 marks) Don't add the dollar sign, a comma seperating thousands or trailing zeros for billions. Write your Answers to the nearest whole number. Residents' Earnings Overseas: Number GDP Components (5 marks) Consider the following National Income Data: Sbillions Personal Income = 1,098 Personal Consumption Expenditures = 520 Property Taxes = 143 Net Indirect Taxes = 213 Personal Income Taxes = 359 Government Transfers = 74 Use the economic indicators in the data above to write an equation and calculate the following indicator: (5 marks) Don't add the dollar sign, a comma seperating thousands or trailing zeros for billions. Write your Answers to the nearest whole number. Personal Savings: NumberThe Aggregate Expenditures Models (30 marks) Consider the Closed Economy with no Government Participation Aggregate Expenditures: AE = C + I Personal Consumption Expenditures: C = 324 + 0.79 Y Gross Investment: I = 598 Note: When your answers have decimals, round to two (2) decimal places: Part 1: We can write the Personal Savings (S) equation as: S = Number Number (Y) (2 marks). Part 2: Calculate the Break-Even disposable income: Number (4 marks) Part 3: Calculate the value of the Average Propensity to Consume (APC) at the break-even disposable income: Number (2 marks) Part 4: We can write the Aggregate Expenditures equation as: AE = Number Number MY). (4 marks) Part 5: Calculate the equilibrium output (Y) for the Closed Economy. Number (4 marks) Part 6: Calculate the value of Personal Consumption Expenditures (C) when the economy is in equilibrium: Number (3 marks) Part 7: Calculate the value of the Average Propensity to Consume (APC) when the economy is in equilibrium: Number 13 marks) Part 8: Calculate Unplanned Inventory Change (UIC) when output is 4,795.24: Number (3 marks) Part 9: The Unplanned Inventory Change (UIC) you calculated in Part $ above represents: Click for List (2 marks) Part 10: Calculate the expenditures multiplier in the model: Number (2 marks)Part 9: The Unplanned Inventory Change (UIC) you calculated in Part & above represents: s how much unsold output businesses are forced o store in inventory how much output businesses are forced to sell out of inventory to meet higher demand i) how much output businesses import over and above exports at the current rate of production how much output businesses export over and above immports at the current rate of production
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


