
Please Answer these questions
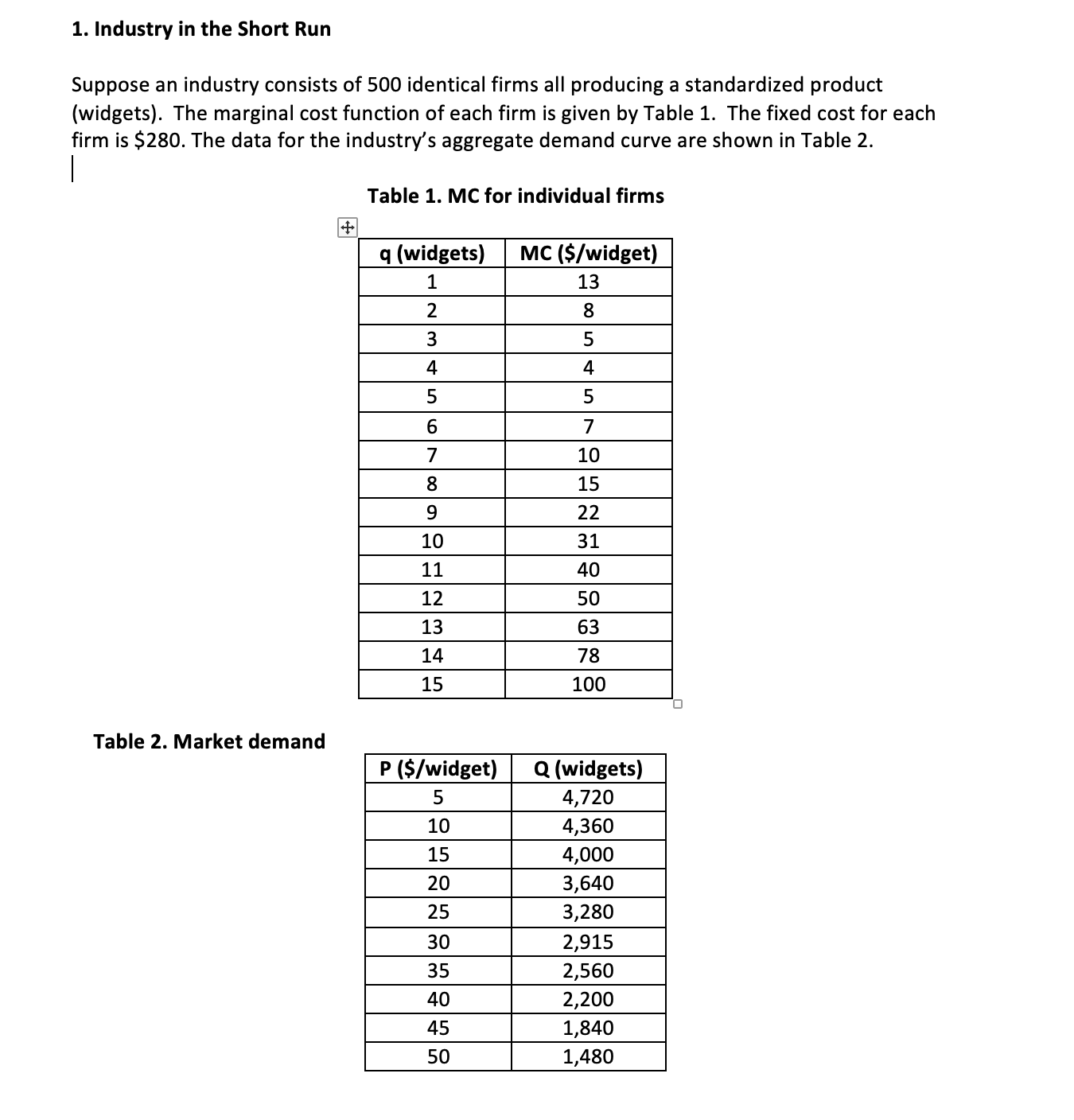
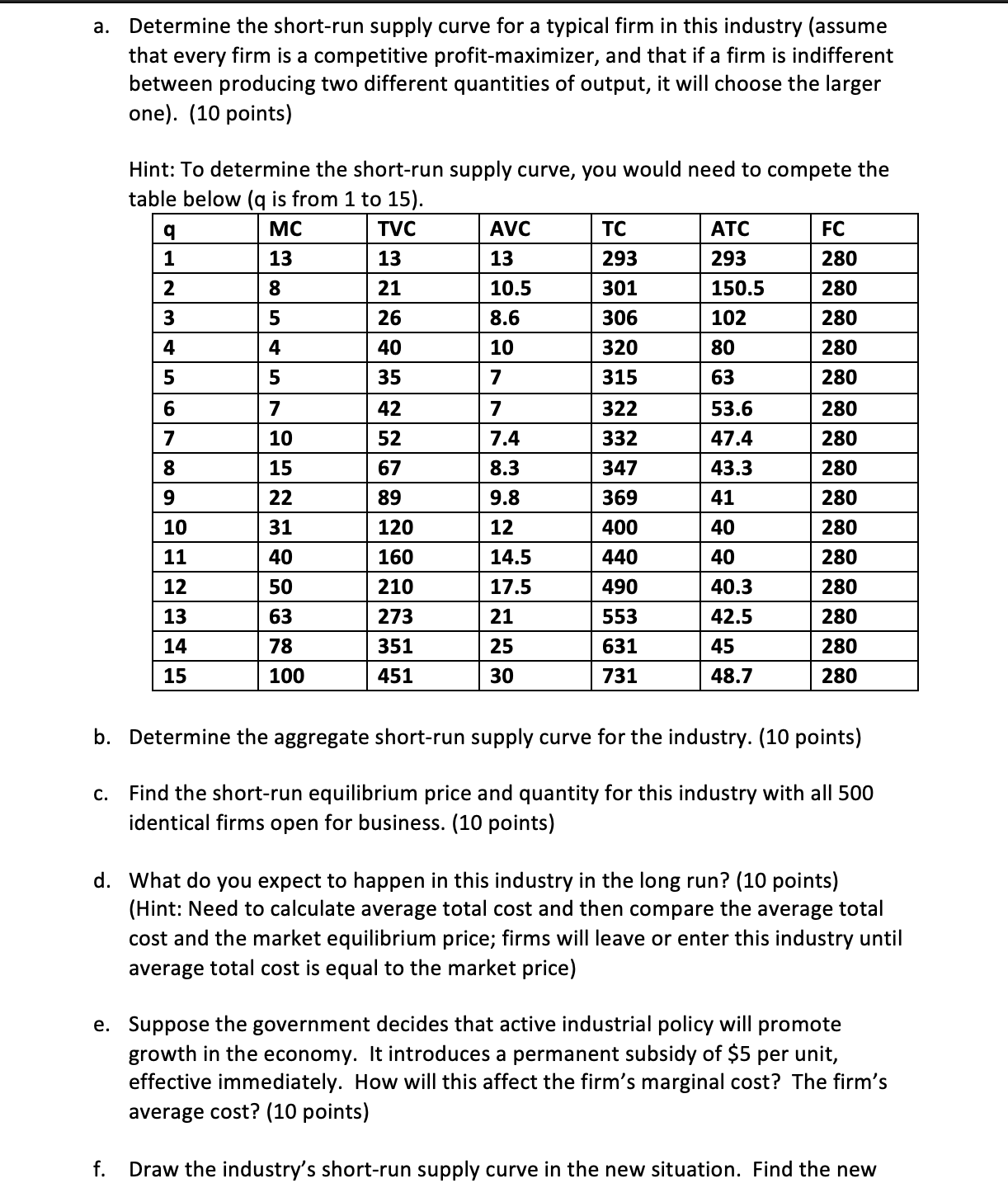
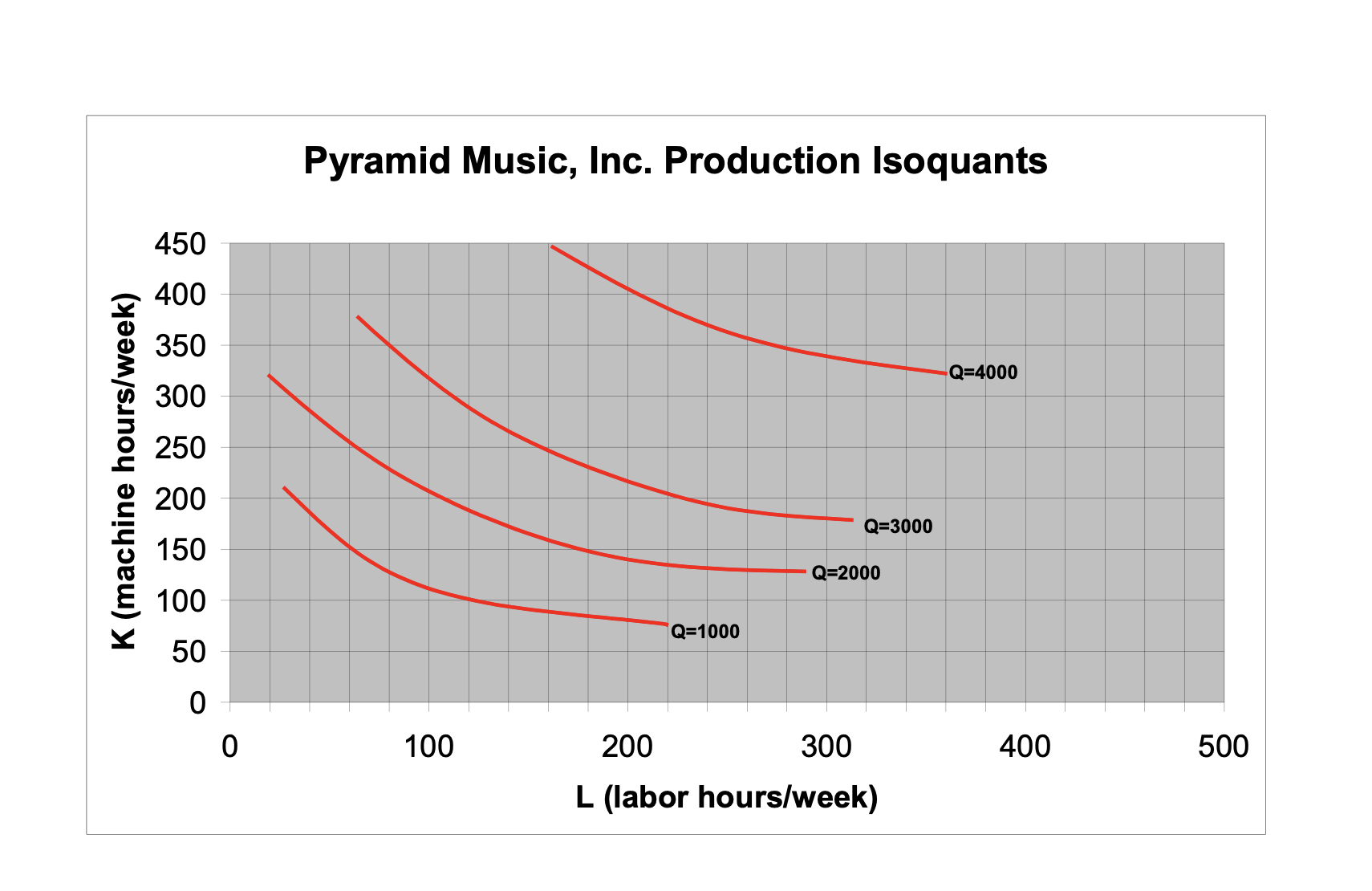
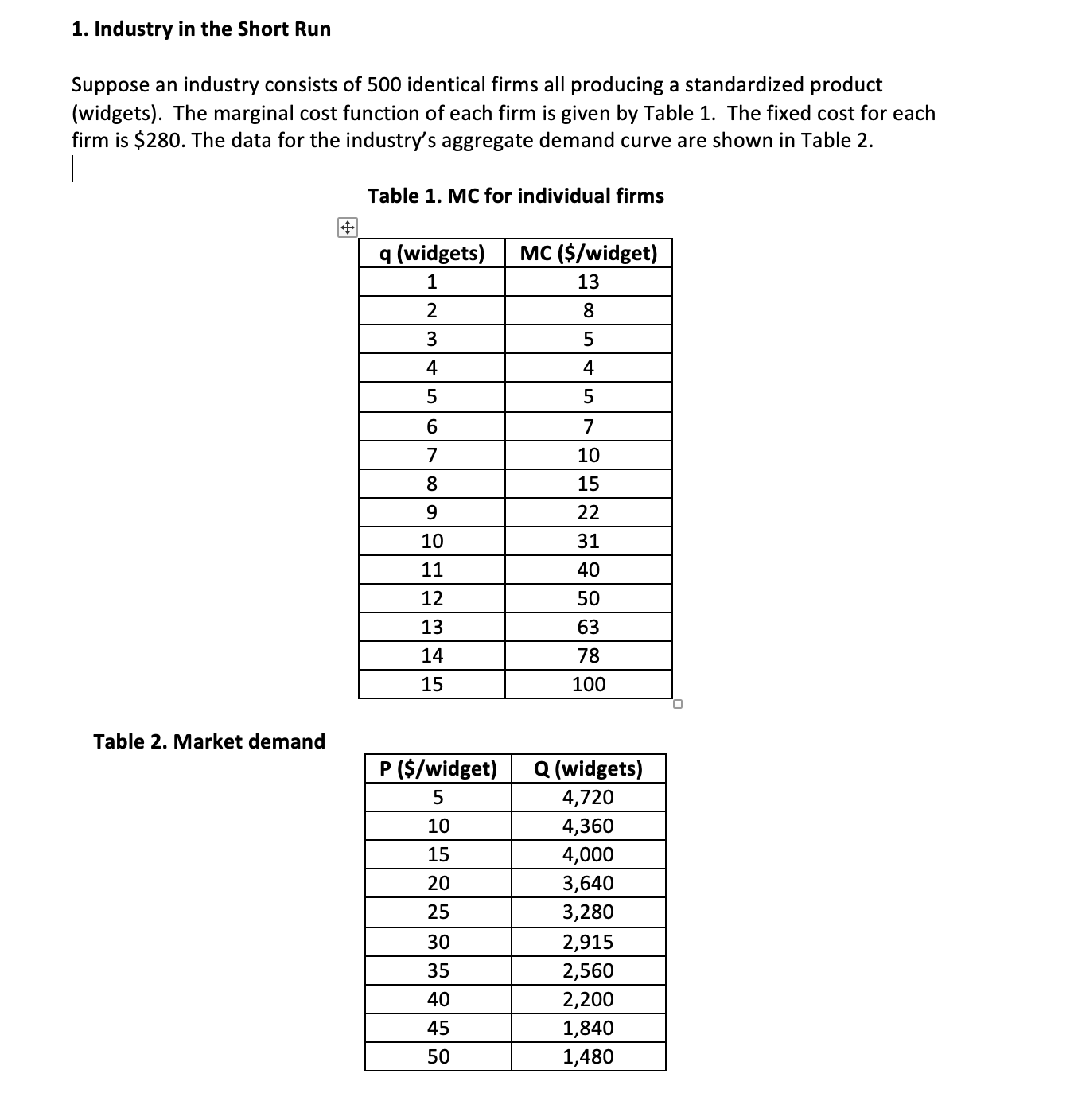
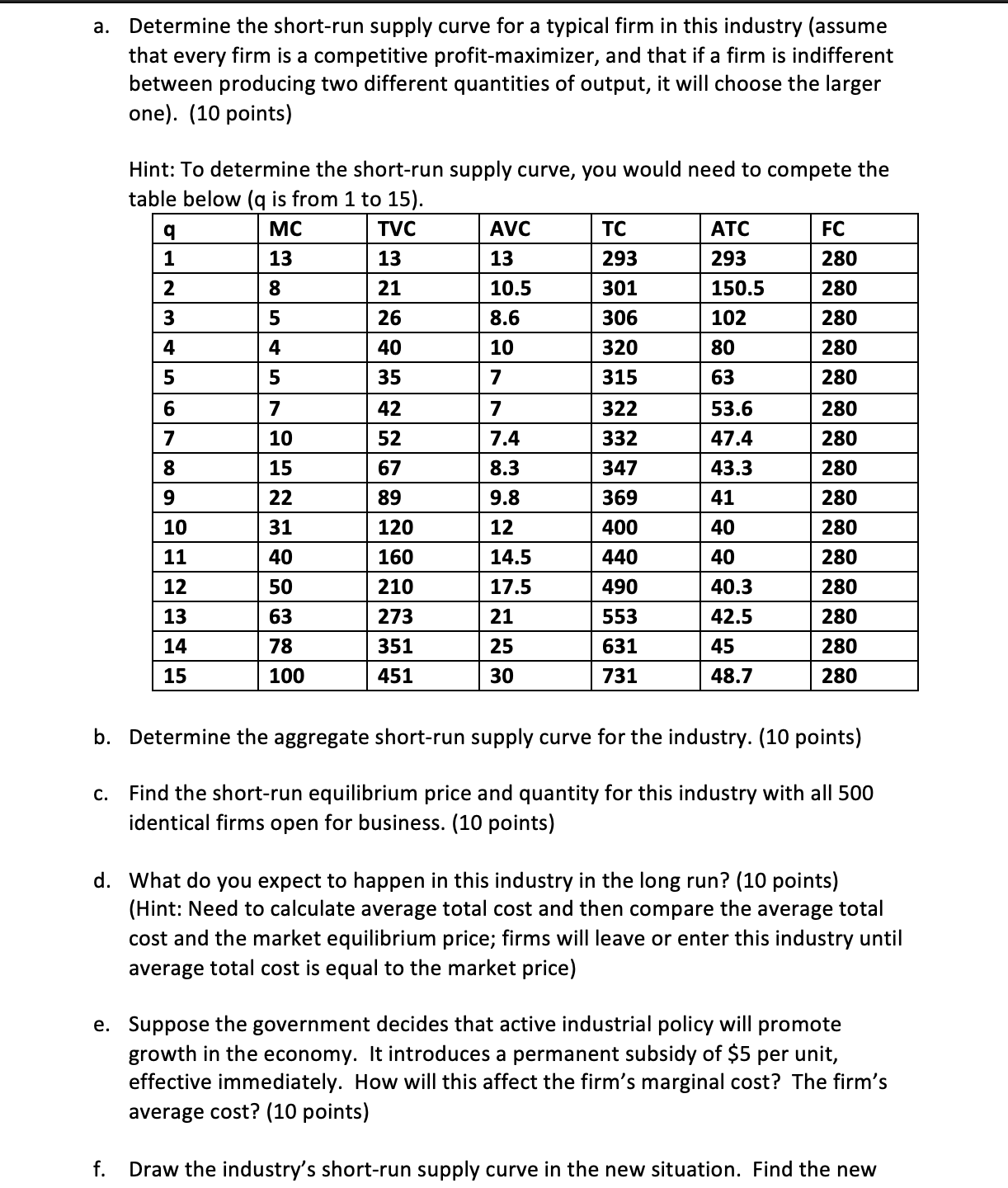
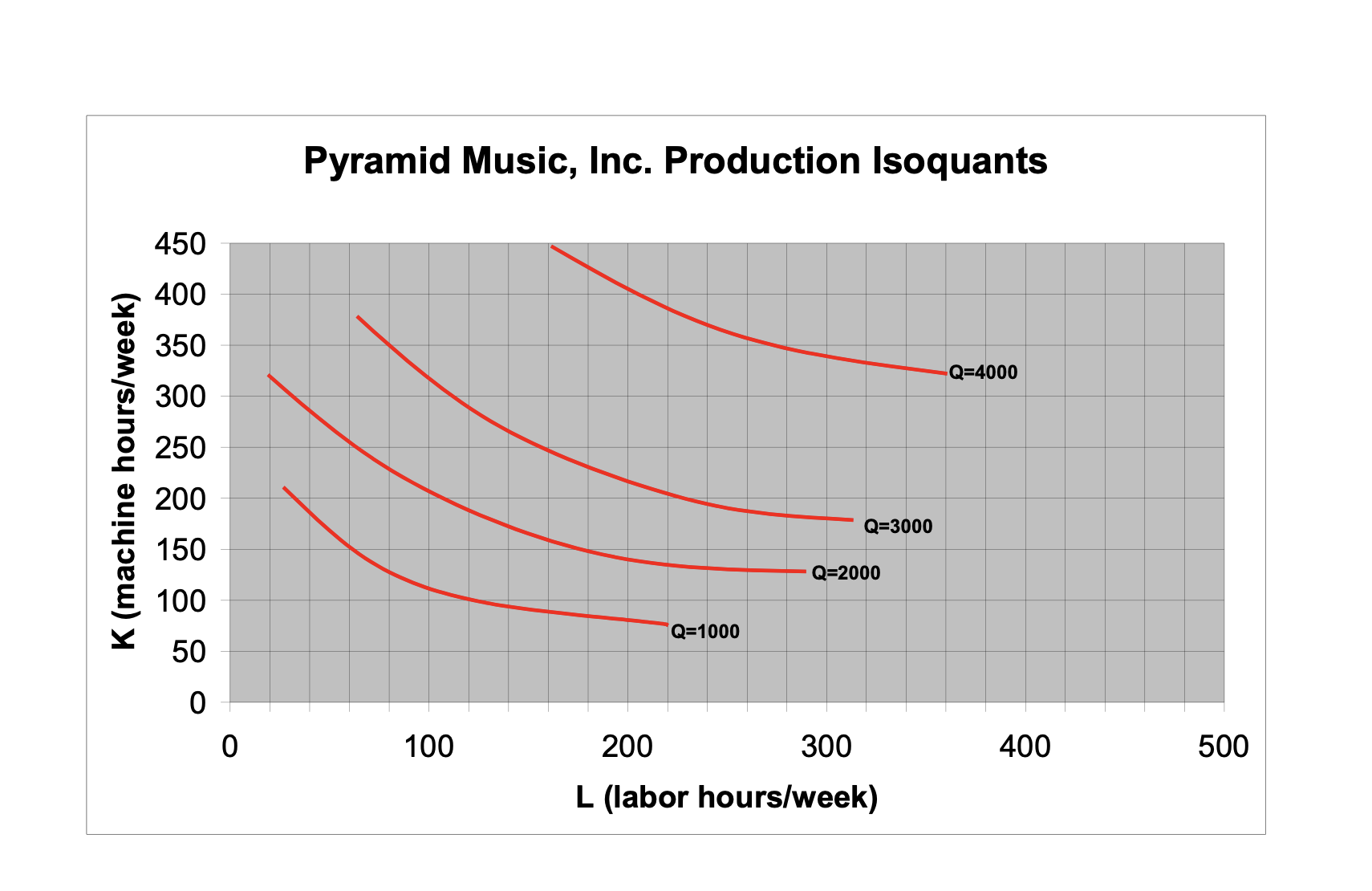
1. Industry in the Short Run Suppose an industry consists of 500 identical firms all producing a standardized product (widgets). The marginal cost function of each firm is given by Table 1. The fixed cost for each firm is $280. The data for the industry's aggregate demand curve are shown in Table 2. Table 1. MC for individual firms Table 2. Market demand a. Determine the short-run supply curve for a typical firm in this industry (assume that every firm is a competitive profit-maximizer, and that if a firm is indifferent between producing two different quantities of output, it will choose the larger one). (10 points) Hint: To determine the shortrun supply curve, you would need to compete the table below (q is from 1 to 15). M _II- E-EI Emmi- mm mm- mm- mm mm mm- _EE- mm- mm- WEE- \"Ei- mm _E- b. Determine the aggregate short-run supply curve for the industry. (10 points) c. Find the shortrun equilibrium price and quantity for this industry with all 500 identical firms open for business. (10 points) d. What do you expect to happen in this industry in the long run? (10 points) (Hint: Need to calculate average total cost and then compare the average total cost and the market equilibrium price; firms will leave or enter this industry until average total cost is equal to the market price) e. Suppose the government decides that active industrial policy will promote growth in the economy. It introduces a permanent subsidy of $5 per unit, effective immediately. How will this affect the firm's marginal cost? The firm's average cost? (10 points) f. Draw the industry's short-run supply curve in the new situation. Find the new 2. Pyramid Music (60 points) The production isoquants for Pyramid Music, a small, independent West Coast recording company, are shown on page 4 of this problem set. Pyramid's primary output is CDs of new artists' music. Assume, in answering parts {a} through (f), that Pyramid has no fixed costs. Please work on the attached diagram {last page) and hand it in with the rest of your problem set answers. Of course, each person's work on the diagrams may be slightly different, with slightly different approximate {but numerical) answers. Correct cost curve answers will reflect the general shapes we discussed in class. (a) In 1985 the wage rate for labor was $10/hour and machines rented for $30/hour. What was the minimum cost of producing 1000, 2000, 3000, and 4000 CD5? (10 points} {b} By 1995, the wage rate had risen to $30/hour; machine rentals remained at $30/hour. What was the minimum cost of producing each of the four quantities from {a} in 1995? (10 points} {c} Explain in words why it is that, although the price of labor rose by a factor of 3, the total cost of producing 1000 CD5 rose by a much lower factor. {10 points} Pyramid Music, Inc. Production Isoquants 450 400 350 -Q=4000 300 250 K (machine hours/week) 200 Q=3000 150 Q=2000 100 Q=1000 50 0 O 100 200 300 400 500 L (labor hours/week)