Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please answer this in full details explain the Contents . . Expected Style / Description Volatility Strategy Invests in Equities, expected to experience acceleration in
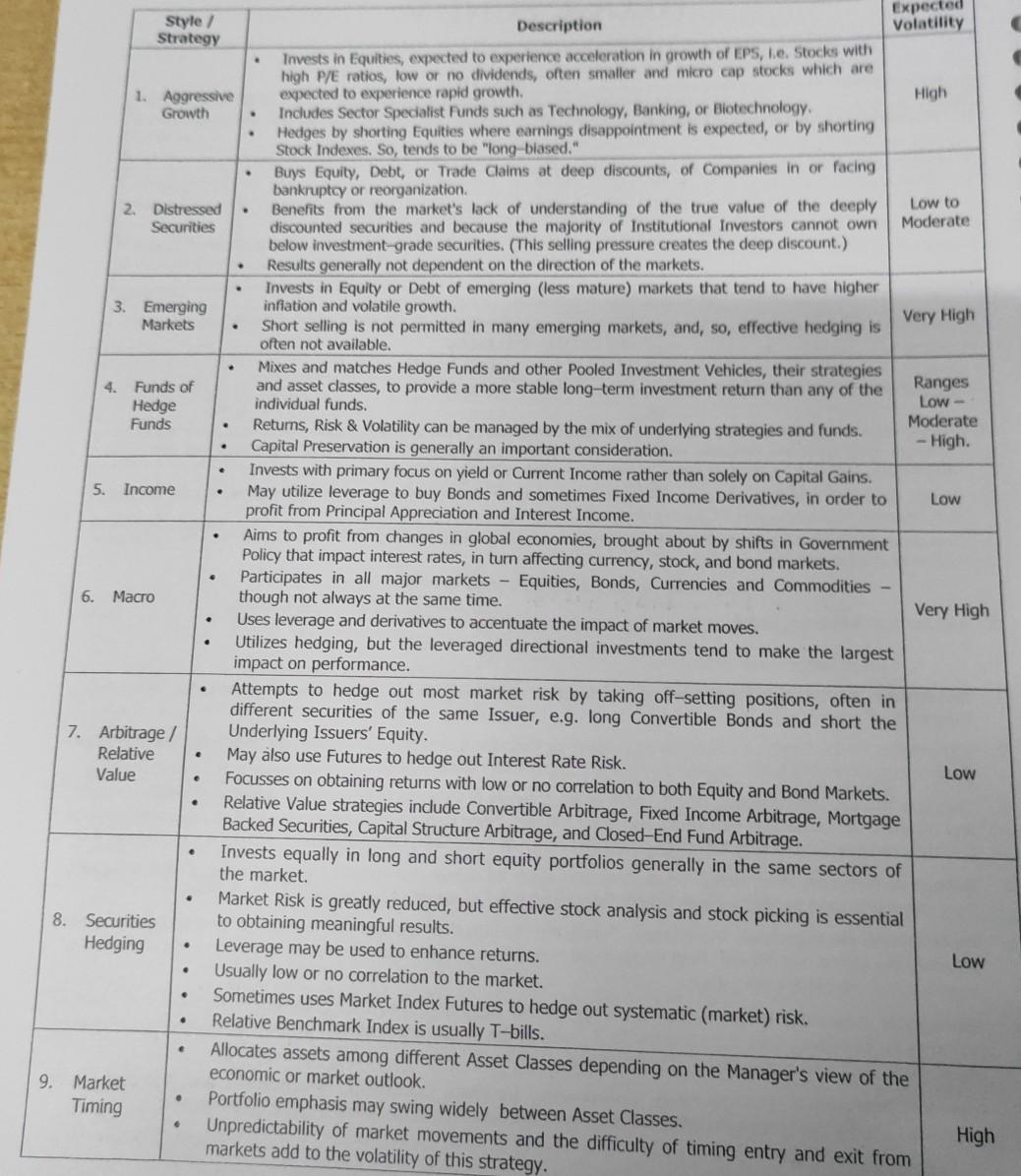

Please answer this in full details explain the Contents
. . Expected Style / Description Volatility Strategy Invests in Equities, expected to experience acceleration in growth of EPS, le. Stocks with high P/E ratios, low or no dividends, often smaller and micro cap stocks which are 1. Aggressive expected to experience rapid growth. High Growth Includes Sector Specialist Funds such as Technology, Banking, or Biotechnology Hedges by shorting Equities where earnings disappointment is expected, or by shorting Stock Indexes. So, tends to be "long-biased." Buys Equity, Debt, or Trade Claims at deep discounts, of Companies in or facing bankruptcy or reorganization Low to 2. Distressed Benefits from the market's lack of understanding of the true value of the deeply Moderate Securities discounted securities and because the majority of Institutional Investors cannot own below investment-grade securities. (This selling pressure creates the deep discount.) Results generally not dependent on the direction of the markets. Invests in Equity or Debt of emerging (less mature) markets that tend to have higher 3. Emerging inflation and volatile growth. Very High Markets Short selling is not permitted in many emerging markets, and, so, effective hedging is often not available. Mixes and matches Hedge Funds and other Pooled Investment Vehicles, their strategies 4. Funds of and asset dasses, to provide a more stable long-term investment return than any of the Ranges Hedge individual funds. Low- Funds Returns, Risk & Volatility can be managed by the mix of underlying strategies and funds. Moderate Capital Preservation is generally an important consideration. - High. Invests with primary focus on yield or Current Income rather than solely on Capital Gains. 5. Income May utilize leverage to buy Bonds and sometimes Fixed Income Derivatives, in order to Low profit from Principal Appreciation and Interest Income. Aims to profit from changes in global economies, brought about by shifts in Government Policy that impact interest rates, in turn affecting currency, stock, and bond markets. Participates in all major markets - Equities, Bonds, Currencies and Commodities 6. though not always at the same time. Very High Uses leverage and derivatives to accentuate the impact of market moves. Utilizes hedging, but the leveraged directional investments tend to make the largest impact on performance. Attempts to hedge out most market risk by taking off-setting positions, often in different securities of the same Issuer, e.g. long Convertible Bonds and short the 7. Arbitrage / Underlying Issuers' Equity. Relative May also use Futures to hedge out Interest Rate Risk. Value Low Focusses on obtaining returns with low or no correlation to both Equity and Bond Markets. Relative Value strategies include Convertible Arbitrage, Fixed Income Arbitrage, Mortgage Backed Securities, Capital Structure Arbitrage, and Closed-End Fund Arbitrage. Invests equally in long and short equity portfolios generally in the same sectors of the market. . . . e 8. Securities Hedging Low . . Market Risk is greatly reduced, but effective stock analysis and stock picking is essential to obtaining meaningful results. Leverage may be used to enhance returns. Usually low or no correlation to the market. Sometimes uses Market Index Futures to hedge out systematic (market) risk. Relative Benchmark Index is usually T-bills. Allocates assets among different Asset Classes depending on the Manager's view of the economic or market outlook. Portfolio emphasis may swing widely between Asset Classes. Unpredictability of market movements and the difficulty of timing entry and exit from markets add to the volatility of this strategy. 9. Market Timing . 6 High Style / Strategy . 10. Oppor- tunistic . 11. Multi Strategy . . 12. Short Selling Expected Description Volatility Investment theme changes from strategy to strategy as opportunities arise to profit from events such as IPOs, sudden price changes often caused by an interim earnings disappointment, hostile bids, and other event-driven opportunities. Variable May utilize several of these investing styles at a given time and is not restricted to any particular investment approach or asset class. Investment approach is diversified by employing various strategies simultaneously to realize short and long-term gains. Strategies may include systems trading such as trend following and various diversified Variable technical strategies. This style of investing allows the Manager to overweight or underweight different strategies to best capitalize on current investment opportunities. Sells Securities short in anticipation of being able to re-purchase them at a future date at a lower price due to the Manager's assessment of the overvaluation of the securities, or the market, or in anticipation of earnings disappointments often due to accounting irregularities, new competition, change of management, etc. Very High Often used as a hedge to offset long-only portfolios and by those who feel the market is approaching a bearish cycle. However, Risk is high. Invests in event-driven situations such as Mergers, Hostile Takeovers, Reorganizations, or Leveraged Buyouts. May involve simultaneous purchase of Stock in Companies being acquired, and the sale of stock in its Acquirer, hoping to profit from the spread between the Current Market Price and the ultimate purchase price of the Company. Moderate May also utilize derivatives to leverage returns and to hedge out interest rate and/or market risk. Results generally not dependent on direction of market. Invests in Securities perceived to be selling at deep discounts to their intrinsic or potential worth. Such Securities may be out of favour or under-followed by Analysts. Low to Long-term holding, patience, and strong discipline are often required until the ultimate Moderate value is recognized by the market. . . 13. Special Situations 14. ValueStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


