Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please assume CUID as 1133557799 Now, you will modify the program code of the Input modulating signal (line 17) to generate a 10-bit digital signal,

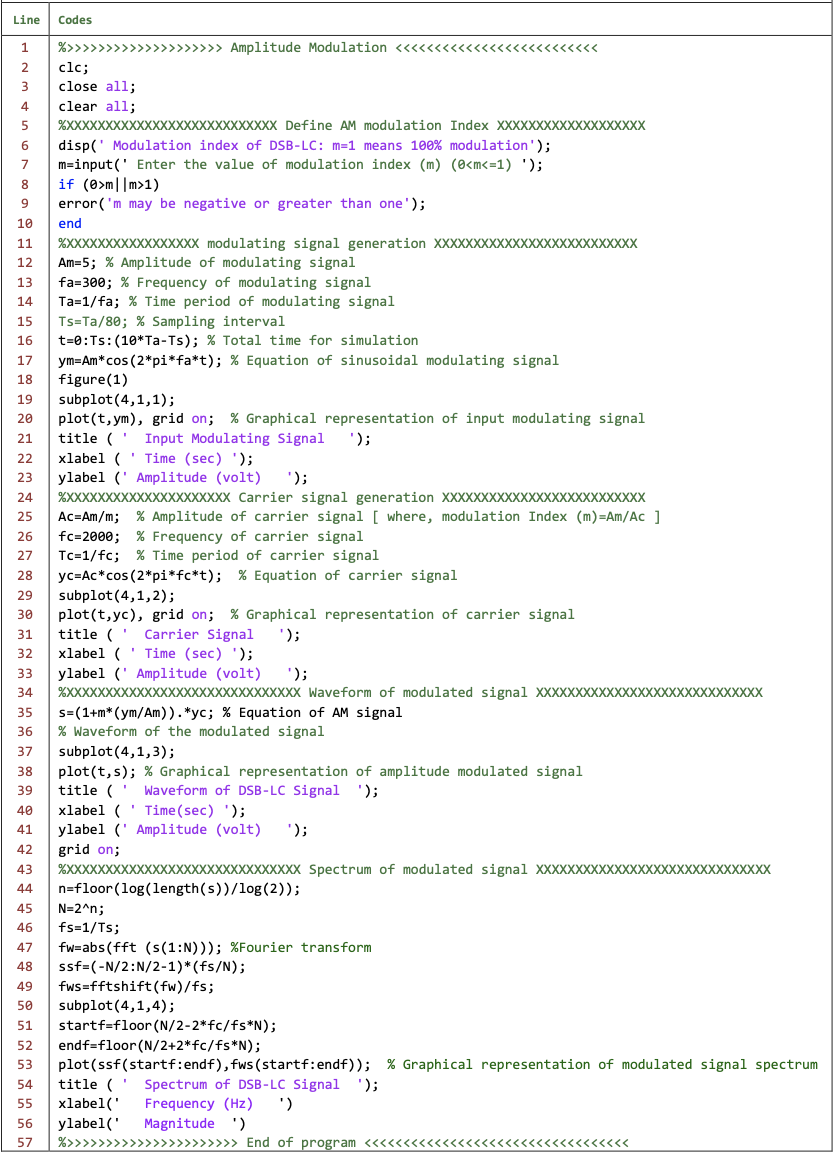
Please assume CUID as 1133557799
Now, you will modify the program code of the Input modulating signal (line 17) to generate a 10-bit digital signal, which corresponds to your own CUID number (10 digits) with each digit spans for a period of Ta. The resultant code will be assigned to the variable ym. You can use the MATLAB functions, ones(1,n) to generate your resultant code, where n is the number of repetitions of the bits to construct each digit. For instance, ones(1,10) will give an array of (1 111111111]. Determine the required number of repetitions for each digit, in terms of Ta (digit period) and Ts (sampling period). The amplitude of each bit will be corresponding to the value of the respective digital your CUID. Write down your new code for ym in the Report File. Line Codes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 %>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> Amplitude Modulation m||m>1) error('m may be negative or greater than one'); end %XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX modulating signal generation XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Am=5; % Amplitude of modulating signal fa=300; % Frequency of modulating signal Ta=1/fa; % Time period of modulating signal Ts=Ta/80; % Sampling interval t=0:Ts:(10*Ta-Ts); % Total time for simulation ym=Am* cos(2*pi*fa*t); % Equation of sinusoidal modulating signal figure(1) subplot(4,1,1); plot(t,ym), grid on; % Graphical representation of input modulating signal title ('Input Modulating Signal '); xlabel ('Time (sec) '); ylabel (' Amplitude (volt) '); %XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Carrier signal generation XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Ac-Am/m; % Amplitude of carrier signal [ where, modulation Index (m)=Am/Ac ] fc=2000; % Frequency of carrier signal TC=1/fc; % Time period of carrier signal yC=Ac* cos(2*pi*fc*t); % Equation of carrier signal subplot(4,1,2); plot(t,yc), grid on; % Graphical representation of carrier signal title(' Carrier Signal '); xlabel (Time (sec) '); ylabel (' Amplitude (volt) '); %XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Waveform of modulated signal XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX S=(1+m* (ym/Am)).*yc; % Equation of AM signal % Waveform of the modulated signal subplot(4,1,3); plot(t,s); % Graphical representation of amplitude modulated signal title ( Waveform of DSB-LC Signal '); xlabel (Time (sec) '); ylabel (Amplitude (volt) '); grid on; %XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Spectrum of modulated signal XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX n=floor(log(length(s)/log(2)); N=2^n; fs=1/Ts; fw=abs(fft (S(1:1))); %Fourier transform ssf=(-N/2:N/2-1)*(fs/N); fws=fftshift(fw/fs; subplot(4,1,4); startf-floor (N/2-2*fc/fs*N); endf-floor(N/2+2*fc/fs*N); plot(ssf (startf:endf), fws (startf:endf)); % Graphical representation of modulated signal spectrum title ( Spectrum of DSB-LC Signal '); xlabel(' Frequency (Hz) ') ylabel(' Magnitude ') %>>>>>>> >>>>>> End of program >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> Amplitude Modulation m||m>1) error('m may be negative or greater than one'); end %XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX modulating signal generation XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Am=5; % Amplitude of modulating signal fa=300; % Frequency of modulating signal Ta=1/fa; % Time period of modulating signal Ts=Ta/80; % Sampling interval t=0:Ts:(10*Ta-Ts); % Total time for simulation ym=Am* cos(2*pi*fa*t); % Equation of sinusoidal modulating signal figure(1) subplot(4,1,1); plot(t,ym), grid on; % Graphical representation of input modulating signal title ('Input Modulating Signal '); xlabel ('Time (sec) '); ylabel (' Amplitude (volt) '); %XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Carrier signal generation XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Ac-Am/m; % Amplitude of carrier signal [ where, modulation Index (m)=Am/Ac ] fc=2000; % Frequency of carrier signal TC=1/fc; % Time period of carrier signal yC=Ac* cos(2*pi*fc*t); % Equation of carrier signal subplot(4,1,2); plot(t,yc), grid on; % Graphical representation of carrier signal title(' Carrier Signal '); xlabel (Time (sec) '); ylabel (' Amplitude (volt) '); %XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Waveform of modulated signal XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX S=(1+m* (ym/Am)).*yc; % Equation of AM signal % Waveform of the modulated signal subplot(4,1,3); plot(t,s); % Graphical representation of amplitude modulated signal title ( Waveform of DSB-LC Signal '); xlabel (Time (sec) '); ylabel (Amplitude (volt) '); grid on; %XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Spectrum of modulated signal XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX n=floor(log(length(s)/log(2)); N=2^n; fs=1/Ts; fw=abs(fft (S(1:1))); %Fourier transform ssf=(-N/2:N/2-1)*(fs/N); fws=fftshift(fw/fs; subplot(4,1,4); startf-floor (N/2-2*fc/fs*N); endf-floor(N/2+2*fc/fs*N); plot(ssf (startf:endf), fws (startf:endf)); % Graphical representation of modulated signal spectrum title ( Spectrum of DSB-LC Signal '); xlabel(' Frequency (Hz) ') ylabel(' Magnitude ') %>>>>>>> >>>>>> End of programStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


