
Please be sure to double click on the attachments to be able to enlarge the images. Thank you.
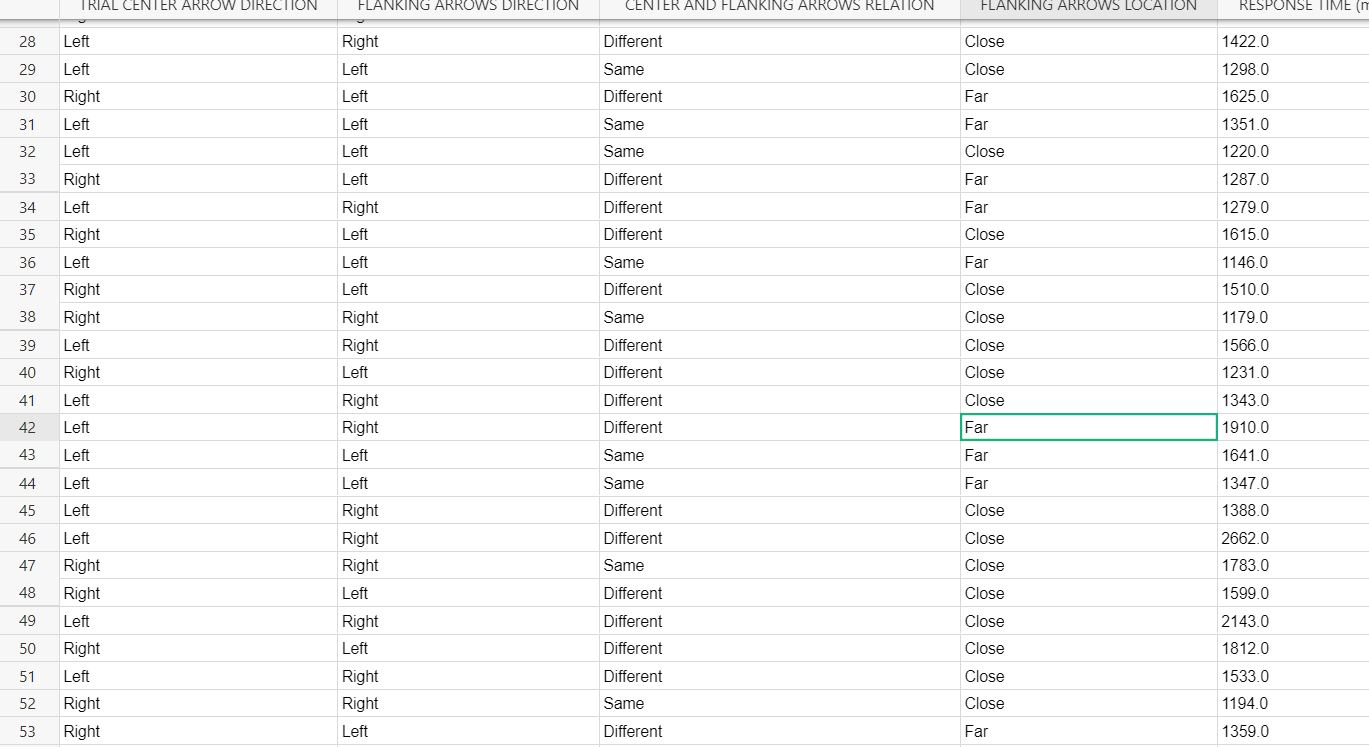
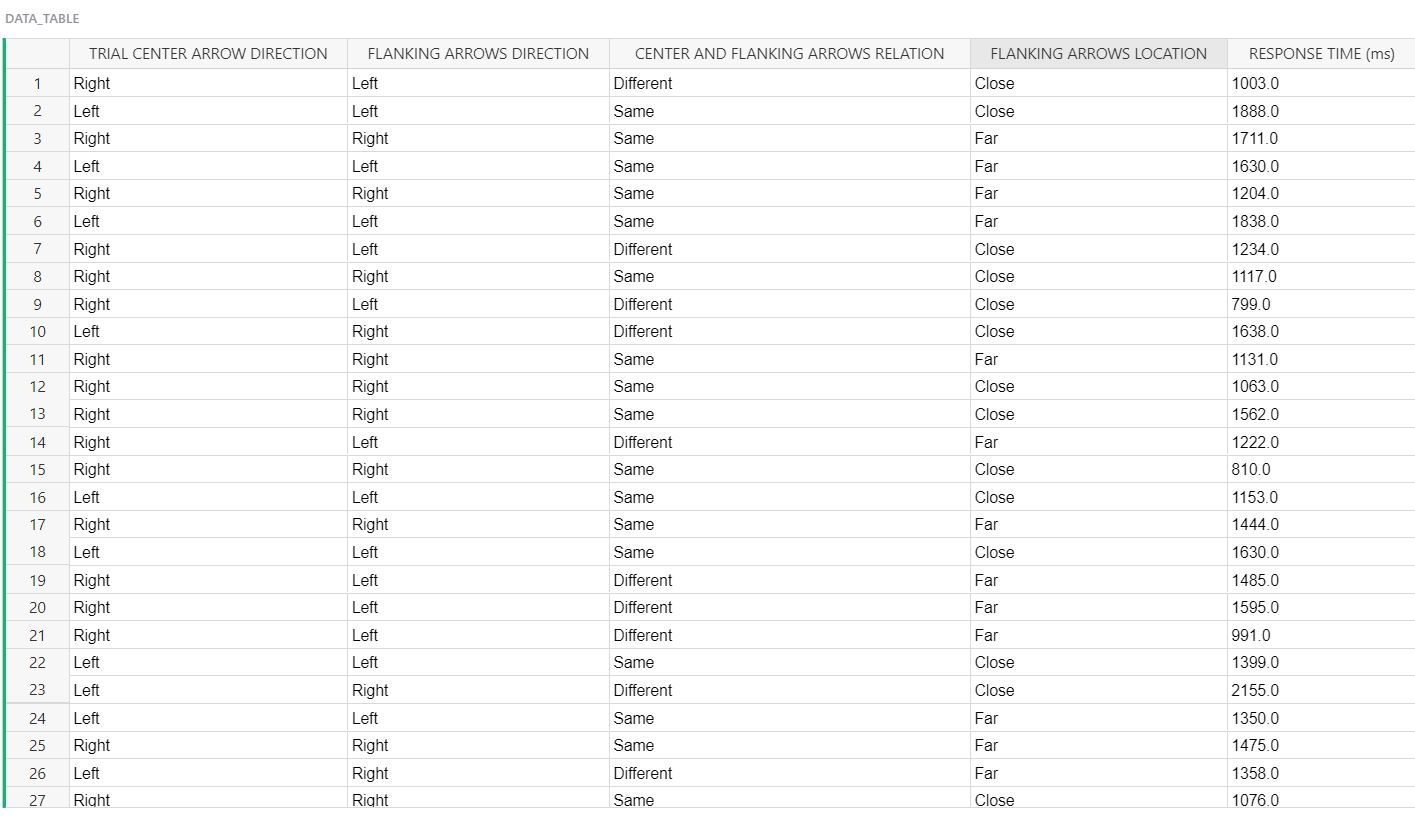
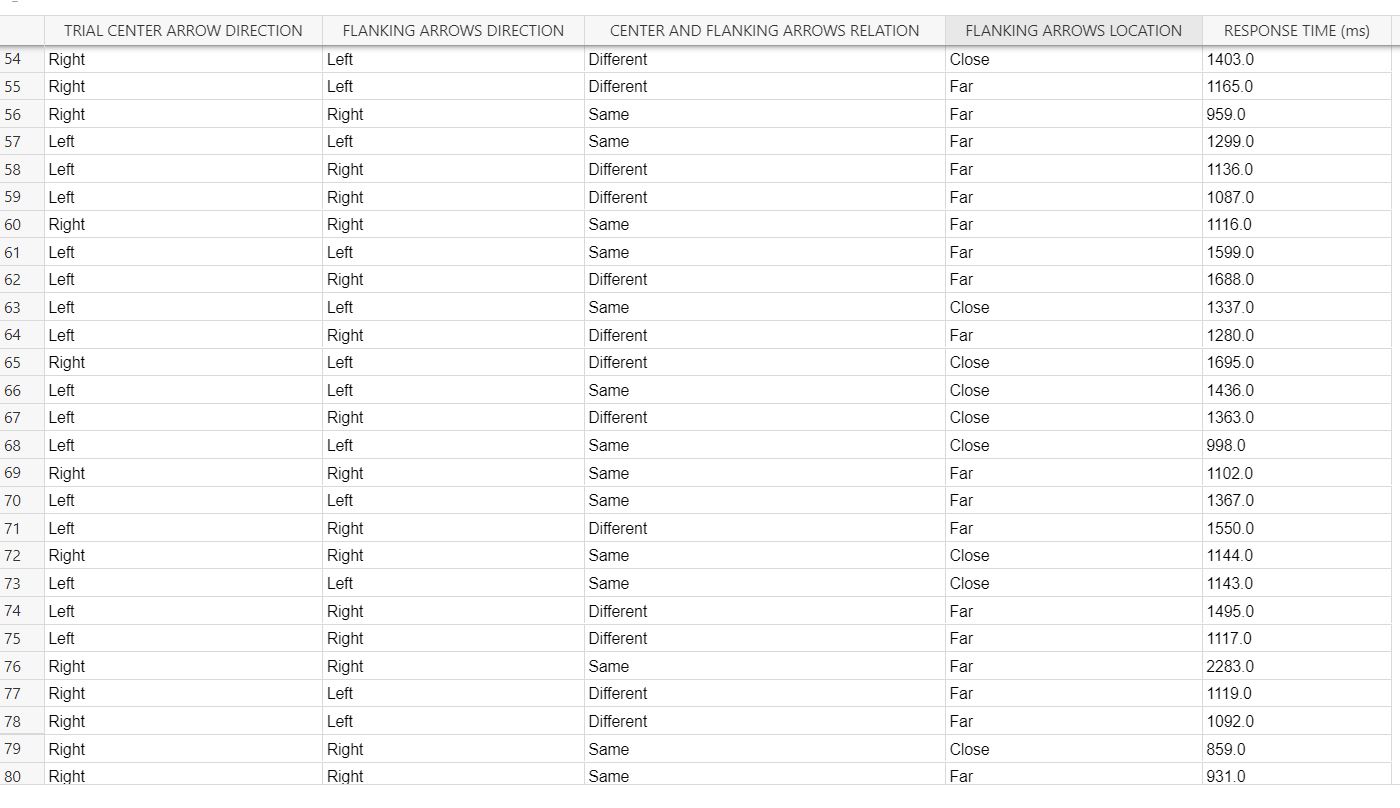
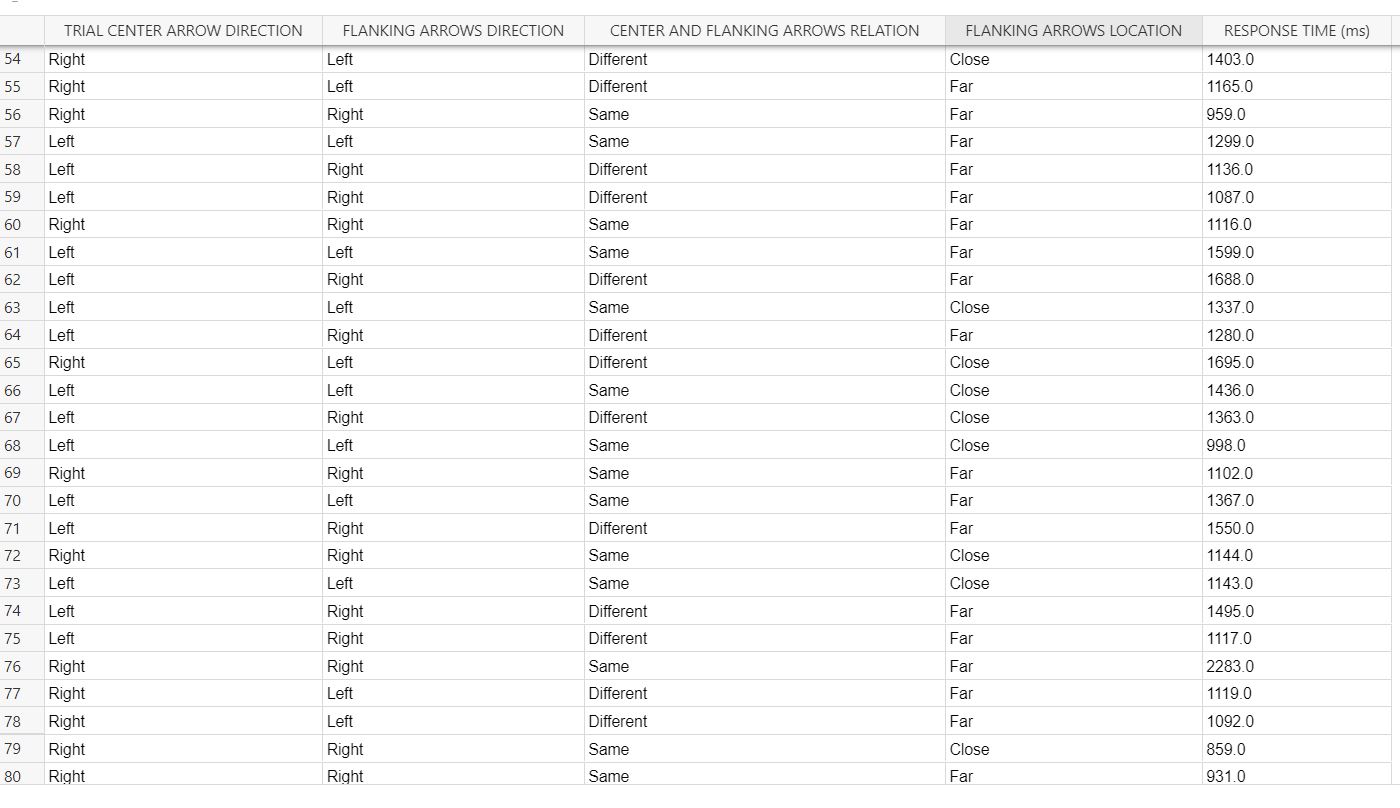
TRIAL CENTER ARROW DIRECTION FLANKING ARROWS DIRECTION CENTER AND FLANKING ARROWS RELATION FLANKING ARROWS LOCATION RESPONSE TIME (n 28 Left Right Different Close 1422.0 29 Left Left Same Close 1298.0 30 Right Left Different Far 1625.0 31 Left Left Same Far 1351.0 32 Left Left Same Close 1220.0 33 Right Left Different Far 1287.0 34 Left Right Different Far 1279.0 35 Right Left Different Close 1615.0 36 Left Left Same Far 1146.0 37 Right Left Different Close 1510.0 38 Right Right Same Close 1179.0 39 Left Right Different Close 1566.0 40 Right Left Different Close 1231.0 41 Left Right Different Close 1343.0 42 Left Right Different Far 1910.0 43 Left Left Same Far 1641.0 44 Left Left Same Far 1347.0 45 Left Right Different Close 1388.0 46 Left Right Different Close 2662.0 47 Right Right Same Close 1783.0 Right Left Different Close 1599.0 49 Left Right Different Close 2143.0 50 Right Left Different Close 1812.0 51 Left Right Different Close 1533.0 52 Right Right Same Close 1194.0 53 Right Left Different Far 1359.0DATJLTAE LE TREAL CENTER ARROW DIRECTiON FLANKING ARROWS DIRECTION CENTER AND FLANKING ARROWS RELATION RANKING mews LOCATION RESPONSE TIME (m5) 1 Right I Left Different ICEDse I 10030 2 Left I Left Same ICiose I 10000 3 Right Right Same Fat 1711.0 4 Left Left Same Fat 1630.0 5 Right Right Same Fat 1204.0 6 Left Left Same Fat 1038.0 7 Right I Left Different 'Close I 1234.0 3 Right Right Same Ciose 1117.0 9 Right I Left Different 'Ciose '790 0 10 Left ' Right Different 'CIose ' 1638.0 11 Right I Right Same I Fat 1131.0 12 Right ' Right Same Chose ' 1003.0 13 Right I Right Same 'Ciose I 1502.0 14 Right I Left Different I Far I 12220 15 Right Right Same Ciose 810 O 16 Left I Left Same Close I 11530 17 Right Right Same Fat 1444.0 18 Left I Left Same ICEthe I 10300 19 Right Left Different Fat 1485.0 20 Right Left Different Fat 1595.0 21 Right Left Different Fat 991 0 22 Left ' Left Same 'CIose ' 1309.0 23 Left Right Different Chose 2155.0 24 Left I Left Same I Fat I 1350.0 25 Right ' Right Same ' Fat 1475.0 26 Left Right Different I Fat 1350.0 __21' Riaht _ Rich! Same _Ciose _ 1016.0 \fWhat methods did we employ in this experiment? On each trial, a central target arrow was presented at the middle of the experiment frame and your task was to quickly determine whether it pointed to the left, . There are two independent variables. The rst is whether the anking arrows point in the same direction as or in a different direction than the target arrow. The second independent variable is the distance between the anking arrows and the target arrow {close or far). The dependent variable was the time between the appearance of the stimulus and your response. Trials where you reported the target direction incorrectly were repeated at a random trial later in the experiment. What do we predict participants will do? Why? The flanking arrows should affect performance. When the anking arrows are close to the target arrow, performance is faster when the flanking arrows point in the same direction as the target and slower when the anking arrows point in the opposite direction. These effects are distance-dependent, and when the anking arrows are far from the target arrow, it does not matter much whether the anking arrow directions are the same as or different than the target. You will use your data to run a Two-way ANOVA (Analysis of Variance} to explore the properties of the flanker effect. This analysis allows you to simultaneously run three related hypothesis tests. The rst test explores a main effect for the congruency of the pointing direction of the target and anking arrows (same or different). The null hypothesis is that the mean reaction times are the same: H0: \"same = \"different- and the altemative hypothesis is that the mean reaction times are different: Ha: \"same i \"different- The second hypothesis test explores whether mean reaction time varies with the location of the ankers relative to the target arrow. The null hypothesis is that the mean reaction times are the same: H03 \"close = l-Ifar: with the alternative hypothesis being that the mean reaction times are different: Ha: \"close # \"far- Finally, you can test for an interaction of the main effects. This test investigates whether there is a difference in the differences of means. For example, the effect of arrow direction might be stronger when the ankers are close to the target and weaker when the ankers are far from the target. The null hypothesis is that the difference of mean reaction times for the two close conditions is equal to the difference of reaction times for the two far conditions: H03 \"same,clcse ' \"differentclose = \"samejar ' \"differentfarv with the alternative hypothesis being that the differences are not equal: Ha: \"same,clcse ' \"differentclose \"samefar ' \"differentfar: For all the tests we will use cr = 0.05. Questions Use the trial-bytrial data to answer these questions. Question Answer Mean RT for center and anking arrows being Same, and the flankers being Far: (The difference between your answer and the correct value must be less-than 0.01.) :1 ' :l Mean RT for center and anking arrows being Different, and the ankers being Far: :I (The difference between your answer and the correct value must be less than 0.01.) :l p-value for relative direction of center and anking arrows (rows): I I :I (The difference between your answer and the correct value must be lees than 0.001 .)_ Fratio for anker location (columns): (The difference between your answer and the correct value must be less than 0.01.) l lu for interaction: (The difference between your answer and the correct value must be less than 0.001.) :I _l Do you reject the null hypothesis for flanker location