Please can someone fill this out and send it back thank you been struggling with this homework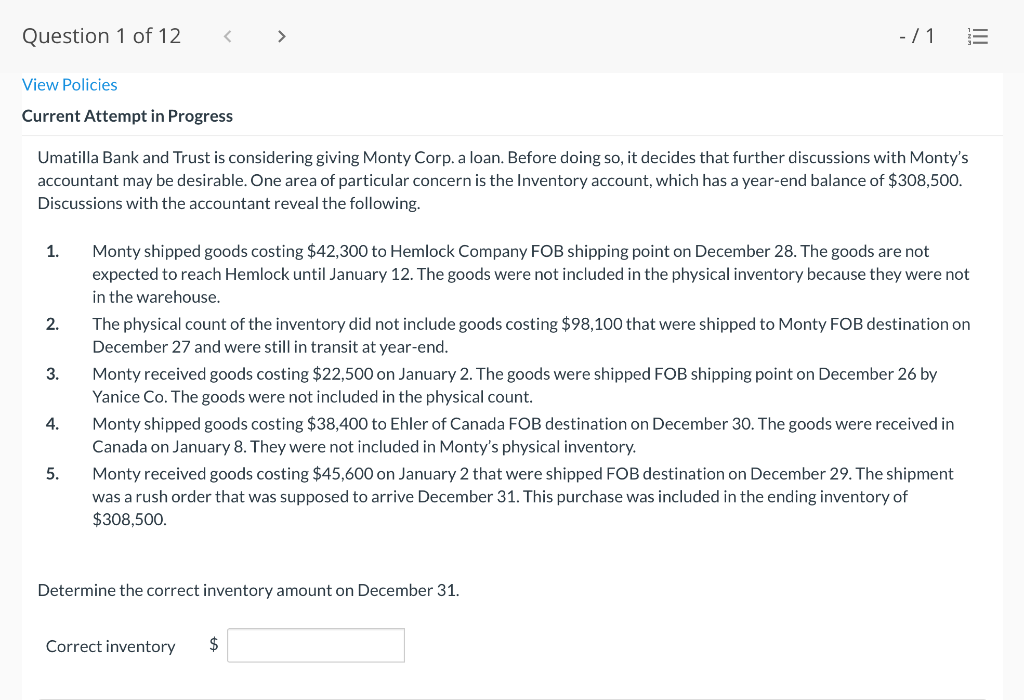
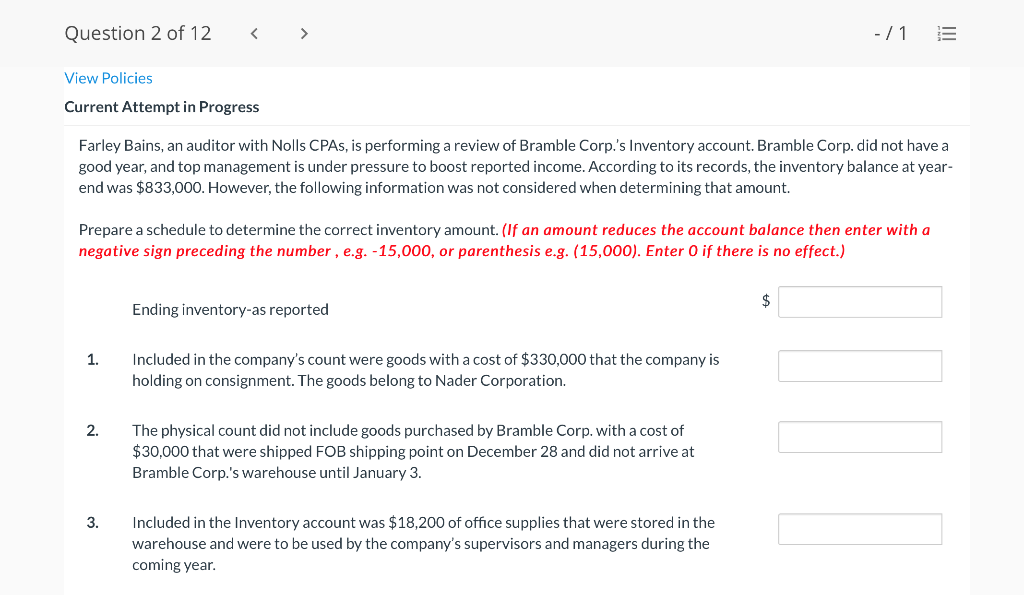
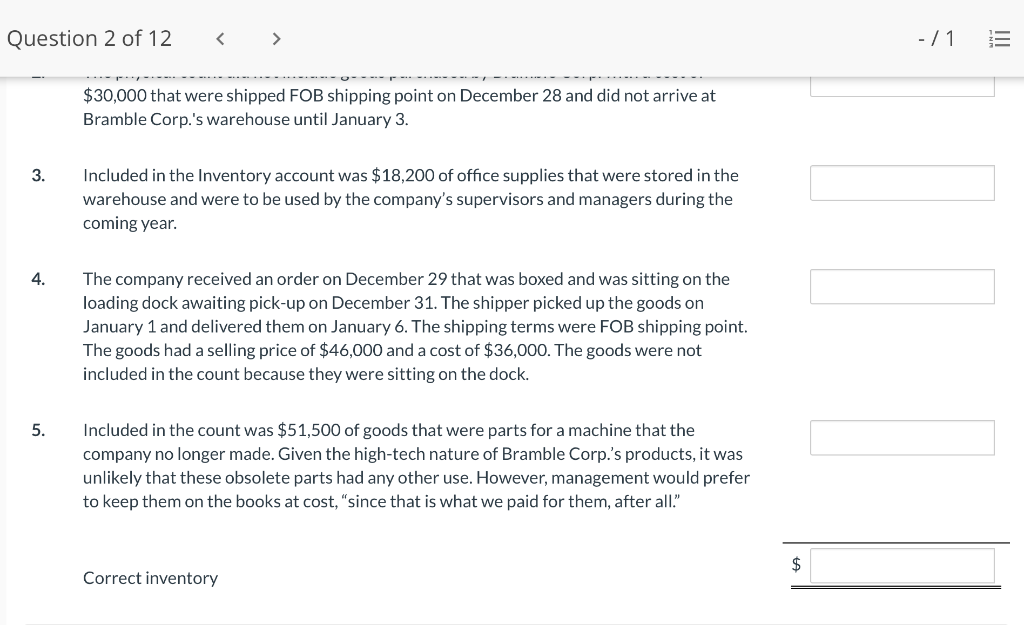
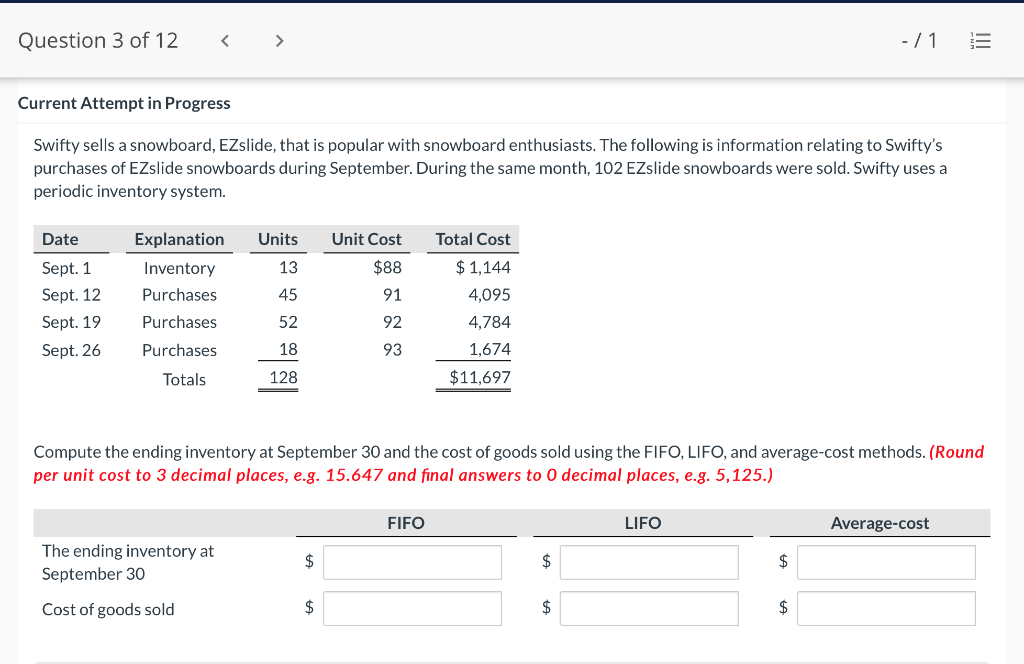
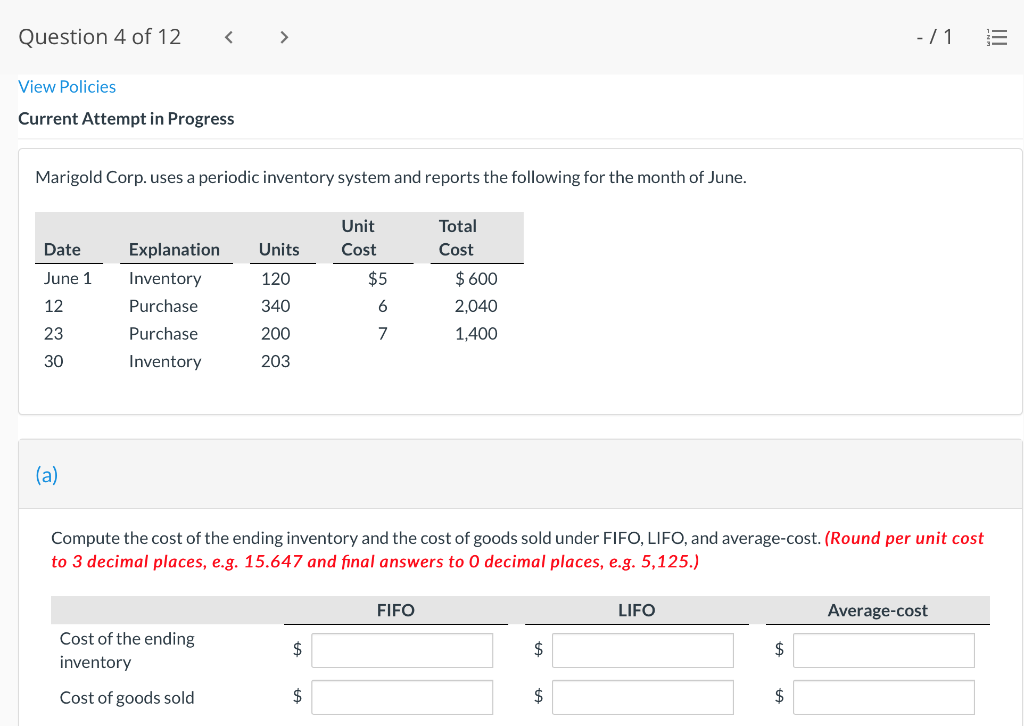
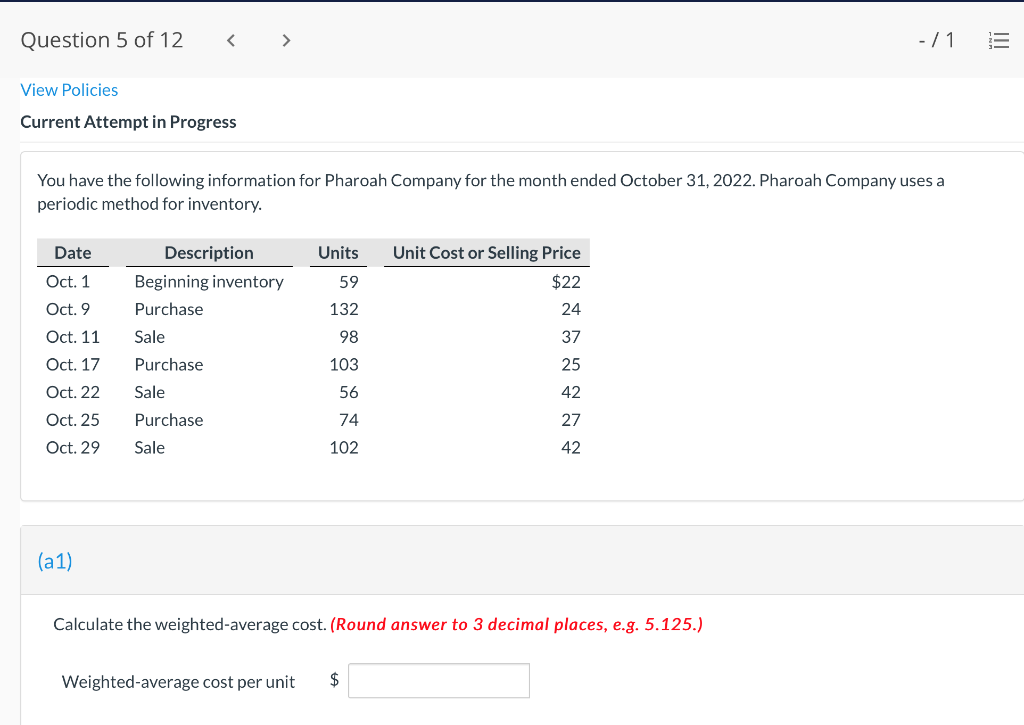
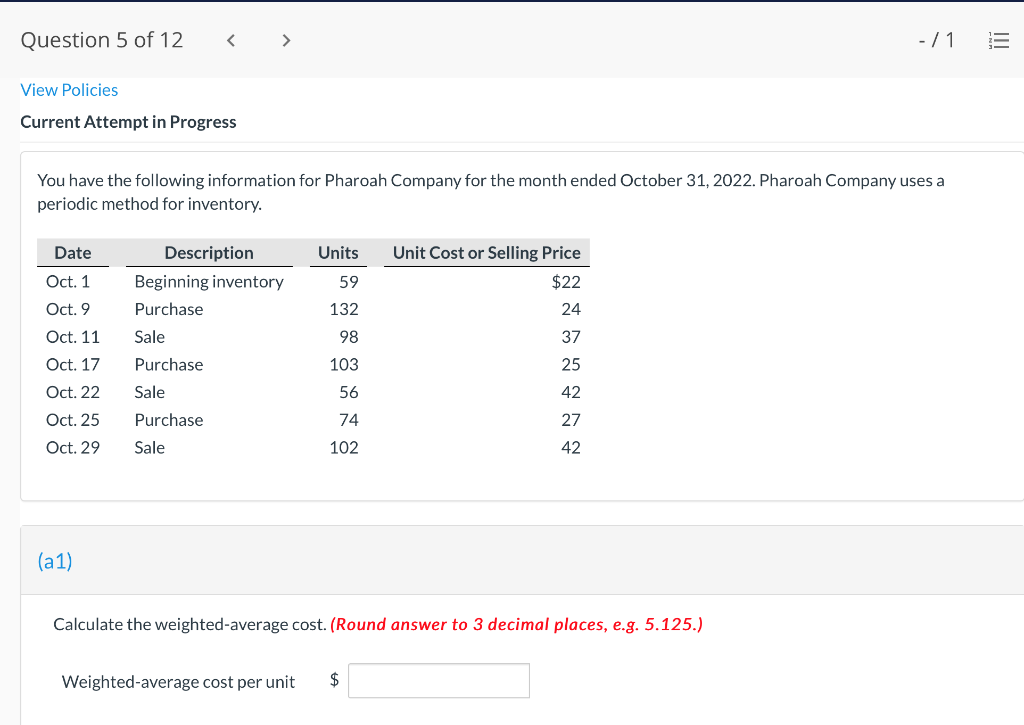
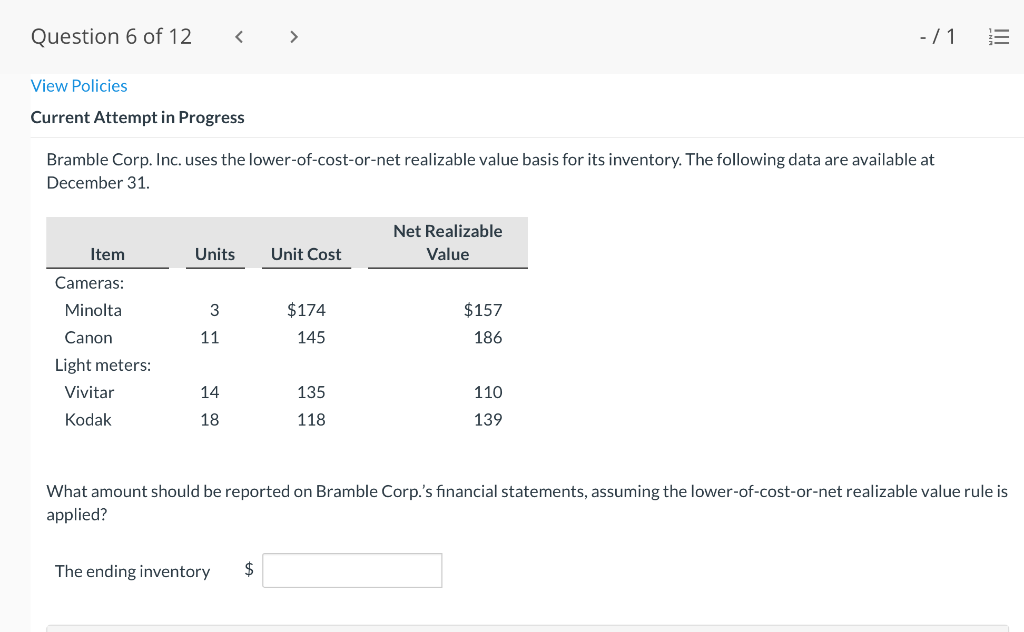
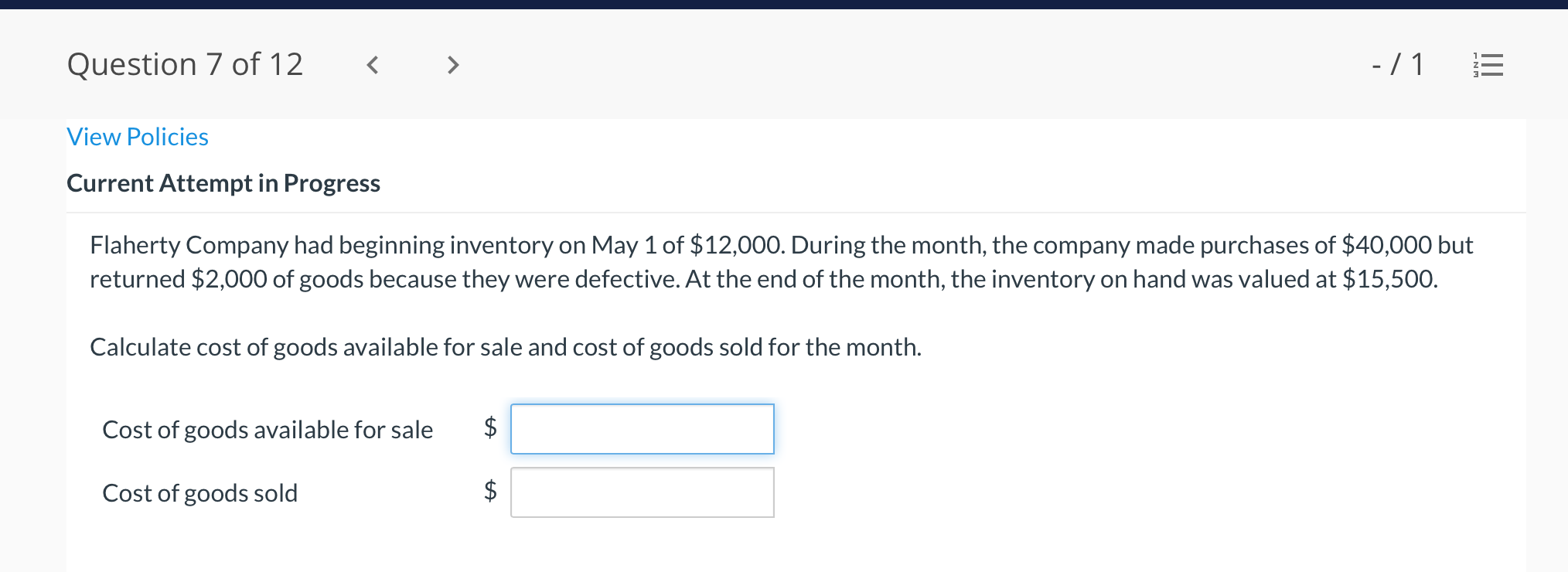
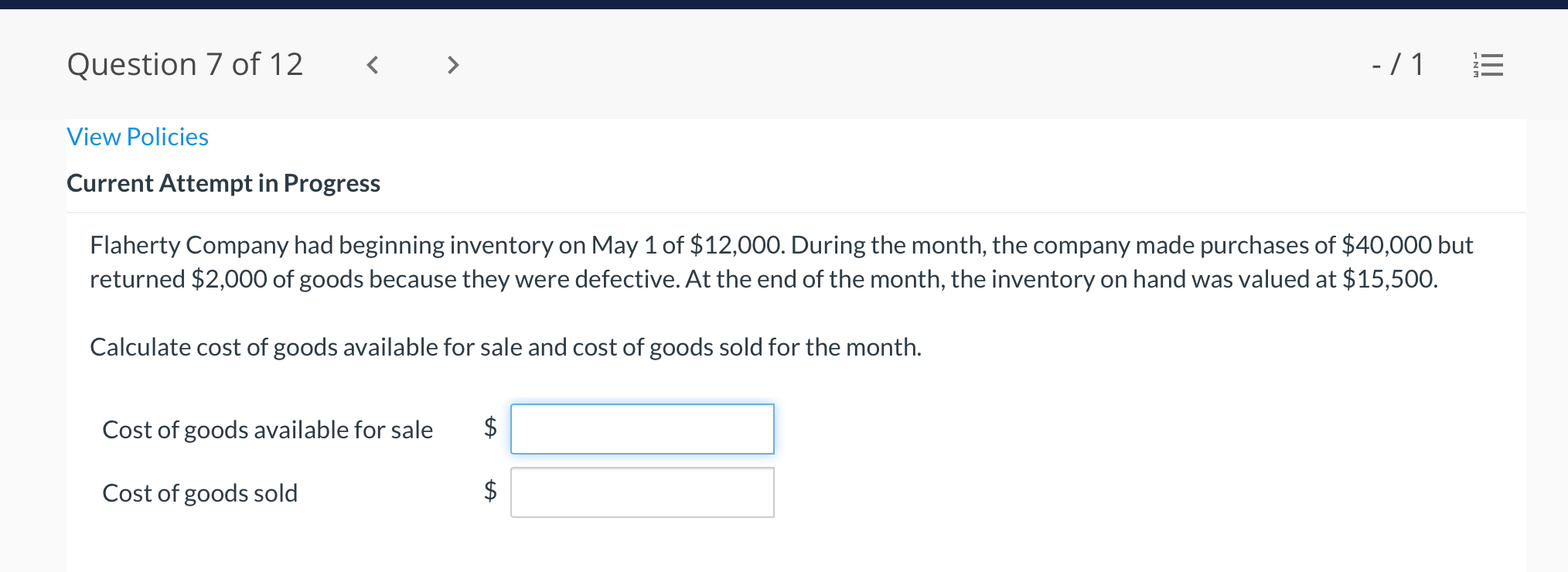
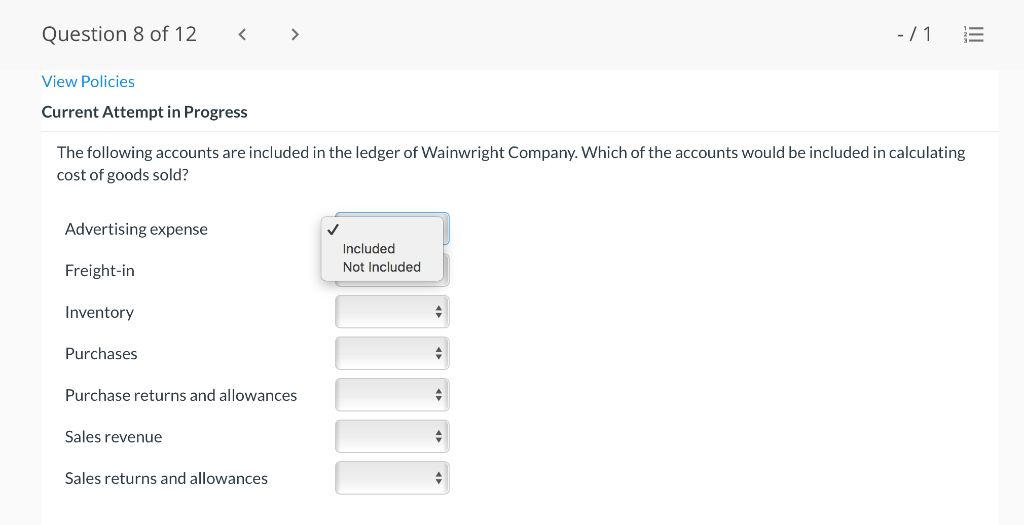
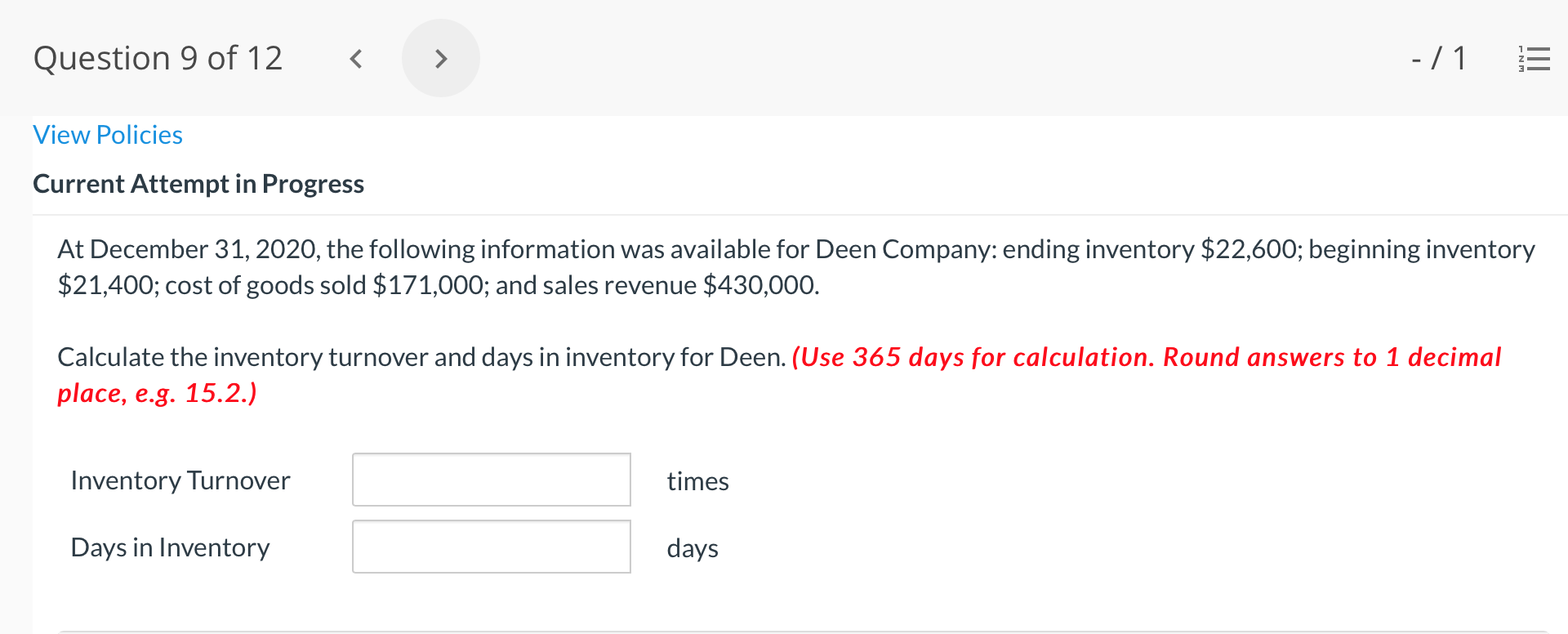
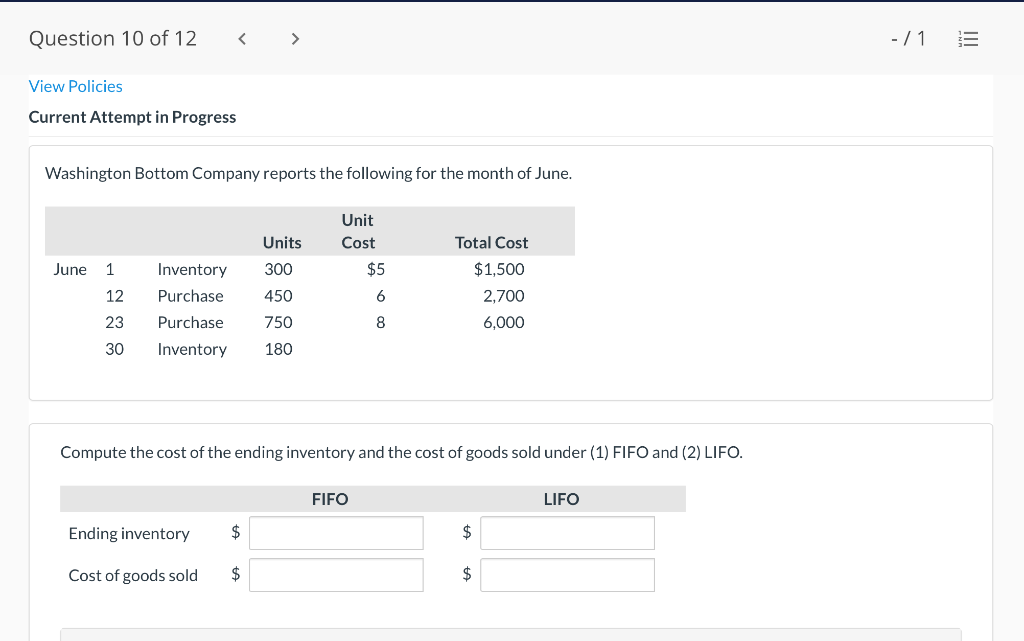
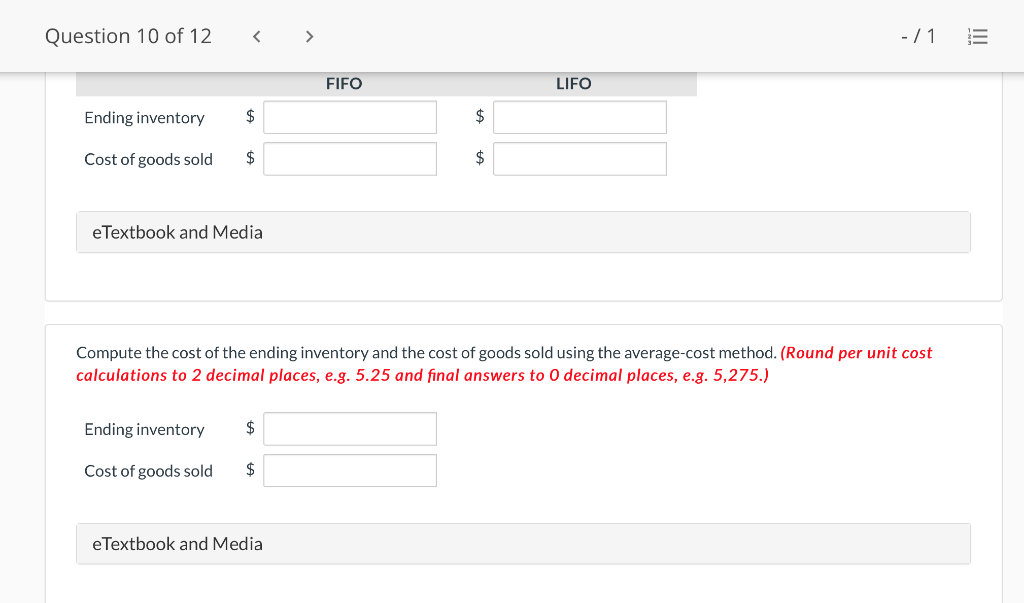
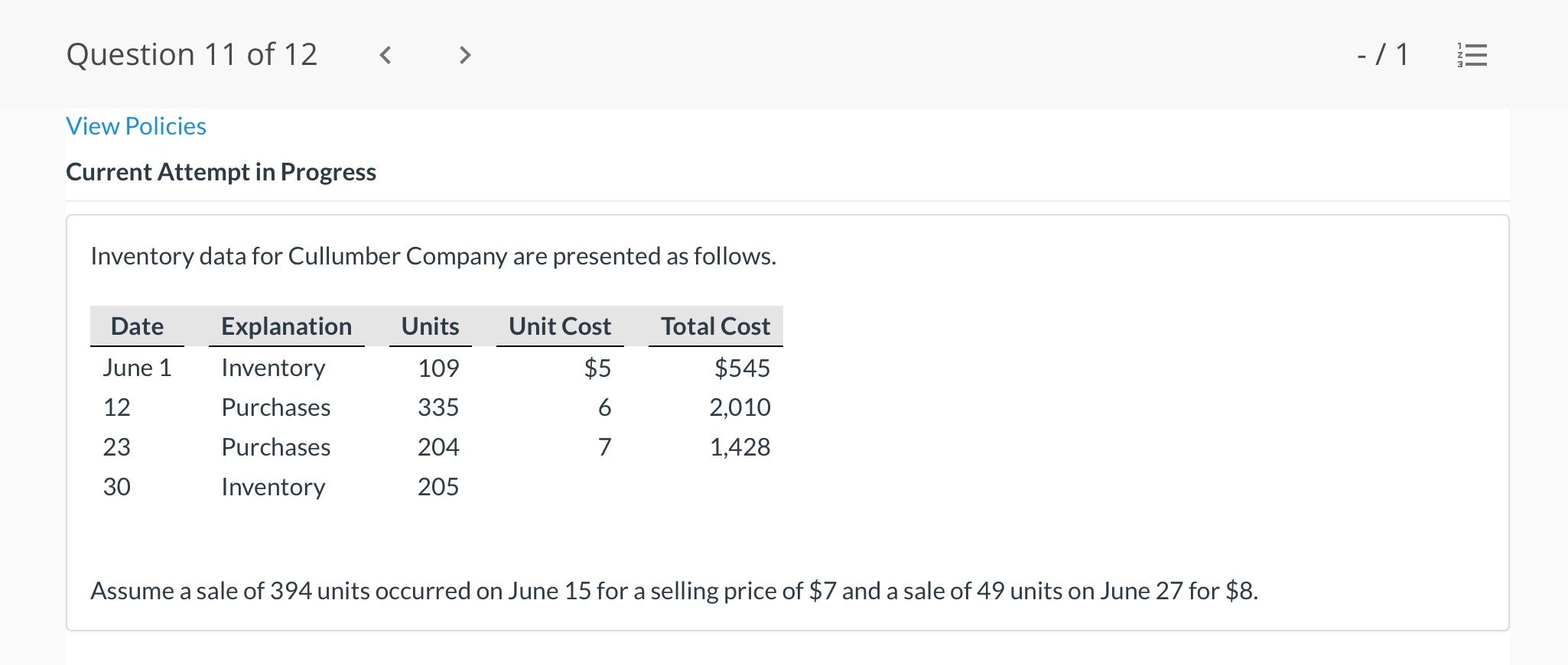
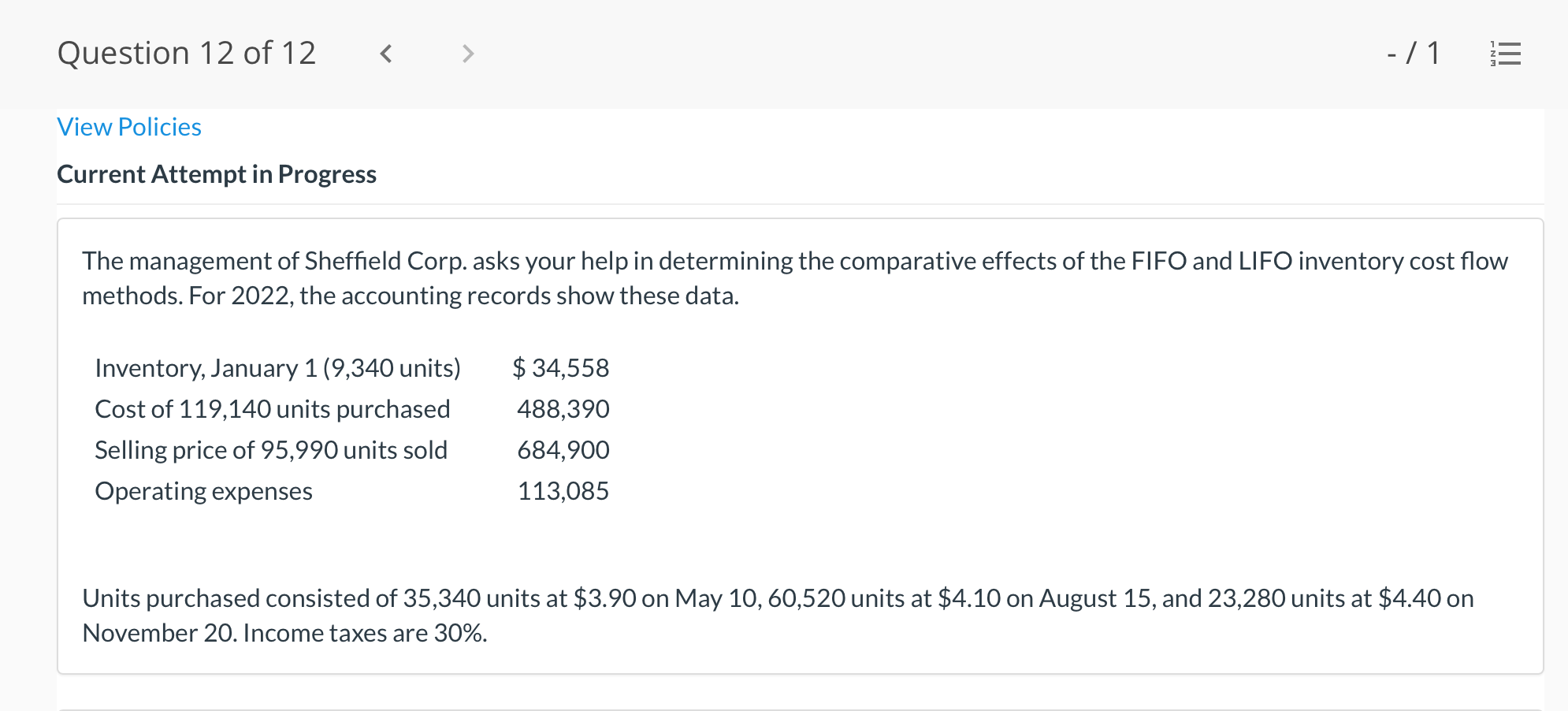
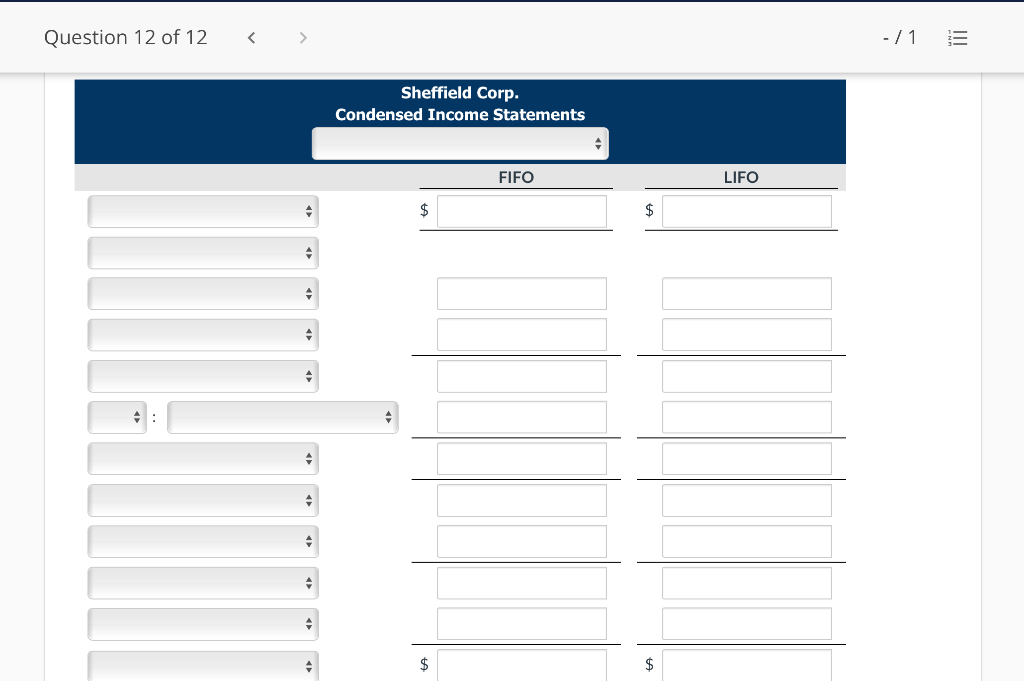
Question 1 of 12 -/1 View Policies Current Attempt in Progress Farley Bains, an auditor with Nolls CPAs, is performing a review of Bramble Corp.'s Inventory account. Bramble Corp. did not have a good year, and top management is under pressure to boost reported income. According to its records, the inventory balance at year- end was $833,000. However, the following information was not considered when determining that amount. Prepare a schedule to determine the correct inventory amount. (If an amount reduces the account balance then enter with a negative sign preceding the number, e.g.-15,000, or parenthesis e.g. (15,000). Enter O if there is no effect.) $ Ending inventory-as reported 1. Included in the company's count were goods with a cost of $330,000 that the company is holding on consignment. The goods belong to Nader Corporation. 2 The physical count did not include goods purchased by Bramble Corp. with a cost of $30,000 that were shipped FOB shipping point on December 28 and did not arrive at Bramble Corp.'s warehouse until January 3. 3. Included in the Inventory account was $18,200 of office supplies that were stored in the warehouse and were to be used by the company's supervisors and managers during the coming year. Question 2 of 12 - 71 III $30,000 that were shipped FOB shipping point on December 28 and did not arrive at Bramble Corp.'s warehouse until January 3. 3. Included in the Inventory account was $18,200 of office supplies that were stored in the warehouse and were to be used by the company's supervisors and managers during the coming year. 4. The company received an order on December 29 that was boxed and was sitting on the loading dock awaiting pick-up on December 31. The shipper picked up the goods on January 1 and delivered them on January 6. The shipping terms were FOB shipping point. The goods had a selling price of $46,000 and a cost of $36,000. The goods were not included in the count because they were sitting on the dock. 5. Included in the count was $51,500 of goods that were parts for a machine that the company no longer made. Given the high-tech nature of Bramble Corp.'s products, it was unlikely that these obsolete parts had any other use. However, management would prefer to keep them on the books at cost, "since that is what we paid for them, after all." $ Correct inventory Question 3 of 12 - / 1 = Current Attempt in Progress Swifty sells a snowboard, EZslide, that is popular with snowboard enthusiasts. The following is information relating to Swifty's purchases of EZslide snowboards during September. During the same month, 102 EZslide snowboards were sold. Swifty uses a periodic inventory system. Date Units Unit Cost Total Cost 13 $88 Explanation Inventory Purchases Purchases 45 Sept. 1 Sept. 12 Sept. 19 Sept. 26 91 52 92 93 $ 1,144 4,095 4,784 1,674 $11,697 Purchases 18 Totals 128 Compute the ending inventory at September 30 and the cost of goods sold using the FIFO, LIFO, and average-cost methods. (Round per unit cost to 3 decimal places, e.g. 15.647 and final answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,125.) FIFO LIFO Average-cost The ending inventory at September 30 $ $ $ Cost of goods sold $ $ $ Question 4 of 12 > - 71 III View Policies Current Attempt in Progress Marigold Corp. uses a periodic inventory system and reports the following for the month of June. Total Unit Cost Date Units Cost June 1 Explanation Inventory Purchase 120 $5 12 6 $ 600 2,040 1,400 23 340 200 203 Purchase 7 30 Inventory (a) Compute the cost of the ending inventory and the cost goods sold under FIFO, LIFO, and average-cost. (Round per unit cost to 3 decimal places, e.g. 15.647 and final answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,125.) FIFO LIFO Average-cost Cost of the ending inventory $ $ $ Cost of goods sold $ $ $ Question 5 of 12 - / 1 View Policies Current Attempt in Progress You have the following information for Pharoah Company for the month ended October 31, 2022. Pharoah Company uses a periodic method for inventory. Date Units Unit Cost or Selling Price $22 Oct. 1 59 Description Beginning inventory Purchase Sale 132 24 Oct. 9 Oct. 11 98 103 Oct. 17 Purchase Oct. 22 Sale 56 37 25 42 27 42 Oct. 25 74 Purchase Sale Oct. 29 102 (a 1) Calculate the weighted average cost. (Round answer to 3 decimal places, e.g. 5.125.) Weighted average cost per unit $ Question 5 of 12 - / 1 View Policies Current Attempt in Progress You have the following information for Pharoah Company for the month ended October 31, 2022. Pharoah Company uses a periodic method for inventory. Date Units Unit Cost or Selling Price $22 Oct. 1 59 Description Beginning inventory Purchase Sale 132 24 Oct. 9 Oct. 11 98 103 Oct. 17 Purchase Oct. 22 Sale 56 37 25 42 27 42 Oct. 25 74 Purchase Sale Oct. 29 102 (a 1) Calculate the weighted average cost. (Round answer to 3 decimal places, e.g. 5.125.) Weighted average cost per unit $ Question 6 of 12 - / 1 2 View Policies Current Attempt in Progress Bramble Corp. Inc. uses the lower-of-cost-or-net realizable value basis for its inventory. The following data are available at December 31 Net Realizable Value Item Units Unit Cost Cameras: Minolta 3 $174 $157 186 11 145 Canon Light meters: Vivitar Kodak 14 135 110 139 18 118 What amount should be reported on Bramble Corp.'s financial statements, assuming the lower-of-cost-or-net realizable value rule is applied? The ending inventory $ Question 7 of 12 -/1 E View Policies Current Attempt in Progress Flaherty Company had beginning inventory on May 1 of $12,000. During the month, the company made purchases of $40,000 but returned $2,000 of goods because they were defective. At the end of the month, the inventory on hand was valued at $15,500. Calculate cost of goods available for sale and cost of goods sold for the month. Cost of goods available for sale $ Cost of goods sold $ e Textbook and Media Save for Later Attempts: 0 of 3 used Submit Answer Question 7 of 12 - 71 View Policies Current Attempt in Progress Flaherty Company had beginning inventory on May 1 of $12,000. During the month, the company made purchases of $40,000 but returned $2,000 of goods because they were defective. At the end of the month, the inventory on hand was valued at $15,500. Calculate cost of goods available for sale and cost of goods sold for the month. Cost of goods available for sale $ Cost of goods sold ta Question 7 of 12 - 71 View Policies Current Attempt in Progress Flaherty Company had beginning inventory on May 1 of $12,000. During the month, the company made purchases of $40,000 but returned $2,000 of goods because they were defective. At the end of the month, the inventory on hand was valued at $15,500. Calculate cost of goods available for sale and cost of goods sold for the month. Cost of goods available for sale $ Cost of goods sold ta Question 8 of 12 - 71 View Policies Current Attempt in Progress The following accounts are included in the ledger of Wainwright Company. Which of the accounts would be included in calculating cost of goods sold? Advertising expense Included Not Included Freight-in Inventory Purchases Purchase returns and allowances Sales revenue Sales returns and allowances Question 9 of 12 - 71 III View Policies Current Attempt in Progress At December 31, 2020, the following information was available for Deen Company: ending inventory $22,600; beginning inventory $21,400; cost of goods sold $171,000; and sales revenue $430,000. Calculate the inventory turnover and days in inventory for Deen. (Use 365 days for calculation. Round answers to 1 decimal place, e.g. 15.2.) Inventory Turnover times Days in Inventory days Question 10 of 12 - 71 View Policies Current Attempt in Progress Washington Bottom Company reports the following for the month of June. Unit Cost Units June 1 300 $5 Total Cost $1,500 2,700 6.000 12 450 Inventory Purchase Purchase Inventory 6 23 750 8 30 180 Compute the cost of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold under (1) FIFO and (2) LIFO. FIFO LIFO Ending inventory $ $ Cost of goods sold $ $ Question 10 of 12 - / 1 FIFO LIFO Ending inventory $ Cost of goods sold $ $ e Textbook and Media Compute the cost of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold using the average-cost method. (Round per unit cost calculations to 2 decimal places, e.g. 5.25 and final answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) Ending inventory $ Cost of goods sold $ e Textbook and Media Question 11 of 12 -/1 III View Policies Current Attempt in Progress Inventory data for Cullumber Company are presented as follows. Date Units Unit Cost Total Cost June 1 109 $5 Explanation Inventory Purchases Purchases Inventory $545 2,010 12 335 6. 7 23 204 1,428 30 205 Assume a sale of 394 units occurred on June 15 for a selling price of $7 and a sale of 49 units on June 27 for $8. Question 12 of 12
























