Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please check if the calculations and interpretation are correct. If there are any errors, please correct them along with the solution process. 1 - way
Please check if the calculations and interpretation are correct. If there are any errors, please correct them along with the solution process.
way ANOVA, a
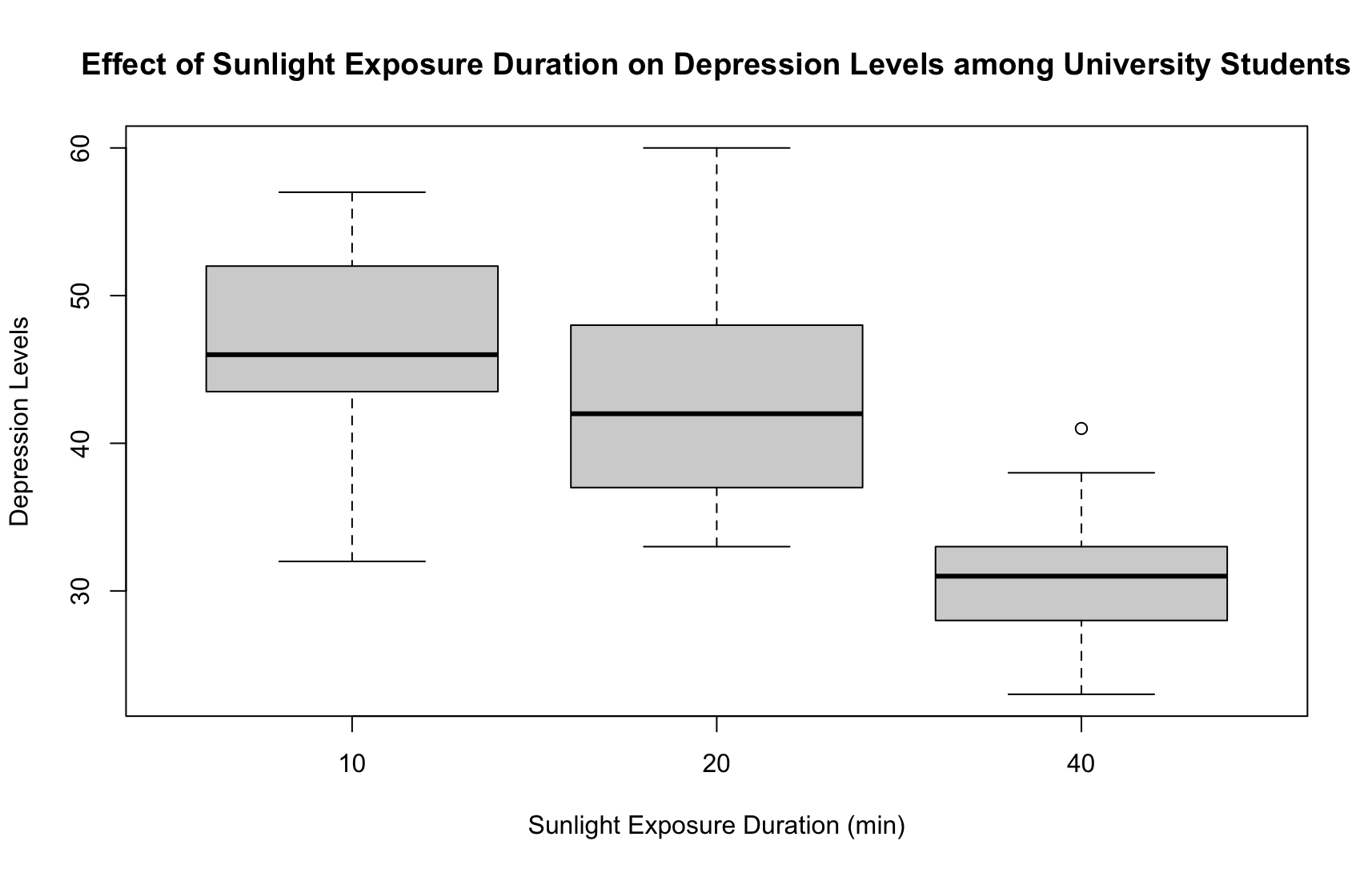
This study investigates how different durations of sunlight exposure affect depression levels in university students. Sixty students will be randomly divided into groups exposed to sunlight for and minutes. Following exposure, their depression levels will be measured and recorded. We predict longer sunlight exposure will correlate with lower depression levels, based on existing research linking sunlight to mood regulation.
The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference in depression levels among university students exposed to different durations of sunlight, while the alternative hypothesis states that there is a significant difference in depression levels among university students exposed to different durations of sunlight.
The descriptive statistics for depression levels among university students exposed to varying durations of sunlight are as follows. In the group exposed to sunlight for minutes, the depression level was found to be M SD For the group exposed to sunlight for minutes, the depression level was M SD Finally, in the group exposed to sunlight for minutes, the depression level was M SD
The oneway ANOVA with a significance level a was conducted to compare the effects of sunlight exposure duration on depression levels. There was a significant difference in depression levels among the different durations of sunlight exposure for the three groups, F p LSD post hoc test results revealed that the group with minutes of sunlight exposure had significantly lower depression levels M SD compared to the group with minutes of sunlight exposure M SD Additionally, the group with minutes of sunlight exposure had significantly lower depression levels compared to the group with minutes of sunlight exposure M SD indicating a beneficial effect of longer sunlight exposure duration. However, there was no significant difference in depression levels between the group with minutes of sunlight exposure and the group with minutes of sunlight exposure.
Taken together, these results suggest that different durations of sunlight exposure do affect university students depression levels. Specifically, our results suggest that students depression levels decrease when they are exposed to a longer duration of sunlight. However, it should be noted that the duration must be long enough to see an effect. The intermediate level of minutes does not appear to decrease depression levels among university students significantly.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


