Question
Please code these 3 functions in OCaml language. DO NOT use recursion nor outside recursive helper methods . There is also a limit to list
Please code these 3 functions in OCaml language. DO NOT use recursion nor outside recursive helper methods. There is also a limit to list library methods, and the only ones you are allowed to use are: [reverse] and [merge] that I have implemented myself, being:
reverse: returns a list that has a reverse order of the one that was passed in. Example: reverse [1; 2; 3] = [3; 2; 1]
merge: Merges 2 lists into a single one, sorting the values at the same time. Example: merge [1; 4; 5] [2; 3; 6; 7; 8; 9] = [1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9]
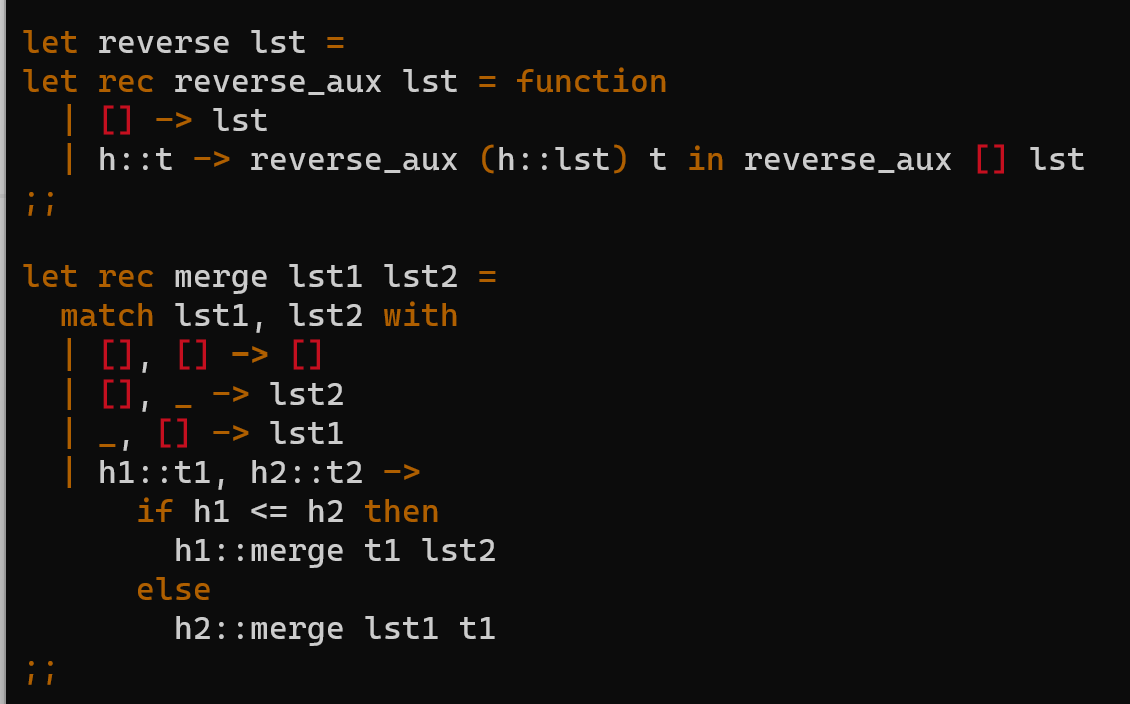 the code that has to be implemented are the following:
the code that has to be implemented are the following: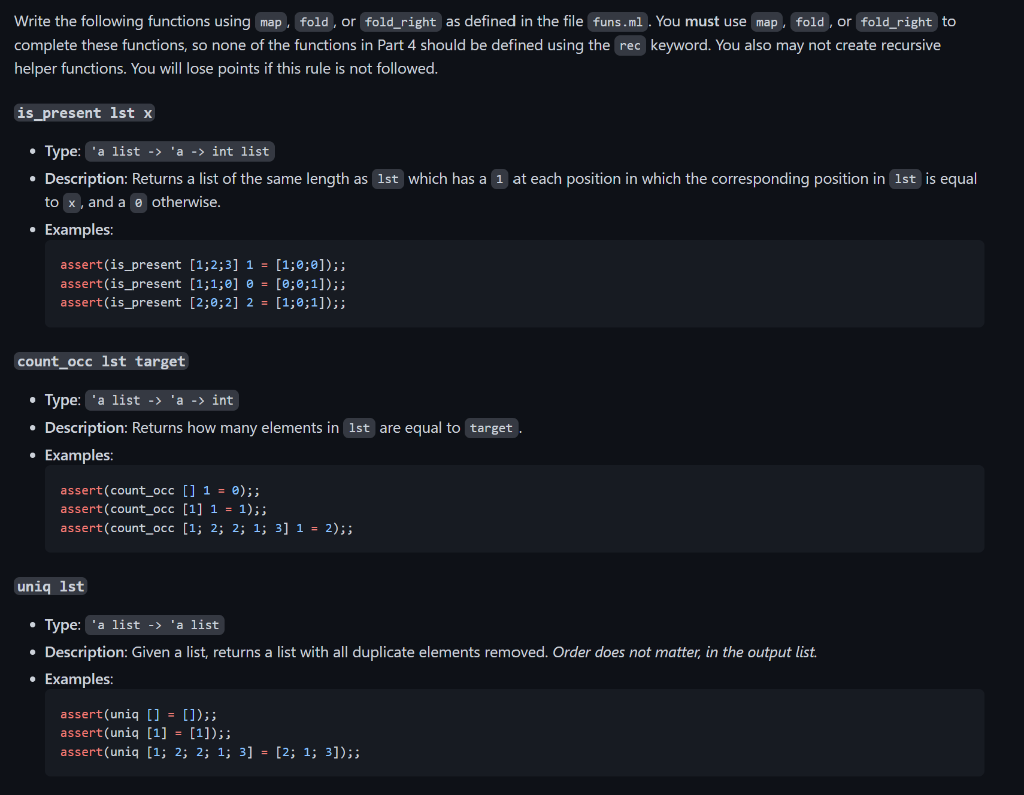
The functions from funs.ml is provided below, along with the typing for each function and their parameter:
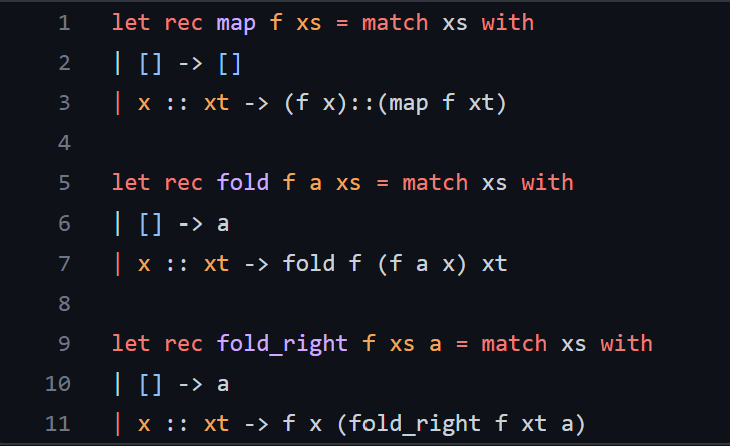
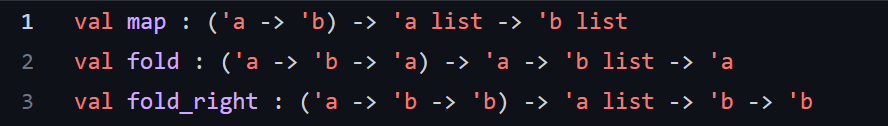
I understand this is a hard code to do with the restrictions spoken above, but please help me with them.
let reverse lst = let rec reverse_aux lst = function [] lst h::t reverse_aux (h::lst) t in reverse_aux [] lst li let rec merge lst1 lst2 match lst1, lst2 with [],[][] ,> lst2 1[] lst1 h1::t1, h2::t2 > if h1 x - Type: 'a list ' a int list - Description: Returns a list of the same length as 1 st which has a 1 at each position in which the corresponding position in 1 st is equal to x, and a otherwise. - Examples: \( \begin{aligned} \text { assert(is_present }[1 ; 2 ; 3] 1 & =[1 ; \theta ; \theta]) ; \\ \text { assert(is_present }[1 ; 1 ; \theta] \theta & =[0 ; \theta ; 1]) ; \\ \text { assert(is_present }[2 ; 0 ; 2] 2 & =[1 ; 0 ; 1]) ;\end{aligned} \) count_occ lst target - Type: 'a list ' a int - Description: Returns how many elements in lst are equal to target. - Examples: assert (count_occ [] 1=0);; assert ( count_occ [1]1=1);; assert(count_occ [1;2;2;1;3]1=2);; uniq lst - Type: 'a list 'a list - Description: Given a list, returns a list with all duplicate elements removed. Order does not matter, in the output list. - Examples: assert( uniq []=[]);; assert( uniq [1]=[1]);; assert( uniq [1;2;2;1;3]=[2;1;3])Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


