PLEASE DO NOT COPY AND PASTE THE SAME ANSWERS AS OTHER POSTERS QUESTIONS AS THEY ARE WRONG AND MISSED A VITAL PART OF INFORMATION.

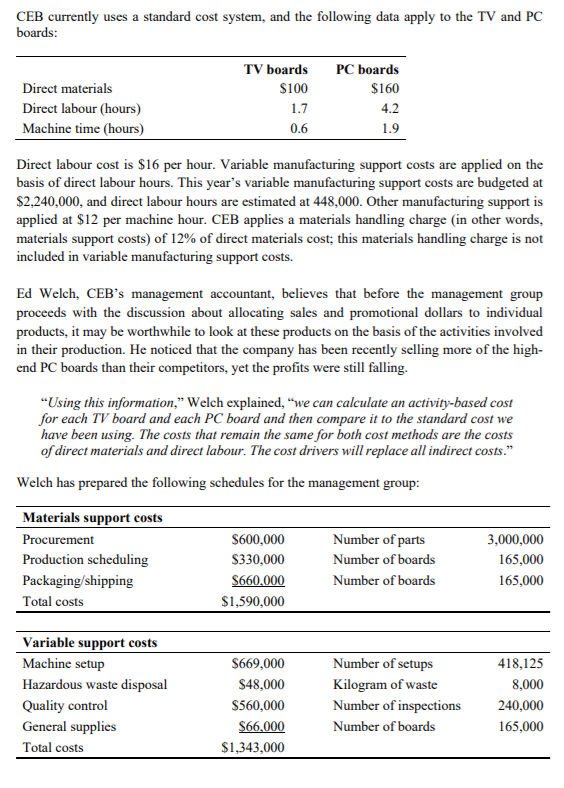
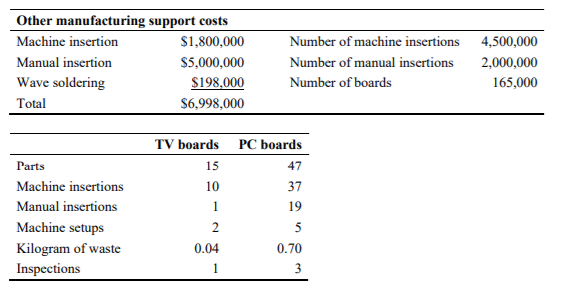
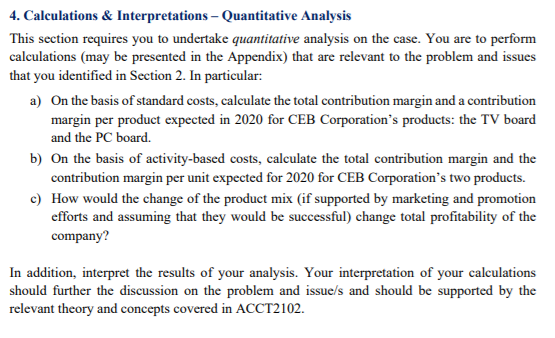
CEB Corporation is an Australian owned printed circuit board manufacturer with customers worldwide including Australia, Asia, USA and Europe. It has grown substantially over the years since its establishment in 1992 and in 2001 went public to acquire additional capital for future growth. Being a public company, CEB is under relatively high performance pressure from its investors who closely monitor the profit margins and cash flows. The profits have been falling over the last three years and its profitability is below the industry average. This has had a negative impact on the company's share price. In addition, the COVID 19 crisis set CEB's targeted profit under a serious threat. Although CEB manufactures several different types of printed-circuit boards, two of the boards account for the majority of the company's sales - a TV circuit board and a PC circuit board. The first of these boards, a TV board, has been a standard in the industry for several years. The market for this type of board is competitive and therefore, price sensitive. The second high- volume product is a PC board of which the manufacturing process is substantially different and more complex relative to that of the TV board. Because the PC board incorporates the latest technology, it can be sold at a premium price. In the recent years, PC boards have become number one product for CEB. The original plan for 2020 was to sell 80,000 of the TV boards at a price of $200 per unit and 130,000 PC boards at $350 per unit. However, CEB's management group is meeting to discuss how to react to the COVID 19 crisis on the top of the already falling profits, and how to spend the sales and promotion budget to protect if not increase the company's profit during the crisis. They are considering several options and discussing which product mix would result in the highest profits. The sales manager Jason Jackman believes that the market share for the TV board could be expanded by concentrating CEB's promotional efforts in this area. Moreover, due to lockdown the sales of TVs are increasing worldwide, generating more demand for TV boards. In response to this suggestion, the production manager Stacey Hu said, "Why don't we go after a bigger market for the PC board? The cost sheets that I reviewed show that the contribution from the PC board is one and a half times the contribution from the TV board. I know we get a premium price for the PC board. Focusing on the PC boards and changing the product mix should help overall profitability." CEB currently uses a standard cost system, and the following data apply to the TV and PC boards: 1.7 4.2 1.9 TV boards PC boards Direct materials $100 $160 Direct labour (hours) Machine time (hours) 0.6 Direct labour cost is $16 per hour. Variable manufacturing support costs are applied on the basis of direct labour hours. This year's variable manufacturing support costs are budgeted at $2,240,000, and direct labour hours are estimated at 448,000. Other manufacturing support is applied at $12 per machine hour. CEB applies a materials handling charge (in other words, materials support costs) of 12% of direct materials cost; this materials handling charge is not included in variable manufacturing support costs. Ed Welch, CEB's management accountant, believes that before the management group proceeds with the discussion about allocating sales and promotional dollars to individual products, it may be worthwhile to look at these products on the basis of the activities involved in their production. He noticed that the company has been recently selling more of the high- end PC boards than their competitors, yet the profits were still falling. "Using this information," Welch explained, "we can calculate an activity-based cost for each TV board and each PC board and then compare it to the standard cost we have been using. The costs that remain the same for both cost methods are the costs of direct materials and direct labour. The cost drivers will replace all indirect costs." Welch has prepared the following schedules for the management group: Materials support costs Procurement $600,000 Number of parts 3,000,000 Production scheduling $330,000 Number of boards 165,000 Packaging/shipping $660,000 Number of boards 165,000 Total costs $1,590,000 Variable support costs Machine setup Hazardous waste disposal Quality control General supplies Total costs $669,000 $48,000 $560,000 $66.000 $1,343,000 Number of setups Kilogram of waste Number of inspections Number of boards 418,125 8,000 240,000 165,000 Other manufacturing support costs Machine insertion $1,800,000 Manual insertion $5,000,000 Wave soldering $198.000 Total $6,998.000 Number of machine insertions Number of manual insertions Number of boards 4,500,000 2,000,000 165,000 TV boards PC boards 15 47 Parts Machine insertions Manual insertions Machine setups Kilogram of waste Inspections 10 1 2 0.04 37 19 5 0.70 3 1 4. Calculations & Interpretations - Quantitative Analysis This section requires you to undertake quantitative analysis on the case. You are to perform calculations (may be presented in the Appendix) that are relevant to the problem and issues that you identified in Section 2. In particular: a) On the basis of standard costs, calculate the total contribution margin and a contribution margin per product expected in 2020 for CEB Corporation's products: the TV board and the PC board. b) On the basis of activity-based costs, calculate the total contribution margin and the contribution margin per unit expected for 2020 for CEB Corporation's two products. c) How would the change of the product mix (if supported by marketing and promotion efforts and assuming that they would be successful) change total profitability of the company? In addition, interpret the results of your analysis. Your interpretation of your calculations should further the discussion on the problem and issues and should be supported by the relevant theory and concepts covered in ACCT2102. CEB Corporation is an Australian owned printed circuit board manufacturer with customers worldwide including Australia, Asia, USA and Europe. It has grown substantially over the years since its establishment in 1992 and in 2001 went public to acquire additional capital for future growth. Being a public company, CEB is under relatively high performance pressure from its investors who closely monitor the profit margins and cash flows. The profits have been falling over the last three years and its profitability is below the industry average. This has had a negative impact on the company's share price. In addition, the COVID 19 crisis set CEB's targeted profit under a serious threat. Although CEB manufactures several different types of printed-circuit boards, two of the boards account for the majority of the company's sales - a TV circuit board and a PC circuit board. The first of these boards, a TV board, has been a standard in the industry for several years. The market for this type of board is competitive and therefore, price sensitive. The second high- volume product is a PC board of which the manufacturing process is substantially different and more complex relative to that of the TV board. Because the PC board incorporates the latest technology, it can be sold at a premium price. In the recent years, PC boards have become number one product for CEB. The original plan for 2020 was to sell 80,000 of the TV boards at a price of $200 per unit and 130,000 PC boards at $350 per unit. However, CEB's management group is meeting to discuss how to react to the COVID 19 crisis on the top of the already falling profits, and how to spend the sales and promotion budget to protect if not increase the company's profit during the crisis. They are considering several options and discussing which product mix would result in the highest profits. The sales manager Jason Jackman believes that the market share for the TV board could be expanded by concentrating CEB's promotional efforts in this area. Moreover, due to lockdown the sales of TVs are increasing worldwide, generating more demand for TV boards. In response to this suggestion, the production manager Stacey Hu said, "Why don't we go after a bigger market for the PC board? The cost sheets that I reviewed show that the contribution from the PC board is one and a half times the contribution from the TV board. I know we get a premium price for the PC board. Focusing on the PC boards and changing the product mix should help overall profitability." CEB currently uses a standard cost system, and the following data apply to the TV and PC boards: 1.7 4.2 1.9 TV boards PC boards Direct materials $100 $160 Direct labour (hours) Machine time (hours) 0.6 Direct labour cost is $16 per hour. Variable manufacturing support costs are applied on the basis of direct labour hours. This year's variable manufacturing support costs are budgeted at $2,240,000, and direct labour hours are estimated at 448,000. Other manufacturing support is applied at $12 per machine hour. CEB applies a materials handling charge (in other words, materials support costs) of 12% of direct materials cost; this materials handling charge is not included in variable manufacturing support costs. Ed Welch, CEB's management accountant, believes that before the management group proceeds with the discussion about allocating sales and promotional dollars to individual products, it may be worthwhile to look at these products on the basis of the activities involved in their production. He noticed that the company has been recently selling more of the high- end PC boards than their competitors, yet the profits were still falling. "Using this information," Welch explained, "we can calculate an activity-based cost for each TV board and each PC board and then compare it to the standard cost we have been using. The costs that remain the same for both cost methods are the costs of direct materials and direct labour. The cost drivers will replace all indirect costs." Welch has prepared the following schedules for the management group: Materials support costs Procurement $600,000 Number of parts 3,000,000 Production scheduling $330,000 Number of boards 165,000 Packaging/shipping $660,000 Number of boards 165,000 Total costs $1,590,000 Variable support costs Machine setup Hazardous waste disposal Quality control General supplies Total costs $669,000 $48,000 $560,000 $66.000 $1,343,000 Number of setups Kilogram of waste Number of inspections Number of boards 418,125 8,000 240,000 165,000 Other manufacturing support costs Machine insertion $1,800,000 Manual insertion $5,000,000 Wave soldering $198.000 Total $6,998.000 Number of machine insertions Number of manual insertions Number of boards 4,500,000 2,000,000 165,000 TV boards PC boards 15 47 Parts Machine insertions Manual insertions Machine setups Kilogram of waste Inspections 10 1 2 0.04 37 19 5 0.70 3 1 4. Calculations & Interpretations - Quantitative Analysis This section requires you to undertake quantitative analysis on the case. You are to perform calculations (may be presented in the Appendix) that are relevant to the problem and issues that you identified in Section 2. In particular: a) On the basis of standard costs, calculate the total contribution margin and a contribution margin per product expected in 2020 for CEB Corporation's products: the TV board and the PC board. b) On the basis of activity-based costs, calculate the total contribution margin and the contribution margin per unit expected for 2020 for CEB Corporation's two products. c) How would the change of the product mix (if supported by marketing and promotion efforts and assuming that they would be successful) change total profitability of the company? In addition, interpret the results of your analysis. Your interpretation of your calculations should further the discussion on the problem and issues and should be supported by the relevant theory and concepts covered in ACCT2102










