Please do the TODO comments for the Distance class in Java. Will thumbs up.

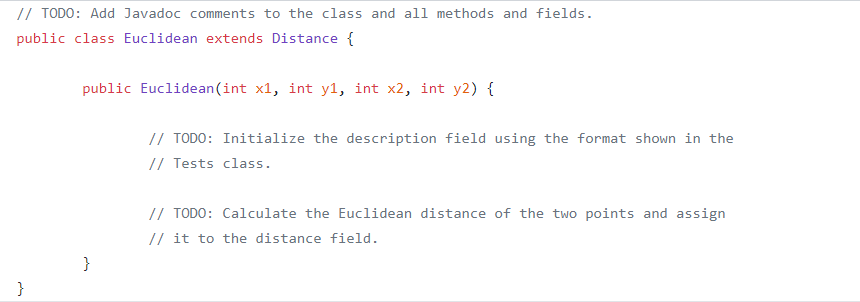
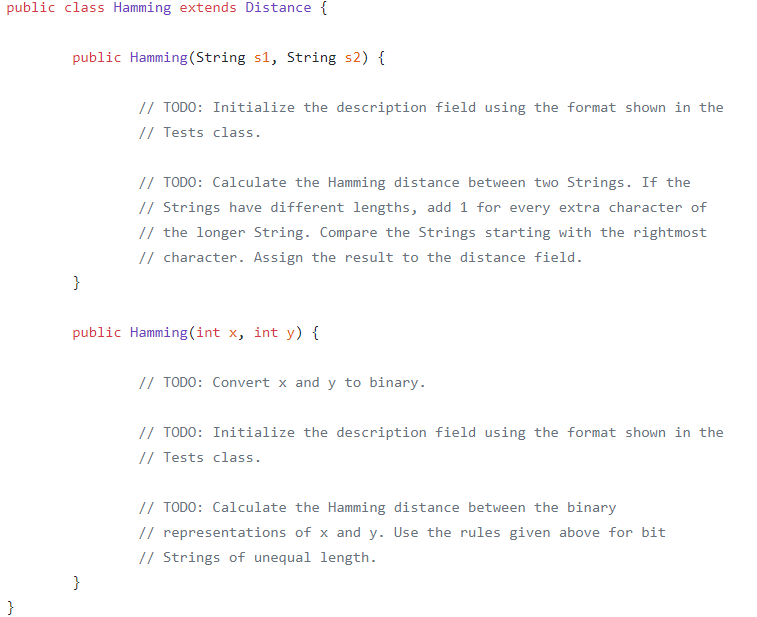

public class Distance { protected String description; protected String distance; public Distance() { // TODO: Initialize the fields using the format shown in the Tests // class. public Distance(int x) { // TODO: Convert x to binary. See the Integer class documentation. String bits = ""; description = "Number of 1s in binary " + x + " (" + bits + ")"; // TODO: Calculate the number of 1s in the binary representation of x, // and assign the result to the distance field. public Distance(String s) { description = "Sum of chars in "" + S + " ""; // TODO: Calculate the sum of the ASCII codes of the characters in the // given String. Assign the sum to the distance field. @Override public String toString() { return description + ":" + distance; // TODO: Add Javadoc comments to the class and all methods and fields. public class Euclidean extends Distance { public Euclidean(int x1, int yl, int x2, int y2) { // TODO: Initialize the description field using the format shown in the // Tests class. // TODO: Calculate the Euclidean distance of the two points and assign // it to the distance field. public class Hamming extends Distance { public Hamming (String s1, String s2) { // TODO: Initialize the description field using the format shown in the // Tests class. // TODO: Calculate the Hamming distance between two Strings. If the // Strings have different lengths, add 1 for every extra character of // the longer String. Compare the Strings starting with the rightmost // character. Assign the result to the distance field. public Hamming(int x, int y){ // TODO: Convert x and y to binary. // TODO: Initialize the description field using the format shown in the // Tests class. // TODO: Calculate the Hamming distance between the binary // representations of x and y. Use the rules given above for bit // Strings of unequal length. public class Tests { public static void main(String[] args) { Distance emptyDist = new Distance(); String emptyDistans = "No argument: 0"; test(emptyDist, emptyDistans, "Distance()"); Distance intDist = new Distance(5); String intDistAns = "Number of 1s in binary 5 (101): 2"; test(intDist, intDistAns, "Distance(int)"); Distance strDist = new Distance ("Hi!"); String strDistAns = "Sum of chars in \"Hi!\": 210"; test (strDist, strDistAns, "Distance(String)"); // Note that a Euclidean object can be assigned to a Distance variable. Distance eucDist = new Euclidean(3, 0, 0, 4); String eucDistans - "Euclidean distance between (3, 0) and (0, 4): 5.0"; test(eucDist, eucDistAns, "Euclidean(int, int, int, int)"); // Note that a Hamming object can be assigned to a Distance variable. Distance strHammDist = new Hamming("cat", "sat"); String strHammDistAns = "Hamming distance between cat and sat: 1"; test(strHammDist, strHammDistans, "Hamming (String, String)"); Distance intHammDist = new Hamming (4, 5); String intHammDistAns = "Hamming distance between 100 and 101: 1"; test(intHammDist, intHammDistans, "Hamming(int, int)"); * A helper method for main that tests the toString output of a Distance * object. The method prints an error message if the output is incorrect. * @param obj a Distance object. * @param ans the correct toString output. * @param testName a description of the constructor used to create obj. public static void test(Distance obj, String ans, String testName) { if (!obj.toString().equals(ans)) { System.out.println("Incorrect " + testName); System.out.println("Expected: " + ans); System.out.println("Returned: " + obj.toString(); System.out.println(); public class Distance { protected String description; protected String distance; public Distance() { // TODO: Initialize the fields using the format shown in the Tests // class. public Distance(int x) { // TODO: Convert x to binary. See the Integer class documentation. String bits = ""; description = "Number of 1s in binary " + x + " (" + bits + ")"; // TODO: Calculate the number of 1s in the binary representation of x, // and assign the result to the distance field. public Distance(String s) { description = "Sum of chars in "" + S + " ""; // TODO: Calculate the sum of the ASCII codes of the characters in the // given String. Assign the sum to the distance field. @Override public String toString() { return description + ":" + distance; // TODO: Add Javadoc comments to the class and all methods and fields. public class Euclidean extends Distance { public Euclidean(int x1, int yl, int x2, int y2) { // TODO: Initialize the description field using the format shown in the // Tests class. // TODO: Calculate the Euclidean distance of the two points and assign // it to the distance field. public class Hamming extends Distance { public Hamming (String s1, String s2) { // TODO: Initialize the description field using the format shown in the // Tests class. // TODO: Calculate the Hamming distance between two Strings. If the // Strings have different lengths, add 1 for every extra character of // the longer String. Compare the Strings starting with the rightmost // character. Assign the result to the distance field. public Hamming(int x, int y){ // TODO: Convert x and y to binary. // TODO: Initialize the description field using the format shown in the // Tests class. // TODO: Calculate the Hamming distance between the binary // representations of x and y. Use the rules given above for bit // Strings of unequal length. public class Tests { public static void main(String[] args) { Distance emptyDist = new Distance(); String emptyDistans = "No argument: 0"; test(emptyDist, emptyDistans, "Distance()"); Distance intDist = new Distance(5); String intDistAns = "Number of 1s in binary 5 (101): 2"; test(intDist, intDistAns, "Distance(int)"); Distance strDist = new Distance ("Hi!"); String strDistAns = "Sum of chars in \"Hi!\": 210"; test (strDist, strDistAns, "Distance(String)"); // Note that a Euclidean object can be assigned to a Distance variable. Distance eucDist = new Euclidean(3, 0, 0, 4); String eucDistans - "Euclidean distance between (3, 0) and (0, 4): 5.0"; test(eucDist, eucDistAns, "Euclidean(int, int, int, int)"); // Note that a Hamming object can be assigned to a Distance variable. Distance strHammDist = new Hamming("cat", "sat"); String strHammDistAns = "Hamming distance between cat and sat: 1"; test(strHammDist, strHammDistans, "Hamming (String, String)"); Distance intHammDist = new Hamming (4, 5); String intHammDistAns = "Hamming distance between 100 and 101: 1"; test(intHammDist, intHammDistans, "Hamming(int, int)"); * A helper method for main that tests the toString output of a Distance * object. The method prints an error message if the output is incorrect. * @param obj a Distance object. * @param ans the correct toString output. * @param testName a description of the constructor used to create obj. public static void test(Distance obj, String ans, String testName) { if (!obj.toString().equals(ans)) { System.out.println("Incorrect " + testName); System.out.println("Expected: " + ans); System.out.println("Returned: " + obj.toString(); System.out.println()