Question
Please don't use CHAT GPT to answer. Fixed Income MCQ, explain the answer please. Question 16: Which of the following statements about convexity are true?
Please don't use CHAT GPT to answer.
Fixed Income MCQ, explain the answer please.
Question 16:
Which of the following statements about convexity are true?
I. Convexity accounts for the curvilinear function of bond rates
II. A bond with a very low coupon and a long maturity will have low convexity III. A bond investor would seek to avoid bonds with high convexity.
IV. Convexity is defined as the rate of change of the slope of the price/yield curve
V. There is an inverse relationship between maturity and convexity
a. I.
b. II. III. IV.
c. I. IV.
d. II. IV. V.
e. I. II. IV. V.
Question 17
The zero-coupon bond spot rates are as follows:
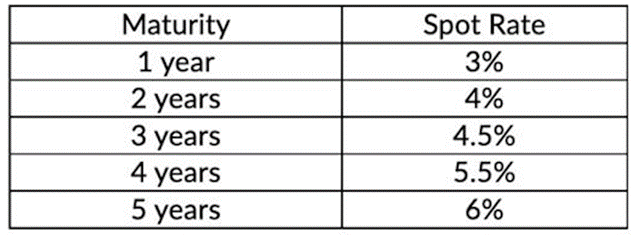
Compute the three-year forward rate for a loan that starts in one year expressed on an annual basis.
a) 1.36%
b) 2.69%
c) 3.50%
d) 6.35%
e) 20.27%
Question 18
The zero-coupon bond spot rates are as follows:
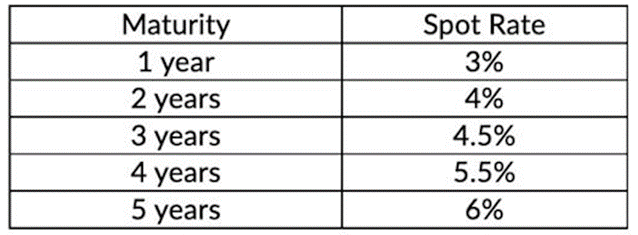
Compute the three-year forward rate for a loan that starts in two years expressed on an annual basis.
a. 2.36%
b. 3.69%
c. 4.50%
d. 7.35%
e. 23.7%
Question 19
Consider two 5-year risk-free bond strategies:
I. Buy a 4-year zero coupon bond with a YTM of 7%
II. Buy a 3-year zero coupon bond with a YTM of 6% then roll the principal plus interest into a 1-year bond at the short rate of r4.
Compute r4
a) 1.0%
b) 2.81%
c) 5.03%
d) 5.64%
e) 10.06%
Question 20
Consider two 4-year risk-free bond strategies:
I. Buy a 4-year zero coupon bond with a YTM of 6%
II. Buy a 3-year zero coupon bond with a YTM of 5% then roll the principal plus interest into a 1-year bond at the short rate of r4.
Compute r4
a. 1.0%
b. 2.8%
c. 5.0%
d. 5.6%
e. 9.05%
Question 21
Consider two 5-year risk-free bond strategies:
I. Buy a 5-year zero coupon bond with a YTM of 6%
Il. Buy a 4-year zero coupon bond with a YTM of 5.5% then roll the principal plus interest into a 1-year bond at the short rate of r5.
Compute r5
a) 1.0%
b) 2.81%
c) 4.03%
d) 5.64%
e) 8.02%
Question 22
Given a bond with maturity 15-year, with a yield 6% and Macaulay duration of 9.12 years. If the market rate contracts by 60 basis points, what will be the change in the price of the bond? (Use the modified approximation)
a. 5.16%
b. 5.47%
c. -5.16%
d. -5.47%
e. 4.26%
Question 23
A bond costs 990 $ with a YTM of 3.50%. Next week the price will rise to 1.1205 as a result of a rate cut to 3.05%. Calculate the dollar duration 1% (DV01)
a. $1.52
b. $1.72
c. $2.51
d. $2.89
Question 24
A bond costs 990 $ with a YTM of 3.50%. Next week the price will rise to 1,025$ as a result of a rate cut to 3.15%. Calculate the dollar duration 1% (DV01).
a. $0.52
b. 50.72
c. $0.91
d. $1.00
e. $1.15
Question 25
Consider two 20-year bonds that trade at the same price. Each bond has a coupon rate of 5%, paid semi-annually, and a face value of 1,000.
The first bond has a nominal YTM of 4.0%, convertible semi-annually, with a redemption value of 1,100 .
The second bond has a nominal YTM of j%, convertible semi-annually, with a redemption value of 800.
Calculate j.
a) 2.46%
b) 3.04%
c) 4.92%
d) 5.22%
e) 6.00%
Question 26
Calculate the duration of a 1% coupon bond (annual payments) with 4 years to maturity and an actuarial yield of 6%.
a) 3 years
b) 3.53 years
c) 3.78 years
d) 3.94 years
e) 4 years
Question 27
Given a 20-year bond which pays a coupon of 7% annually with a YTM or 8%, a modified duration of 16.3 and a convexity of 268.2. Suppose that the actuarial yield drops to 6.5%. What will be the change in the estimated price under the duration with convexity rule?
a. +22.51%
b. -22.51%
c. +30.1%
d. -30.1%
e. +27,46%
Question 28
Assume that the yield curve is flat at 2%. Calculate the convexity of a bullet portfolio with a single stream of $1500 paid at the end of the 4th year.
a. 19.22
b. 185.54
c. 188.47
d. 190.25
e. 223.65
Question 29 :
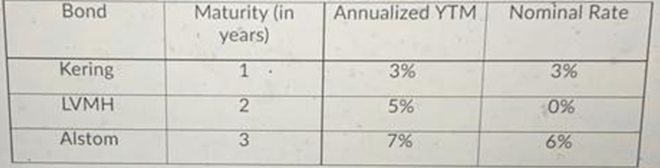
All three bonds have a par value of 100 . Construct a dedicated portfolio (cash-flow matching strategy) that funds exactly these liabilities.
What fraction of the Kering bonds should be purchased?
a. 0.8657
b. 0.9717
c. 1.0000
d. 1.0134
e. 1.0225
Question 30
For your dedicated portfolio above with Kering, LVMH and Alstom bonds, what would be the total outflow of funds today to build the portfolio that funds exactly these commitments?
a. $220.61
b. $250.35
c. $270.22
d. $300.00
e. $302.00
Question 31
What does the conversion premium measure?
-The strike price at which the bonds are converted, and the shares are bought
-The sensitivity of the bond to the underlying stock
-The cheapness of the Convertible bond
-The difference between the current stock price and the conversion price
-To which extent the Bond is an Equity like type of hybrid
Question 32
The Dividend protection is a feature of the Convertible bond that aims to protect the Issuer in case he pays a high dividend during the life of the bond.
-Vrai
-Faux
Question 33
While being long a Convertible Bond it is forbidden to go short the stock of the underlying
-Vrai
-Faux
Question 34
Bond with share warrants attached are common securities used in private markets
-Vrai
-Faux
Question 35
In private markets Bonds with share warrants attached are often subordinated to the bank debt
-Vrai
-Faux
Question 36
Identify all the market risks inherent to a convertible bond. (multiple answers)
Equity Risk
Credit risk
Liquidity risk
Conversion risk
Volatality risk
Interest rate risk
Question 37
If the share price trades above the conversion price this means the convertible bond trades at a premium with a delta higher than 50%
-Vrai
-Faux
Question 38
If the share price trades much lower than the original issue price of the CB than both delta and vega are small
-Vrai
-Faux
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|} \hline Maturity & Spot Rate \\ \hline 1 year & 3% \\ \hline 2 years & 4% \\ \hline 3 years & 4.5% \\ \hline 4 years & 5.5% \\ \hline 5 years & 6% \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|c|c|} \hline Maturity & Spot Rate \\ \hline 1 year & 3% \\ \hline 2 years & 4% \\ \hline 3 years & 4.5% \\ \hline 4 years & 5.5% \\ \hline 5 years & 6% \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|} \hline Bond & Maturity(inyears) & Annualized YTM & Nominal Rate \\ \hline Kering & 1 & 3% & 3% \\ \hline LVMH & 2 & 5% & 0% \\ \hline Alstom & 3 & 7% & 6% \\ \hline \end{tabular}Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


