Please give a summary
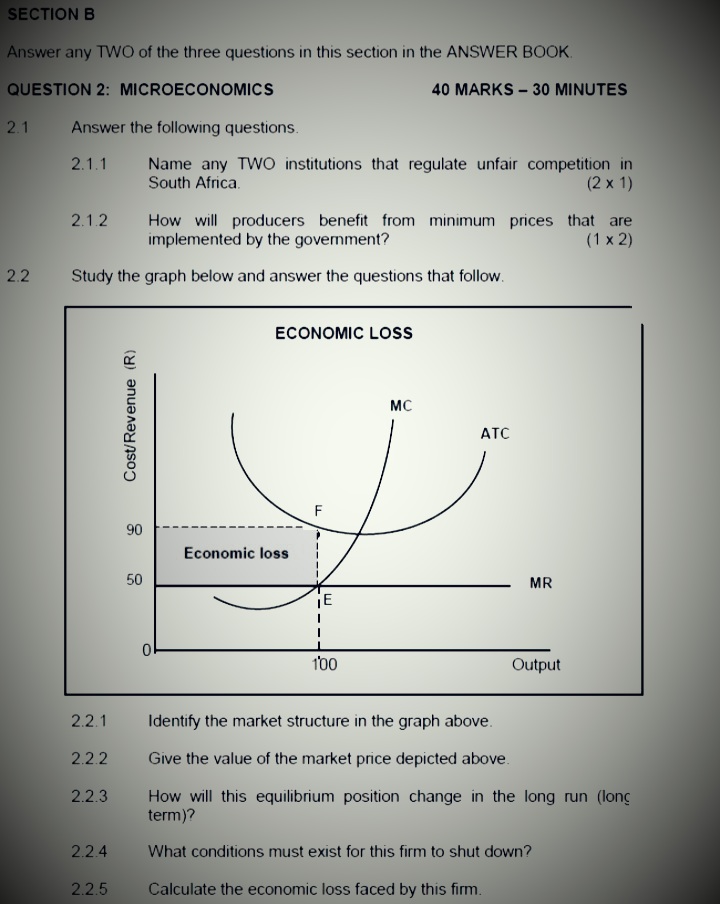
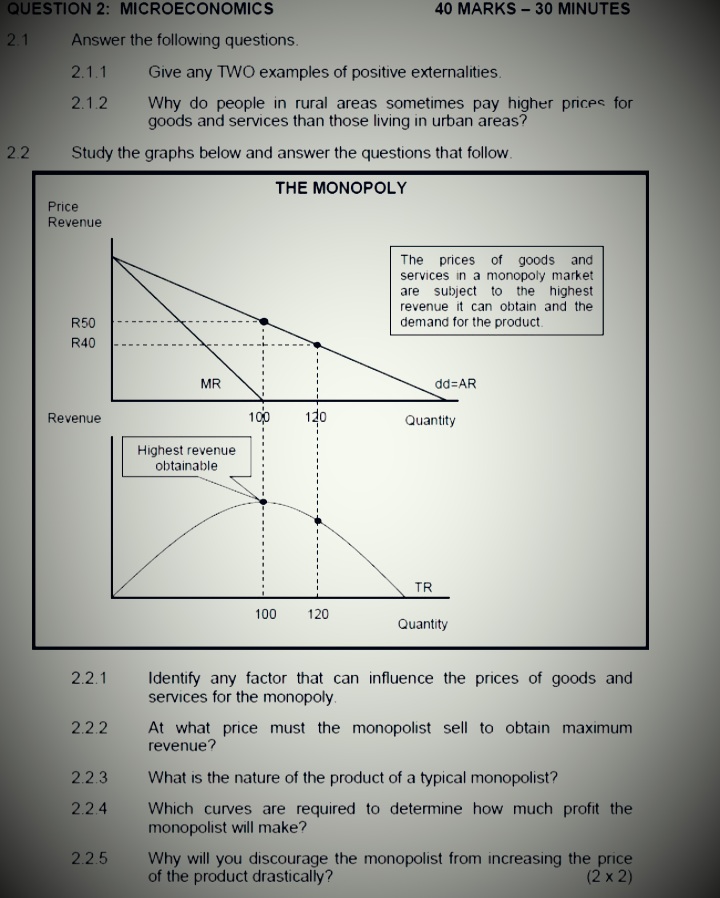
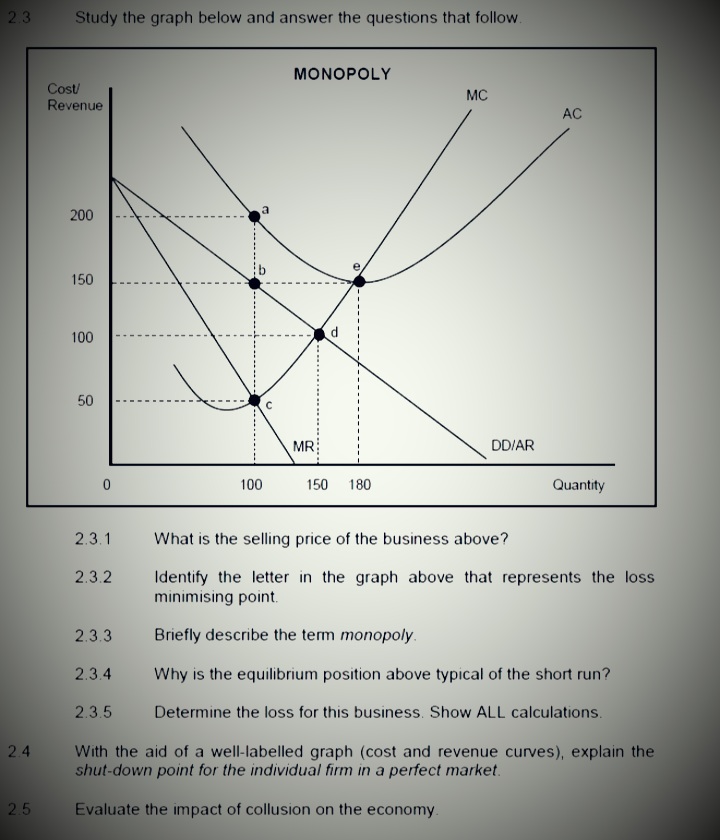
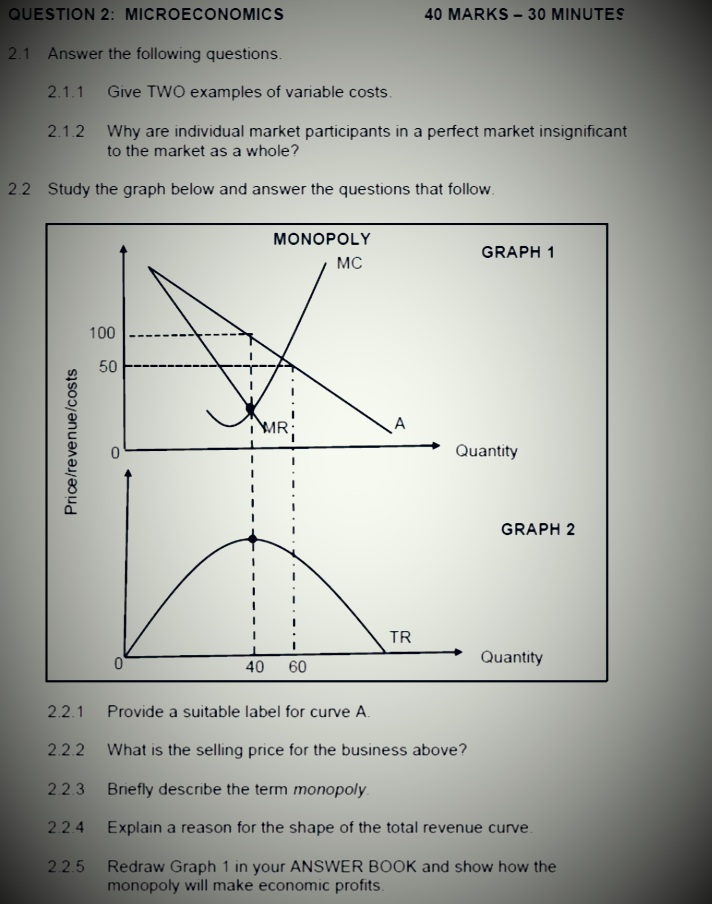
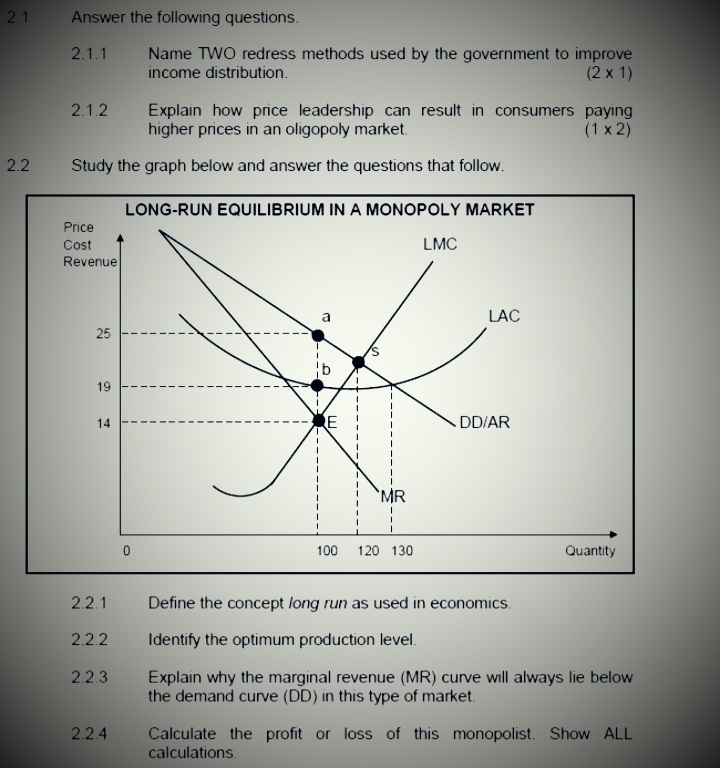
SECTION B Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS - 30 MINUTES 2.1 Answer the following questions. 2.1.1 Name any TWO institutions that regulate unfair competition in South Africa. (2 x 1) 2.1.2 How will producers benefit from minimum prices that are implemented by the goverment? (1 x 2) 2.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. ECONOMIC LOSS MC Cost/Revenue (R) ATC F 90 Economic loss 50 MR E 100 Output 2.2.1 Identify the market structure in the graph above. 2.2.2 Give the value of the market price depicted above. 2.2.3 How will this equilibrium position change in the long run (long term)? 2.2.4 What conditions must exist for this firm to shut down? 2.2.5 Calculate the economic loss faced by this firm.QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS - 30 MINUTES 2.1 Answer the following questions. 2.1.1 Give any TWO examples of positive externalities. 2.1.2 Why do people in rural areas sometimes pay higher prices for goods and services than those living in urban areas? 2.2 Study the graphs below and answer the questions that follow. THE MONOPOLY Price Revenue The prices of goods and services in a monopoly market are subject to the highest revenue it can obtain and the R50 demand for the product R40 MR dd=AR Revenue 100 120 Quantity Highest revenue obtainable TR 100 120 Quantity 2.2.1 Identify any factor that can influence the prices of goods and services for the monopoly. 2.2.2 At what price must the monopolist sell to obtain maximum revenue? 2.2.3 What is the nature of the product of a typical monopolist? 2.2.4 Which curves are required to determine how much profit the monopolist will make? 2.2.5 Why will you discourage the monopolist from increasing the price of the product drastically? (2 x 2)2.3 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow MONOPOLY Cost/ MC Revenue AC 200 150 100 d 50 C MR: DD/AR 0 100 150 180 Quantity 2.3.1 What is the selling price of the business above? 2.3.2 Identify the letter in the graph above that represents the loss minimising point. 2.3.3 Briefly describe the term monopoly. 2.3.4 Why is the equilibrium position above typical of the short run? 2.3.5 Determine the loss for this business. Show ALL calculations. 2.4 With the aid of a well-labelled graph (cost and revenue curves), explain the shut-down point for the individual firm in a perfect market. 2.5 Evaluate the impact of collusion on the economy.QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS - 30 MINUTES 2.1 Answer the following questions. 2.1.1 Give TWO examples of variable costs 2.1.2 Why are individual market participants in a perfect market insignificant to the market as a whole? 2.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. MONOPOLY GRAPH 1 MC 100 50 Price/revenue/costs Quantity GRAPH 2 TR 40 60 Quantity 2.2.1 Provide a suitable label for curve A. 2.2.2 What is the selling price for the business above? 2.2.3 Briefly describe the term monopoly 2.2.4 Explain a reason for the shape of the total revenue curve. 2.2.5 Redraw Graph 1 in your ANSWER BOOK and show how the monopoly will make economic profits.2.1 Answer the following questions. 2.1.1 Name TWO redress methods used by the government to improve income distribution. (2 x 1) 2.1.2 Explain how price leadership can result in consumers paying higher prices in an oligopoly market. (1 x 2) 2.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. LONG-RUN EQUILIBRIUM IN A MONOPOLY MARKET Price Cost LMC Revenue a LAC 25 19 14 E DD/AR MR 0 100 120 130 Quantity 2.2.1 Define the concept long run as used in economics 2.2.2 Identify the optimum production level. 2.2.3 Explain why the marginal revenue (MR) curve will always lie below the demand curve (DD) in this type of market. 2.2.4 Calculate the profit or loss of this monopolist. Show ALL calculations