almost done just need the last couple
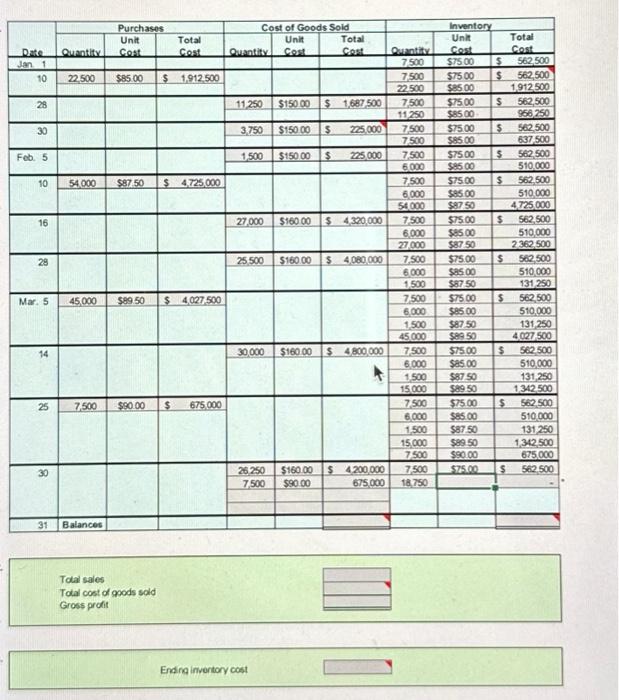
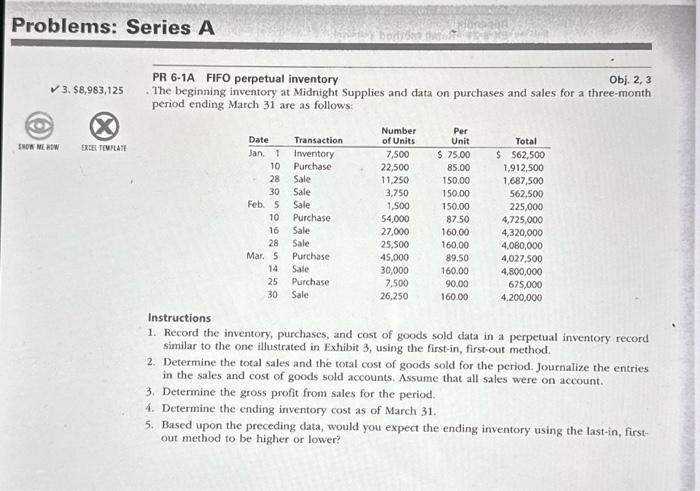
PR 6-2A LIFO perpetual inventory Obj. 2, 3 The beginning inventory at Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are shown in Problem 6-1A. Instructions 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 4, using the last-in, first-out method. . 2. Determine the total sales, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profit from sales for the period. 3. Determine the ending inventory cost as of March 31. PR 6-3A Weighted average cost method with perpetual inventory Obj. 2, 3 The beginning inventory for Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are shown in Problem 6-1A. Instructions 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 5, using the weighted average cost method. 2. Determine the total sales, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profit from sales for the period. 3. Determine the ending inventory cost as of March 31. PR 6-4A Periodic inventory by three methods Obj. 2,3 The beginning inventory for Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are slkwn in Problem 6-1A. Instructions 1. Determine the inventory on March 31 and the cost of goods sold for the three-month period, using the first-in, first-out method and the periodic inventory system. 2. Determine the inventory on March 31 and the cost of goods sold for the three-month period, using the last-in, first-out method and the periodic inventory system. 3. Determine the inventory on March 31 and the cost of goods sold for the three-month period, using the weighted average cost method and the periodic inventory system. Round the weighted average unit cost to the nearest cent. 4. Compare the gross profit and the March 31 inventories, using the following column headings: Problems: Series A 3,$8,983,125 PR 6-1A FIFO perpetual inventory Obj. 2, 3 . The beginning inventory at Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period ending March 31 are as follows: Instructions 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 3, using the first-in, first-out method. 2. Determine the total sales and the total cost of goods sold for the period. Journalize the entries in the sales and cost of goods sold accounts. Assume that all sales were on account. 3. Determine the gross profit from sales for the period. 4. Determine the ending inventory cost as of March 31. 5. Based upon the preceding data, would you expect the ending inventory using the last-in, firstout method to be higher or lower? Total sales Total cost of goods sold Gross profit Ending inventory cost PR 6-2A LIFO perpetual inventory Obj. 2, 3 The beginning inventory at Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are shown in Problem 6-1A. Instructions 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 4, using the last-in, first-out method. . 2. Determine the total sales, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profit from sales for the period. 3. Determine the ending inventory cost as of March 31. PR 6-3A Weighted average cost method with perpetual inventory Obj. 2, 3 The beginning inventory for Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are shown in Problem 6-1A. Instructions 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 5, using the weighted average cost method. 2. Determine the total sales, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profit from sales for the period. 3. Determine the ending inventory cost as of March 31. PR 6-4A Periodic inventory by three methods Obj. 2,3 The beginning inventory for Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are slkwn in Problem 6-1A. Instructions 1. Determine the inventory on March 31 and the cost of goods sold for the three-month period, using the first-in, first-out method and the periodic inventory system. 2. Determine the inventory on March 31 and the cost of goods sold for the three-month period, using the last-in, first-out method and the periodic inventory system. 3. Determine the inventory on March 31 and the cost of goods sold for the three-month period, using the weighted average cost method and the periodic inventory system. Round the weighted average unit cost to the nearest cent. 4. Compare the gross profit and the March 31 inventories, using the following column headings: \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline \multirow[b]{2}{*}{ Date } & \multicolumn{3}{|c|}{ Purchases } & \multicolumn{3}{|c|}{ Cost of Goods Sold } & \multicolumn{3}{|c|}{ Inventory } \\ \hline & Quantity. & UnitCost & TotalCost & Quantity & UnitCest & TotalCost & Quantity & UnitCost & TotalCost \\ \hline tan1 & & & & & & & 7500 & 57500 & 5562,500 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{10} & 22.500 & $8500 & \$ 1,912,500 & & & & 7,500 & 57500 & $562,500 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 22500 & 52500 & 1,912500 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{28} & & & & 11250 & $15000 & $1,687,500 & 7,500 & $7500 & 5562,500 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 11250 & 58500 & 966.250 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{30} & & & & 3,750 & $15000 & 225,000 & 7,500 & 57500 & $562,500 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 7500 & 58500 & 637500 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{ Fob 5} & & & & 1,500 & $15000 & 5225,000 & 7,500 & 57500 & 5562,500 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 6000 & $8500 & 510,000 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{3}{*}{10} & 54,000 & $87.50 & s 4,725,000 & & & & 7,500 & 57500 & $62,500 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 6,000 & ses00 & 510,000 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 54000 & & 4725,000 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{2}{*}{16} & & & & 27,000 & $16000 & $4,320,000 & 7.500 & $7500 & 5562,500 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 6,00027,000 & 5850058950 & 510,0002362,500 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{3}{*}{28} & & & & 25.500 & $16000 & $4,060,000 & 7,500 & $7500 & \begin{tabular}{|ll} 5 & 502,500 \\ \end{tabular} \\ \hline & & & & & & & 6.000 & ses00 & 510,000 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 1,500 & 58750 & 131250 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{4}{*}{ Mar. 5} & 45,000 & $8950 & $4,027,500 & & & & 7.500 & 57500 & 5562,500 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 6.000 & 5200 & 510,000 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 1,500 & 58750 & 131,250 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 45000 & 89950 & 4,027500 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{3}{*}{14} & & & & 30,000 & $16000 & s 4,800,000 & 7,500 & 57500 & s 562,500 \\ \hline & & & & & & + & 6.000 & ses0 & 510,000 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 150015000 & 5895058750 & 131,2501,342500 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{5}{*}{25} & 7,500 & $9000 & 675,000 & & & & 7500 & $7500 & $$502500 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 6000 & ses00 & 510,000 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 1,500 & $87.50 & 131,250 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 15,000 & 59950 & 1,342,500 \\ \hline & & & & & & & 7500 & $90,00 & 675,000 \\ \hline \multirow[t]{3}{*}{30} & & & & 26.250 & $16000 & 54,200,000 & 7,500 & 57500 & $52,500 \\ \hline & & & & 7,500 & $9000 & 675,000 & 18.750 & & - \\ \hline & & & & & & & & & \\ \hline 31 & Balances & & & & & & & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} Tolal sales Tolal cost of goods sold Gross profit Ending imvertory cost