Please help answer these:
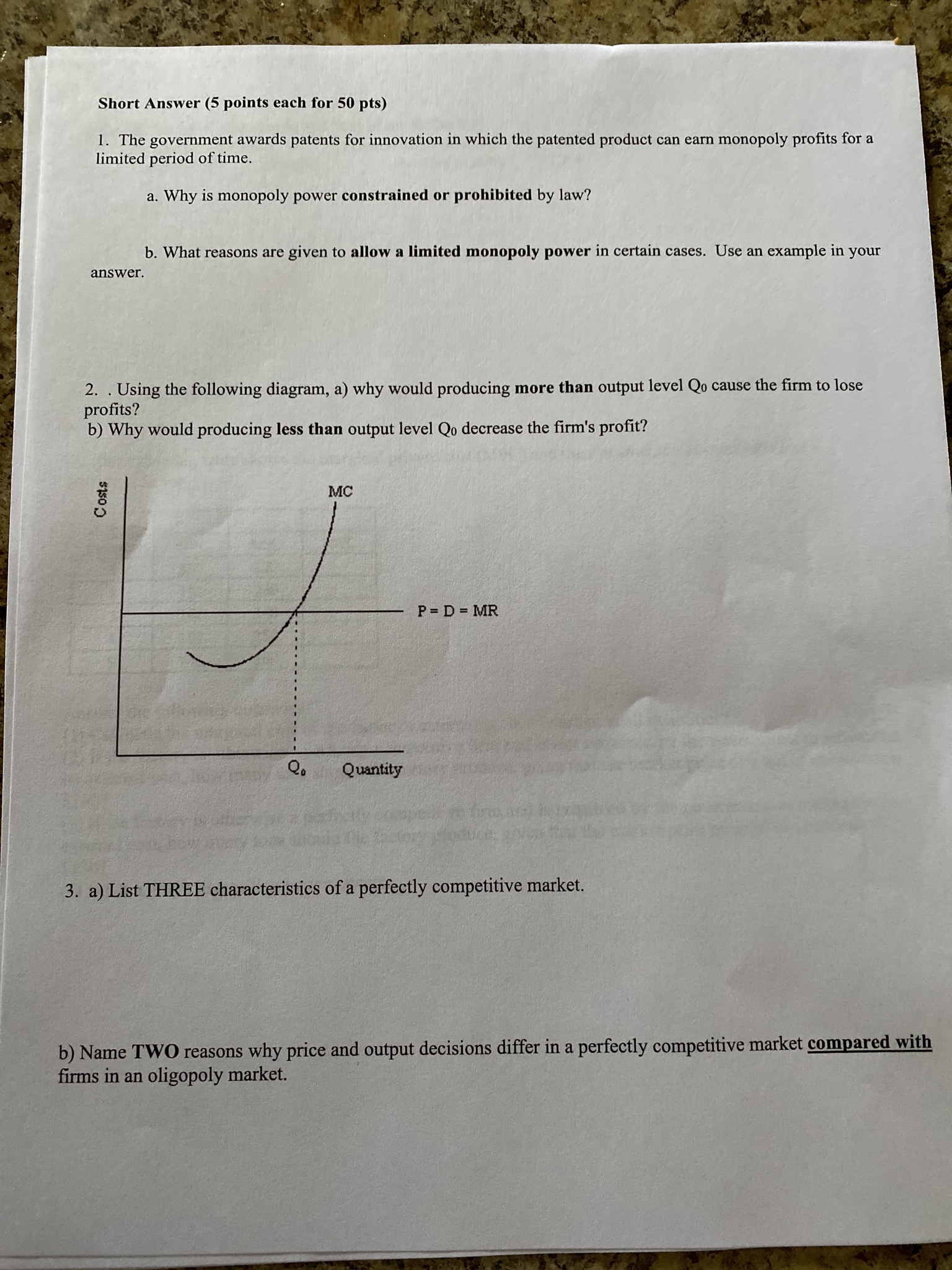
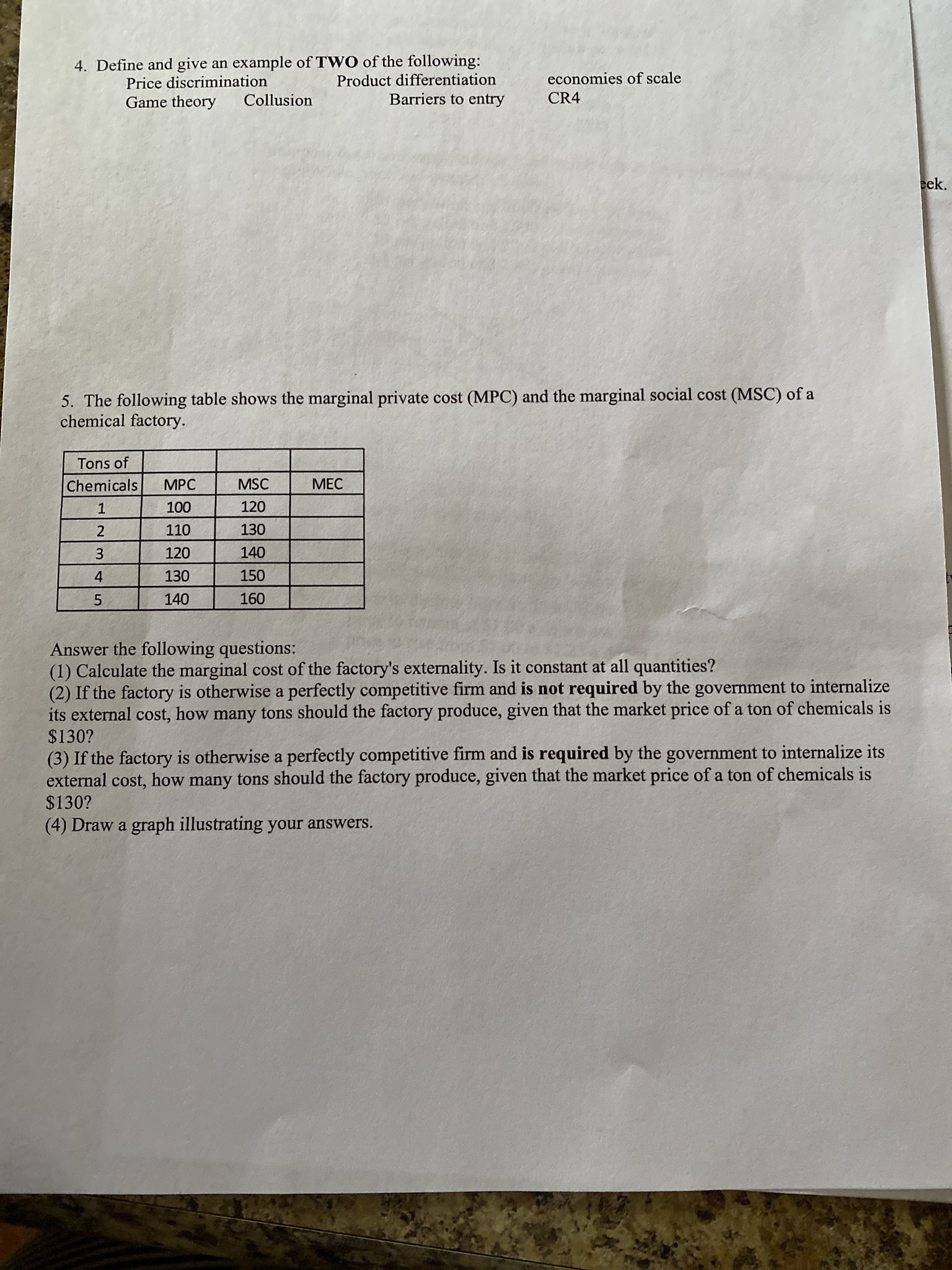
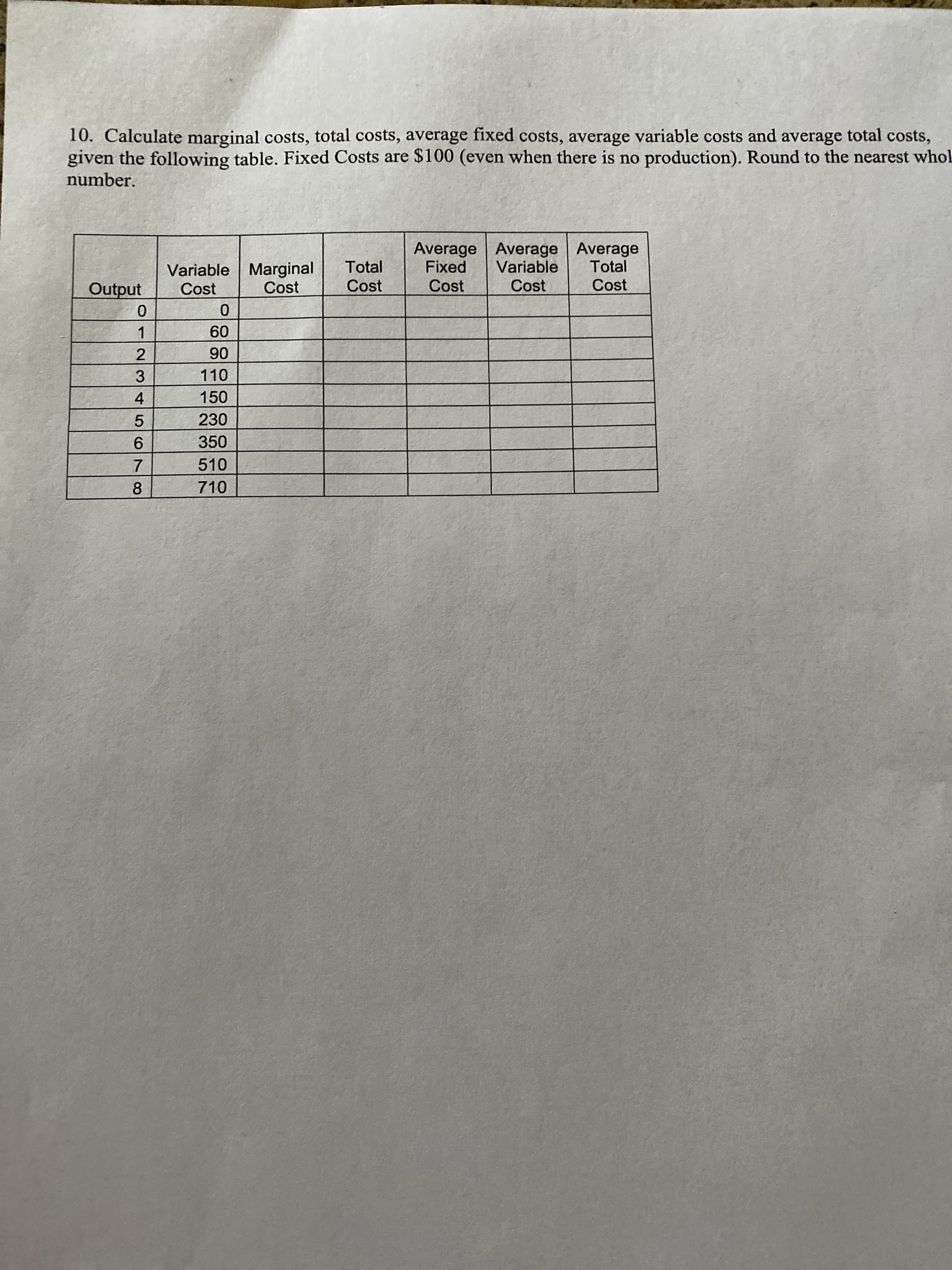
PPF with Biased Technological Change 35 Capris 2 Pecan Pies 6. This graph shows what happens to the production possibilities frontier for pecan pies and capri pants with biased technological change. a) Give an example of a technological change that would cause the PPF to shift out for capris but not for pecan pies? b) Before technological change occurs, is production of 2 pecan pies and 5 capri pants efficient, inefficient or unattainable? Explain. c) After technological change occurs, is production of 2 pecan pies and 25 capri pants efficient, inefficient or unattainable? Explain. d) What does the shape of the PPF (bowed outward) illustrate about the nature of resources? 7. Given the market share information in the table below, calculate the four firm concentration ratio and the Herfindahl index. Firm Number | Market Share (%) 35 V A W N 25 15 15 1013. The short run is a period during which: A. some inputs are variable and no inputs are fixed. B. some inputs are variable and some inputs are fixed. C. no inputs are variable and all inputs are fixed. no inputs are variable and some inputs are fixed. 14. The increase in output obtained by hiring an additional worker is known as: A. the average product. B. the marginal product. C. the total product. D. value added. 15. Costs that are spent and cannot be changed in the period of time under consideration are called: A. variable costs. B. total costs. C. marginal costs. D. fixed costs. 16. A perfectly competitive firm facing a price of $10 decides to produce 100 widgets. If its marginal producing the last widget is $12 and it is seeking to maximize profit, the firm should: A. produce more widgets. B. produce fewer widgets. C. continue producing 100 widgets. D. shut down. 17. In order to maximize profit, a perfectly competitive firm should produce that quantity: A. where AR=ATC. B. where economic profits are greater than zero. C. where MR=MC. D. where fixed costs and variable costs are covered. 18. A perfectly competitive firm will be profitable if price at the profit-maximizing quantity is above: A. MC. B. AVC. C. ATC. D. AFC.1. To graphically demonstrate the principle of increasing marginal opportunity cost the production possibility curve must be: A. flat. B. straight. bowed out. bowed in. Good Y Y2 Y1 YO XO X1 X2 Good X Refer to the graph above. As you move from point A to point B: A. production efficiency is increased because we have more of good X. B. production efficiency is decreased because we have less of good Y. C. production efficiency is decreased because we are no longer on the production possibility curve. D. the change in efficiency is unclear. Which of the following would likely result in an increase in the demand for beef? A. A decrease in the supply of beef. An increase in family incomes. An increase in the price of feed grains. A decrease in the price of pork. The more the current price exceeds the equilibrium price, the: A. greater the resulting shortage will be. B. smaller the resulting shortage will be. C. greater the resulting surplus will be. D. smaller the resulting surplus will be. Suppose a market has an excess demand and price starts to rise. What will the rise in price cause? A. A fall in both quantity supplied and quantity demanded. B. A rise in both quantity supplied and quantity demanded. C. A rise in quantity supplied and a fall in quantity demanded. D. A fall in quantity supplied and a rise in quantity demanded.24. Which of the following are most likely to be in violation of the Sherman and Clayton Antitrust Acts? A. Conglomerate mergers. B. Horizontal mergers. C. Vertical mergers. D. Diagonal mergers. 25. Game theory is designed to study situations where agent's decisions are: A. interdependent. B. independent. C. constrained. D. uninformed Continue to Next PageYou may use this sheet and have a calculator with you when you take the Final Exam Elasticity (Q1-Q2)/avgQ divided by (P1-P2)/avgP Point elasticity 1/slope x P/Q Cross-price elasticity % change in demand for good X divided by % change in Price of good Y Income Elasticity (% change in Q)/(% change in Income) Choice of Inputs to Production Marginal Product of Labor (the variable input): MPL = A TPL /AL Optimization rule with one choice: value of MPL >=wage rate Optimization with many variable inputs: MPa/Pa = MPb/Pb = ... = MPz/Pz Cost Equations Profit = Total revenue minus total cost II = TR - TC Total revenue = price times quantity TR = PxQ Total cost = wages x number of labor hours hired plus rent times # units capital employed => TC = wL + TC = WL + rK = VC + FC MC = ATC/AQ ATC = TC/Q = AVC + AFC AVC = VC/Q AFC= FC/Q A stands for "change in" as when we move from Q1 to Q2, then AQ would stand for (Q2-Q1) CR4: the sum of the market share of the top four firms in an industry HHI: the sum of the squared market shares of all the firms in the industryShort Answer (5 points each for 50 pts) limited period of time. 1. The government awards patents for innovation in which the patented product can earn monopoly profits for a a. Why is monopoly power constrained or prohibited by law? b. What reasons are given to allow a limited monopoly power in certain cases. Use an example in your answer . 2. . Using the following diagram, a) why would producing more than output level Qo cause the firm to lose profits? b) Why would producing less than output level Qo decrease the firm's profit? Costs MC P = D = MR Q. Quantity 3. a) List THREE characteristics of a perfectly competitive market. b) Name TWO reasons why price and output decisions differ in a perfectly competitive market compared with firms in an oligopoly market.Price Price DO (11) Quantity Price Price P1 DO DO (III) Q1 QO Quantity ( IV) Q1 Q0 Quantity 8. Refer to the graphs above. A recent report indicates that the device known as the right heart catheter used to diagnose heart conditions poses more risks than previously thought. The effect of the report on the market for right heart catheters is best shown by which of the graphs above? A. I B. II C. III D. IV 9. In general, the greater the elasticity the: A. smaller the responsiveness of price to changes in quantity. B. smaller the responsiveness of quantity to changes in price. C. larger the responsiveness of price to changes in quantity. D. larger the responsiveness of quantity to changes in price. 10. If the price of a good goes up by 5% and, in response, the quantity demanded falls by 15%, the price elasticity of demand would be: A. .05. B. 3. C. 0.3333. D. 0.15. 1 1. An elasticity of supply of 2.7 means that: A. supply is inelastic. B. quantity supplied changes 2.7 units for each 1% change in price. C. quantity supplied changes 2.7% for each 1% change in price. D. price changes by 2.7% for each 1% change in quantity supplied. 12. Economic profit is: A. total revenue minus explicit measurable costs. B. explicit revenues minus explicit costs. C. implicit and explicit revenues minus implicit and explicit costs. D. implicit and explicit revenues minus implicit costs.4. Define and give an example of TWO of the following: Price discrimination Product differentiation economies of scale Game theory Collusion Barriers to entry CR4 eek. 5. The following table shows the marginal private cost (MPC) and the marginal social cost (MSC) of a chemical factory. Tons of Chemicals MPC MSC MEC 100 120 2 110 130 120 140 4 130 150 UT 140 160 Answer the following questions: (1) Calculate the marginal cost of the factory's externality. Is it constant at all quantities? (2) If the factory is otherwise a perfectly competitive firm and is not required by the government to internalize its external cost, how many tons should the factory produce, given that the market price of a ton of chemicals is $130? (3) If the factory is otherwise a perfectly competitive firm and is required by the government to internalize its external cost, how many tons should the factory produce, given that the market price of a ton of chemicals is $130? (4) Draw a graph illustrating your answers.Price, Costs MC ATC AVC Q1 Q2 Q3 04 Output 19. Refer to the graph above. If the market price is P4 the firm will produce: A. Q2 and incur a loss. B. Q3 and break even. C. Q3 and earn a profit. Q4 and earn a profit. 20. If a perfectly competitive firm finds that price is less than average variable cost it should: A. not adjust output if marginal cost equals price. B. shutdown immediately. C. D. increase output until price equals marginal cost. decrease output until price equals marginal cost. 21. There are many restaurants in the city of Raleigh, each one offering food and services that differ from those of its competitors. There is also free entry of sellers into the market and each seller serves a very small fraction of the total number of meals served each day. The restaurant industry in Raleigh is best categorized as: A. an oligopoly. B. monopolistically competitive. C. a pure monopoly. D. perfectly competitive. 22. The top four firms in the industry have 10 percent, 8 percent, 8 percent, and 6 percent of the market. The four-firm concentration ratio of this market is: A. 8. B. 32. C. 66. D. 264. 23. A natural monopoly: A. has an average total cost curve that reaches minimum possible average total cost at a low level of output. B. is usually subject to antitrust suits. C. is usually allowed to choose its price so as to maximize profits in the United States. D. occurs when a single firm can supply the entire market demand for a product at a lower average tot cost than would be possible if two or more firms supplied the market.10. Calculate marginal costs, total costs, average fixed costs, average variable costs and average total costs, given the following table. Fixed Costs are $100 (even when there is no production). Round to the nearest who number. Average Average Average Variable | Marginal Total Fixed Variable Total Output Cost Cost Cost Cost Cost Cost 0 0 1 60 2 90 3 110 4 150 5 230 6 350 7 0o 510 710