Please help as much as you can, i can split it into multiple questions if necessary
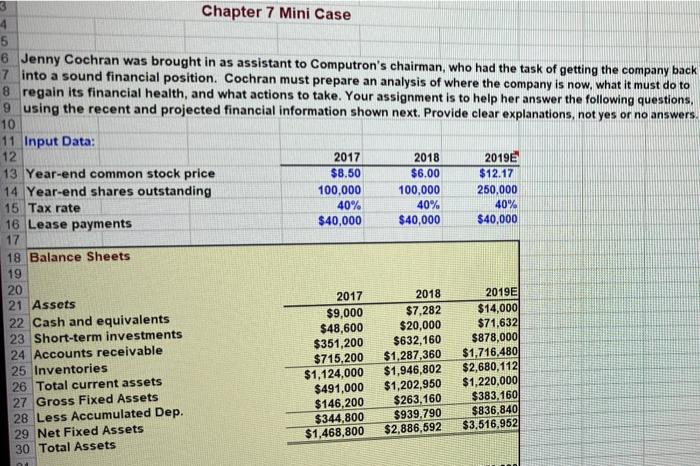
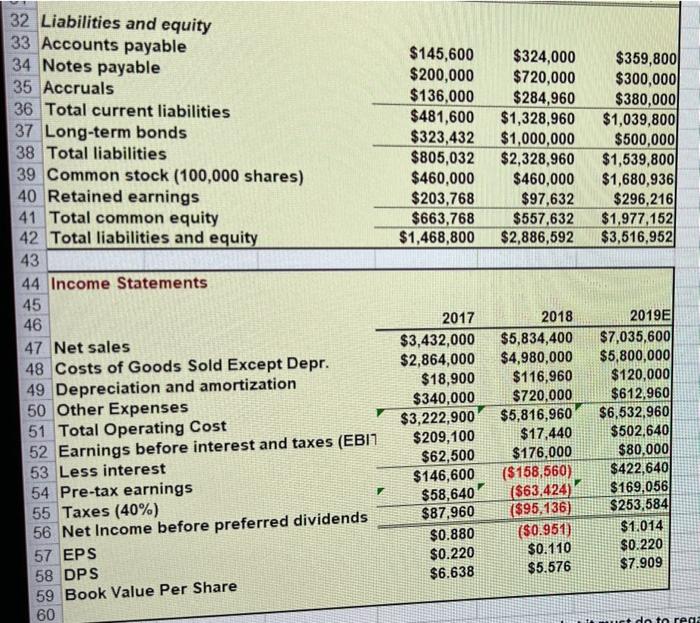
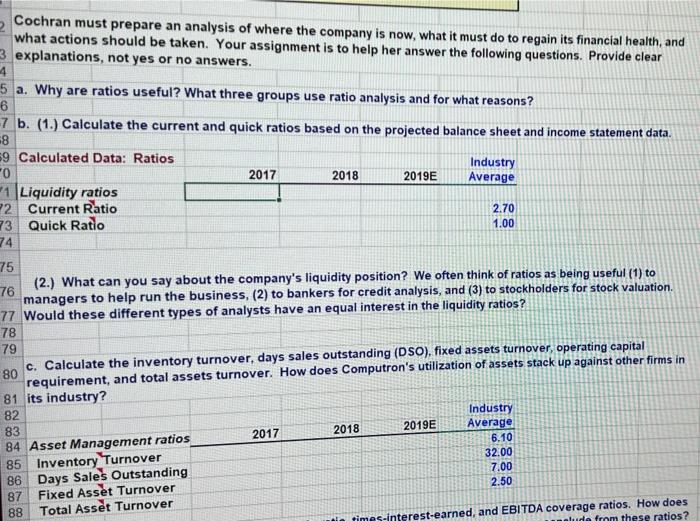
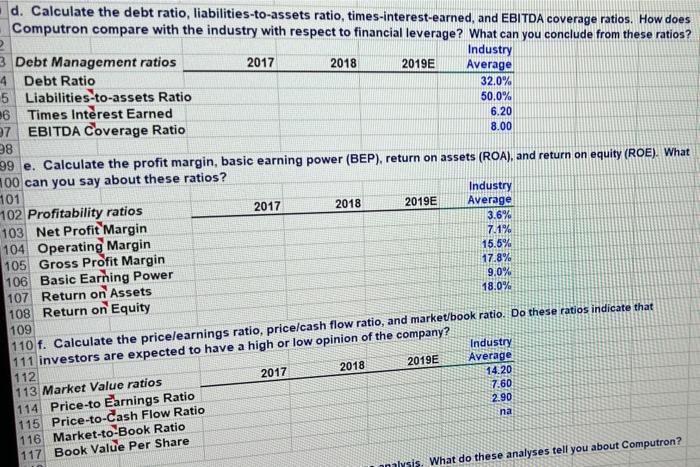
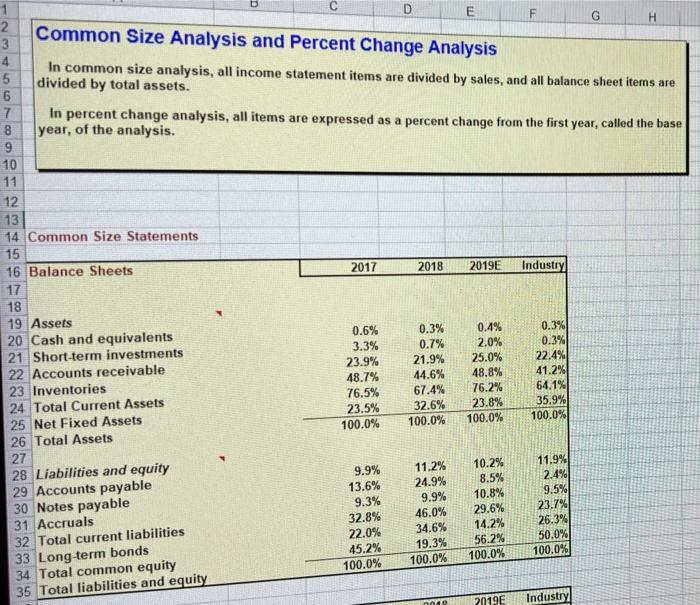
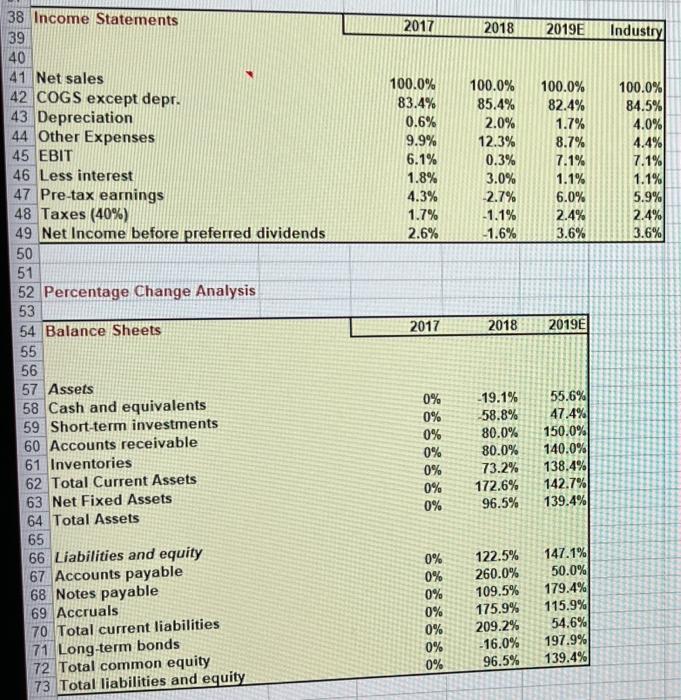
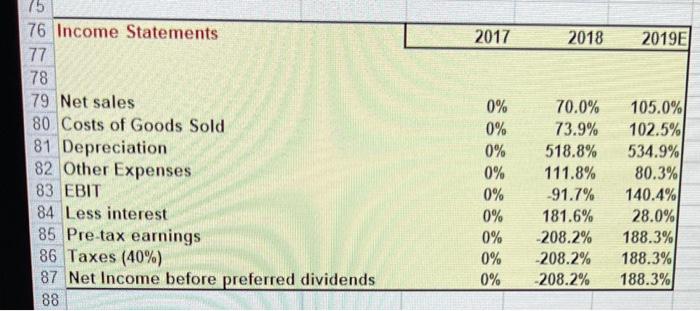
3 Chapter 7 Mini Case 5 6 Jenny Cochran was brought in as assistant to Computron's chairman, who had the task of getting the company back 7 into a sound financial position. Cochran must prepare an analysis of where the company is now, what it must do to 8 regain its financial health, and what actions to take. Your assignment is to help her answer the following questions, 9 using the recent and projected financial information shown next. Provide clear explanations, not yes or no answers 10 11 Input Data: 12 2017 2018 2019 13 Year-end common stock price $8.50 $6.00 $12.17 14 Year-end shares outstanding 100,000 100,000 250,000 15 Tax rate 40% 40% 40% 16 Lease payments $40,000 $40,000 $40,000 17 18 Balance Sheets 19 20 21 Assets 2017 2018 2019E 22 Cash and equivalents $9,000 $7,282 $14,000 $48,600 23 Short-term investments $20,000 $71.632 $351,200 $632,160 $878,000 24 Accounts receivable $715,200 $1,287,360 $1,716,4801 25 Inventories $1,124,000 $1,946,802 $2,680,112 26 Total current assets $491,000 $1,202,950 $1,220,000 27 Gross Fixed Assets $146,200 $263.160 $383,160 28 Less Accumulated Dep. $344,800 $939.790 $836,840 29 Net Fixed Assets $1,468.800 $2,886,592 $3,516,952 30 Total Assets $145,600 $200,000 $136,000 $481,600 $323,432 $805,032 $460,000 $203,768 $663,768 $1,468,800 $324,000 $720,000 $284,960 $1,328,960 $1,000,000 $2,328,960 $460,000 $97,632 $557,632 $2,886,592 $359,800 $300,000 $380,000 $1,039,800 $500,000 $1,539,8001 $1,680,936 $296,216 $1,977,152 $3,516,952 32 Liabilities and equity 33 Accounts payable 34 Notes payable 35 Accruals 36 Total current liabilities 37 Long-term bonds 38 Total liabilities 39 Common stock (100,000 shares) 40 Retained earnings 41 Total common equity 42 Total liabilities and equity 43 44 Income Statements 45 46 47 Net sales 48 Costs of Goods Sold Except Depr. 49 Depreciation and amortization 50 Other Expenses 51 Total Operating Cost 52 Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT 53 Less interest 54 Pre-tax earnings 55 Taxes (40%) 56 Net Income before preferred dividends 57 EPS 58 DPS 59 Book Value Per Share 60 2017 $3,432,000 $2,864,000 $18,900 $340,000 $3,222,900 $209,100 $62,500 $146,600 $58,640 $87,960 $0.880 $0.220 $6.638 2018 $5,834,400 $4,980,000 $116,960 $720,000 $5,816,960 $17.440 $176,000 ($ 158,560) ($63,424) ($95,136) ($0.951) $0.110 $5.576 2019E $7,035,600 $5,800,000 $120,000 $612,960 $6,532,960 $502,640 $80,000 $422,640 $169,056 $253,584 $1.014 $0.220 $7.909 I do to rega Cochran must prepare an analysis of where the company is now, what it must do to regain its financial health, and what actions should be taken. Your assignment is to help her answer the following questions. Provide clear 3 explanations, not yes or no answers. 4 5 a. Why are ratios useful? What three groups use ratio analysis and for what reasons? 6 -7 b. (1.) Calculate the current and quick ratios based on the projected balance sheet and income statement data. 8 59 Calculated Data: Ratios 0 Industry 2017 2018 2019E Average *1 Liquidity ratios 2 Current Ratio 2.70 73 Quick Ratio 1.00 74 75 76 (2.) What can you say about the company's liquidity position? We often think of ratios as being useful (1) to managers to help run the business, (2) to bankers for credit analysis, and (3) to stockholders for stock valuation. 77 Would these different types of analysts have an equal interest in the liquidity ratios? 78 79 c. Calculate the inventory turnover, days sales outstanding (DSO), fixed assets turnover, operating capital requirement, and total assets turnover. How does Computron's utilization of assets stack up against other firms in 81 its industry? 82 Industry 83 2017 2018 Average 2019E 84 Asset Management ratios 6.10 85 Inventory Turnover 32.00 86 Days Sales Outstanding 7.00 2.50 87 Fixed Asset Turnover 88 Total Asset Turnover in times-interest-earned, and EBITDA coverage ratios. How does nude from these ratios? 80 d. Calculate the debt ratio, liabilities-to-assets ratio, times-interest-earned, and EBITDA coverage ratios. How does Computron compare with the industry with respect to financial leverage? What can you conclude from these ratios? 3 Debt Management ratios Industry 2017 2018 2019E 4 Debt Ratio Average 5 Liabilities-to-assets Ratio 32.0% 50.0% 6 Times Interest Earned 6.20 7 EBITDA Coverage Ratio 8.00 38 99 e. Calculate the profit margin, basic earning power (BEP), return on assets (ROA), and return on equity (ROE). What 100 can you say about these ratios? 101 Industry 102 Profitability ratios 2017 2018 2019E Average 3.6% 103 Net Profit Margin 7.1% 104 Operating Margin 15.5% 105 Gross Profit Margin 17.8% 106 Basic Earning Power 9.0% 107 Return on Assets 18.0% 108 Return on Equity 109 110 f. Calculate the pricelearnings ratio, price cash flow ratio, and market/book ratio. Do these ratios indicate that Industry 111 investors are expected to have a high or low opinion of the company? 2019E Average 112 2018 2017 7.60 2.90 14.20 na 113 Market Value ratios 114 Price to Earnings Ratio 115 Price-to-Cash Flow Ratio 116 Market-to-Book Ratio 117 Book Value Per Share analysis. What do these analyses tell you about Computron? 119 g. Perform a common size analysis and percent change analysis. What do these analyses tell you about Computron? 120 121 See the worksheet with the TAB "Common Size and % Change" 122 123 124 1. What are some potential problems and limitations of financial ratio analysis? 125 126 J. What are some qualitative factors analysts should consider when evaluating a company's likely future financial 127 performance? 128 F Common Size Analysis and Percent Change Analysis 1 C 2 D E F G H 3 4 In common size analysis, all income statement items are divided by sales, and all balance sheet items are 5 divided by total assets. 6 7 In percent change analysis, all items are expressed as a percent change from the first year, called the base 8 year, of the analysis. 9 10 11 12 13 14 Common Size Statements 15 16 Balance Sheets 2017 2018 2019E Industry 17 18 19 Assets 20 Cash and equivalents 0.6% 0.3% 0.4% 0.3% 21 Short-term investments 3.3% 0.7% 2.0% 0.3% 22 Accounts receivable 23.9% 21.9% 25.0% 22.4% 23 Inventories 48.7% 44.6% 48.8% 41.2% 76.5% 67.4% 76.2% 24 Total Current Assets 64.1% 23.5% 32.6% 23.8% 35.9% 25 Net Fixed Assets 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% 26 Total Assets 27 28 Liabilities and equity 11.2% 10.2% 11.9% 29 Accounts payable 24.9% 13.6% 8.5% 2.4% 30 Notes payable 9.9% 10.8% 9.5% 31 Accruals 32.8% 46.0% 29.6% 23.7% 32 Total current liabilities 22.0% 34.6% 14.2% 26.3% 19,3% 33 Long-term bonds 50.0% 56.2% 34 Total common equity 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% 35 Total liabilities and equity 2019E Industry 9.9% 9.3% 45.2% AD 2017 2018 2019E Industry 38 Income Statements 39 40 41 Net sales 42 COGS except depr. 43 Depreciation 44 Other Expenses 45 EBIT 46 Less interest 47 Pre-tax earnings 48 Taxes (40%) 49 Net Income before preferred dividends 50 51 52 Percentage Change Analysis 53 54 Balance Sheets 55 100.0% 83.4% 0.6% 9.9% 6.1% 1.8% 4.3% 1.7% 2.6% 100.0% 85.4% 2.0% 12.3% 0.3% 3.0% 2.7% -1.1% -1.6% 100.0% 82.4% 1.7% 8.7% 7.1% 1.1% 6.0% 2.4% 100.0% 84.5% 4.0% 4.4% 7.1% 1.1% 5.9% 2.4% 3.6% 3.6% 2017 2018 2019E 56 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% -19.1% -58.8% 80.0% 80.0% 73.2% 172.6% 96.5% 55.6% 47.4% 150.0% 140.0% 138.4% 142.7% 139.4% 0% 0% 57 Assets 58 Cash and equivalents 59 Short-term investments 60 Accounts receivable 61 Inventories 62 Total Current Assets 63 Net Fixed Assets 64 Total Assets 65 66 Liabilities and equity 67 Accounts payable 68 Notes payable 69 Accruals 70 Total current liabilities 71 Long-term bonds 72 Total common equity 73 Total liabilities and equity 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 122.5% 260.0% 109.5% 175.9% 209.2% -16.0% 96.5% 147.1% 50.0% 179.4% 115.9% 54.6% 197.9% 139.4% 2017 2018 2019E 75 76 Income Statements 77 78 79 Net sales 80 Costs of Goods Sold 81 Depreciation 82 Other Expenses 83 EBIT 84 Less interest 85 Pre-tax earnings 86 Taxes (40%) 87 Net Income before preferred dividends 88 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 70.0% 73.9% 518.8% 111.8% -91.7% 181.6% -208.2% -208.2% 208.2% 105.0% 102.5% 534.9% 80.3% 140.4% 28.0% 188.3% 188.3% 188.3% 3 Chapter 7 Mini Case 5 6 Jenny Cochran was brought in as assistant to Computron's chairman, who had the task of getting the company back 7 into a sound financial position. Cochran must prepare an analysis of where the company is now, what it must do to 8 regain its financial health, and what actions to take. Your assignment is to help her answer the following questions, 9 using the recent and projected financial information shown next. Provide clear explanations, not yes or no answers 10 11 Input Data: 12 2017 2018 2019 13 Year-end common stock price $8.50 $6.00 $12.17 14 Year-end shares outstanding 100,000 100,000 250,000 15 Tax rate 40% 40% 40% 16 Lease payments $40,000 $40,000 $40,000 17 18 Balance Sheets 19 20 21 Assets 2017 2018 2019E 22 Cash and equivalents $9,000 $7,282 $14,000 $48,600 23 Short-term investments $20,000 $71.632 $351,200 $632,160 $878,000 24 Accounts receivable $715,200 $1,287,360 $1,716,4801 25 Inventories $1,124,000 $1,946,802 $2,680,112 26 Total current assets $491,000 $1,202,950 $1,220,000 27 Gross Fixed Assets $146,200 $263.160 $383,160 28 Less Accumulated Dep. $344,800 $939.790 $836,840 29 Net Fixed Assets $1,468.800 $2,886,592 $3,516,952 30 Total Assets $145,600 $200,000 $136,000 $481,600 $323,432 $805,032 $460,000 $203,768 $663,768 $1,468,800 $324,000 $720,000 $284,960 $1,328,960 $1,000,000 $2,328,960 $460,000 $97,632 $557,632 $2,886,592 $359,800 $300,000 $380,000 $1,039,800 $500,000 $1,539,8001 $1,680,936 $296,216 $1,977,152 $3,516,952 32 Liabilities and equity 33 Accounts payable 34 Notes payable 35 Accruals 36 Total current liabilities 37 Long-term bonds 38 Total liabilities 39 Common stock (100,000 shares) 40 Retained earnings 41 Total common equity 42 Total liabilities and equity 43 44 Income Statements 45 46 47 Net sales 48 Costs of Goods Sold Except Depr. 49 Depreciation and amortization 50 Other Expenses 51 Total Operating Cost 52 Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT 53 Less interest 54 Pre-tax earnings 55 Taxes (40%) 56 Net Income before preferred dividends 57 EPS 58 DPS 59 Book Value Per Share 60 2017 $3,432,000 $2,864,000 $18,900 $340,000 $3,222,900 $209,100 $62,500 $146,600 $58,640 $87,960 $0.880 $0.220 $6.638 2018 $5,834,400 $4,980,000 $116,960 $720,000 $5,816,960 $17.440 $176,000 ($ 158,560) ($63,424) ($95,136) ($0.951) $0.110 $5.576 2019E $7,035,600 $5,800,000 $120,000 $612,960 $6,532,960 $502,640 $80,000 $422,640 $169,056 $253,584 $1.014 $0.220 $7.909 I do to rega Cochran must prepare an analysis of where the company is now, what it must do to regain its financial health, and what actions should be taken. Your assignment is to help her answer the following questions. Provide clear 3 explanations, not yes or no answers. 4 5 a. Why are ratios useful? What three groups use ratio analysis and for what reasons? 6 -7 b. (1.) Calculate the current and quick ratios based on the projected balance sheet and income statement data. 8 59 Calculated Data: Ratios 0 Industry 2017 2018 2019E Average *1 Liquidity ratios 2 Current Ratio 2.70 73 Quick Ratio 1.00 74 75 76 (2.) What can you say about the company's liquidity position? We often think of ratios as being useful (1) to managers to help run the business, (2) to bankers for credit analysis, and (3) to stockholders for stock valuation. 77 Would these different types of analysts have an equal interest in the liquidity ratios? 78 79 c. Calculate the inventory turnover, days sales outstanding (DSO), fixed assets turnover, operating capital requirement, and total assets turnover. How does Computron's utilization of assets stack up against other firms in 81 its industry? 82 Industry 83 2017 2018 Average 2019E 84 Asset Management ratios 6.10 85 Inventory Turnover 32.00 86 Days Sales Outstanding 7.00 2.50 87 Fixed Asset Turnover 88 Total Asset Turnover in times-interest-earned, and EBITDA coverage ratios. How does nude from these ratios? 80 d. Calculate the debt ratio, liabilities-to-assets ratio, times-interest-earned, and EBITDA coverage ratios. How does Computron compare with the industry with respect to financial leverage? What can you conclude from these ratios? 3 Debt Management ratios Industry 2017 2018 2019E 4 Debt Ratio Average 5 Liabilities-to-assets Ratio 32.0% 50.0% 6 Times Interest Earned 6.20 7 EBITDA Coverage Ratio 8.00 38 99 e. Calculate the profit margin, basic earning power (BEP), return on assets (ROA), and return on equity (ROE). What 100 can you say about these ratios? 101 Industry 102 Profitability ratios 2017 2018 2019E Average 3.6% 103 Net Profit Margin 7.1% 104 Operating Margin 15.5% 105 Gross Profit Margin 17.8% 106 Basic Earning Power 9.0% 107 Return on Assets 18.0% 108 Return on Equity 109 110 f. Calculate the pricelearnings ratio, price cash flow ratio, and market/book ratio. Do these ratios indicate that Industry 111 investors are expected to have a high or low opinion of the company? 2019E Average 112 2018 2017 7.60 2.90 14.20 na 113 Market Value ratios 114 Price to Earnings Ratio 115 Price-to-Cash Flow Ratio 116 Market-to-Book Ratio 117 Book Value Per Share analysis. What do these analyses tell you about Computron? 119 g. Perform a common size analysis and percent change analysis. What do these analyses tell you about Computron? 120 121 See the worksheet with the TAB "Common Size and % Change" 122 123 124 1. What are some potential problems and limitations of financial ratio analysis? 125 126 J. What are some qualitative factors analysts should consider when evaluating a company's likely future financial 127 performance? 128 F Common Size Analysis and Percent Change Analysis 1 C 2 D E F G H 3 4 In common size analysis, all income statement items are divided by sales, and all balance sheet items are 5 divided by total assets. 6 7 In percent change analysis, all items are expressed as a percent change from the first year, called the base 8 year, of the analysis. 9 10 11 12 13 14 Common Size Statements 15 16 Balance Sheets 2017 2018 2019E Industry 17 18 19 Assets 20 Cash and equivalents 0.6% 0.3% 0.4% 0.3% 21 Short-term investments 3.3% 0.7% 2.0% 0.3% 22 Accounts receivable 23.9% 21.9% 25.0% 22.4% 23 Inventories 48.7% 44.6% 48.8% 41.2% 76.5% 67.4% 76.2% 24 Total Current Assets 64.1% 23.5% 32.6% 23.8% 35.9% 25 Net Fixed Assets 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% 26 Total Assets 27 28 Liabilities and equity 11.2% 10.2% 11.9% 29 Accounts payable 24.9% 13.6% 8.5% 2.4% 30 Notes payable 9.9% 10.8% 9.5% 31 Accruals 32.8% 46.0% 29.6% 23.7% 32 Total current liabilities 22.0% 34.6% 14.2% 26.3% 19,3% 33 Long-term bonds 50.0% 56.2% 34 Total common equity 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% 35 Total liabilities and equity 2019E Industry 9.9% 9.3% 45.2% AD 2017 2018 2019E Industry 38 Income Statements 39 40 41 Net sales 42 COGS except depr. 43 Depreciation 44 Other Expenses 45 EBIT 46 Less interest 47 Pre-tax earnings 48 Taxes (40%) 49 Net Income before preferred dividends 50 51 52 Percentage Change Analysis 53 54 Balance Sheets 55 100.0% 83.4% 0.6% 9.9% 6.1% 1.8% 4.3% 1.7% 2.6% 100.0% 85.4% 2.0% 12.3% 0.3% 3.0% 2.7% -1.1% -1.6% 100.0% 82.4% 1.7% 8.7% 7.1% 1.1% 6.0% 2.4% 100.0% 84.5% 4.0% 4.4% 7.1% 1.1% 5.9% 2.4% 3.6% 3.6% 2017 2018 2019E 56 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% -19.1% -58.8% 80.0% 80.0% 73.2% 172.6% 96.5% 55.6% 47.4% 150.0% 140.0% 138.4% 142.7% 139.4% 0% 0% 57 Assets 58 Cash and equivalents 59 Short-term investments 60 Accounts receivable 61 Inventories 62 Total Current Assets 63 Net Fixed Assets 64 Total Assets 65 66 Liabilities and equity 67 Accounts payable 68 Notes payable 69 Accruals 70 Total current liabilities 71 Long-term bonds 72 Total common equity 73 Total liabilities and equity 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 122.5% 260.0% 109.5% 175.9% 209.2% -16.0% 96.5% 147.1% 50.0% 179.4% 115.9% 54.6% 197.9% 139.4% 2017 2018 2019E 75 76 Income Statements 77 78 79 Net sales 80 Costs of Goods Sold 81 Depreciation 82 Other Expenses 83 EBIT 84 Less interest 85 Pre-tax earnings 86 Taxes (40%) 87 Net Income before preferred dividends 88 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 70.0% 73.9% 518.8% 111.8% -91.7% 181.6% -208.2% -208.2% 208.2% 105.0% 102.5% 534.9% 80.3% 140.4% 28.0% 188.3% 188.3% 188.3%