Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
PLEASE HELP Company Description and Overview Tonia Odenburg and Tara Evans were life-long friends. One earned a degree in accounting and the other became a
PLEASE HELP 
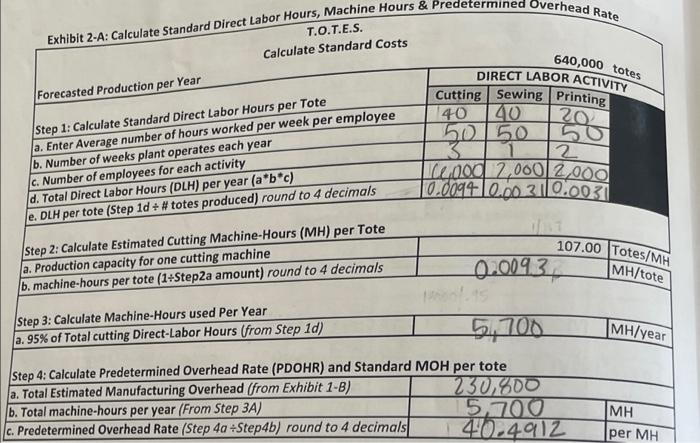
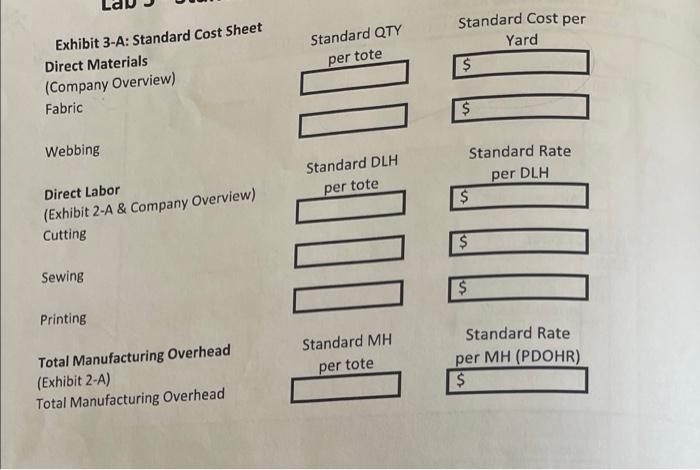
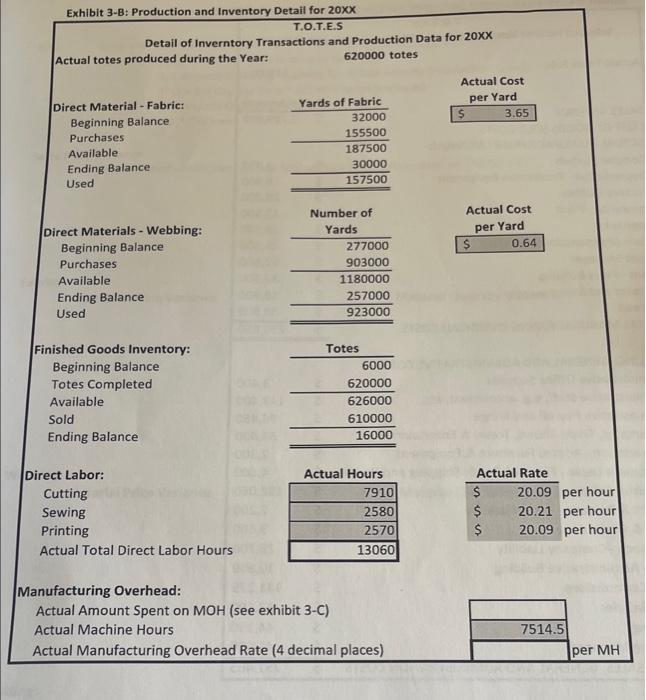
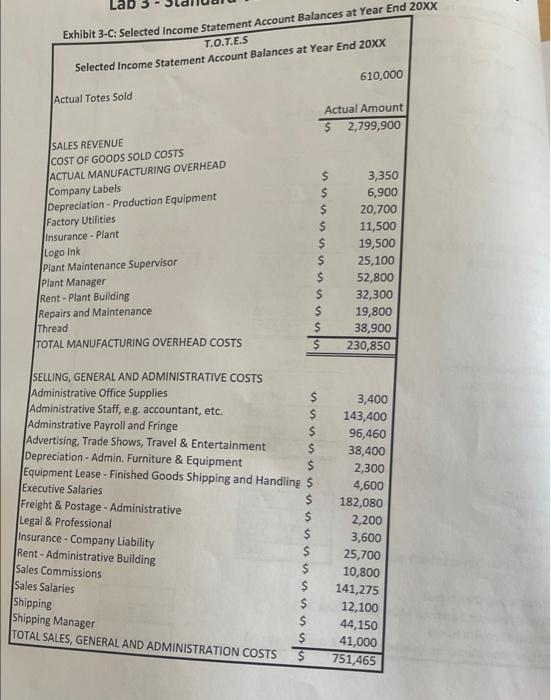


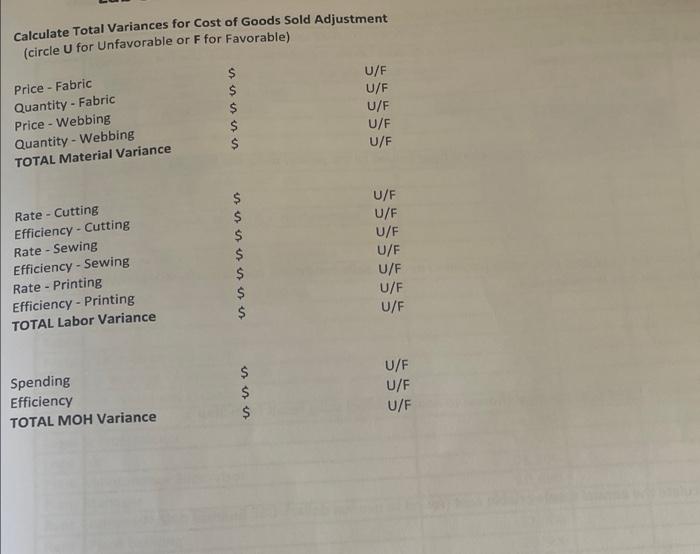
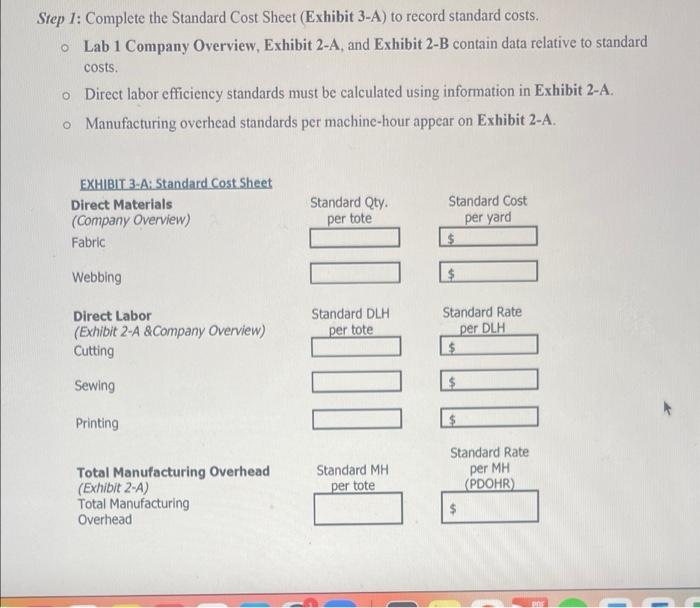
Company Description and Overview Tonia Odenburg and Tara Evans were life-long friends. One earned a degree in accounting and the other became a nutritionist. Both were accomplished seamstresses were concerned about the impact plastic grocery bags had on the environment and had created reusable grocery bags for their personal use. After numerous compliments on the design and strength of their bags from store clerks and customers, they developed a business plan and started T.O.T.E.S. They called their version of the grocery bag a tote and sold them to grocery stores and small community farms. The company has grown rapidly and is now operating near capacity Current Operations Employees Tonia is the president and Tara is the controller. Both individuals work full time and are salaried. Other employees include: Full-Time Salaried Employees: Plant Manager Plant Mainenance Supervisor Other Administrative Staff (Accountant, Receptionist, Finished Good Warehouse Manager) Hourly Employees: 3 Employee(s) in the cutting department 1 Employee(s) in the sewing department 2 Part-time employee(s) in the printing department The hourly employees are all considered direct labor employees. Historically, the hourly employees earn an average of $20 per hour, including fringe benefits and payroll taxes. All hourly employees work 40 hours each week, except for the part-time employee(s) who works 20 hours each week Materials Each grocery bag requires 1/4 yard of 60 wide fabric and 1-1/2 yards of webbing. The fabric costs $3.63 per yard. Webbing costs $0.65 per yard. Thread is purchased in 500-yard spools and is considered an indirect material. After the totes pass quality control they are silk-screened with a customer's logo and the T.O.T.E.S. label is attached. Both the logo ink and the company labels are indirect materials. Manufacturing Overhead T.O.T.E.S. allocates manufacturing overhead using a plantwide overhead rate based on machine hours in the cutting department. The cutting machines operate 95% of the hours worked by the cutting department employees. The plant operates 50 weeks per year. Inventory T.O.T.E.S. operates on a just-in-time basis in regards to both raw materials and finished goods. Work-in- process inventory is negligible at the end of each month. The company has found that it needs to have 15% of the following month's production requirements on hand at the end of each month in order to meet sales projections. They plan to have 20% of the fabric and 5% of the webbing required for the following month's production on hand at the end of each month. Sales Forecast In the upcoming year, T.O.T.E.S. management forecasted sales of 640,000 totes. Each tote sells for $4.51. Tara estimated annual revenue and expenses based on that level of sales and production. Her estimates are shown on Exhibit 1-A. Exhibit 2-A: Calculate Standard Direct Labor Hours, Machine Hours & Predetermined Overhead Rate T.O.T.E.S. Calculate Standard Costs Forecasted Production per Year 640,000 totes DIRECT LABOR ACTIVITY Cutting Sewing Printing 20 Step 1: Calculate Standard Direct Labor Hours per Tote a. Enter Average number of hours worked per week per employee b. Number of weeks plant operates each year c. Number of employees for each activity d. Total Direct Labor Hours (DLH) per year (a*b*c) e. DLH per tote (Step 1d + # totes produced) round to 4 decimals 40 20 50 50 3 2 L200 2,000 2,000 10.009410.00 310.0031 Step 2: Calculate Estimated Cutting Machine-Hours (MH) per Tote a. Production capacity for one cutting machine b. machine-hours per tote (1+Step2a amount) round to 4 decimals 107.00 Totes/MH MH/tote 0.0093 MH/year Step 3: Calculate Machine-Hours used Per Year a. 95% of Total cutting Direct-Labor Hours (from Step 1d) 5,700 Step 4: Calculate Predetermined Overhead Rate (PDOHR) and Standard MOH per tote a. Total Estimated Manufacturing Overhead (from Exhibit 1-B) 130.800 b. Total machine-hours per year (From Step 3A) 5,700 C. Predetermined Overhead Rate (Step 4a +Step4b) round to 4 decimals 140.4912 MH per MH Standard QTY Standard Cost per Yard $ per tote Exhibit 3-A: Standard Cost Sheet Direct Materials (Company Overview) Fabric $ Webbing Standard Rate Standard DLH per DLH per tote Direct Labor (Exhibit 2-A & Company Overview) Cutting OOO 002 Sewing Printing Standard MH Standard Rate per MH (PDOHR) $ Total Manufacturing Overhead (Exhibit 2-A) Total Manufacturing Overhead per tote Exhibit 3-B: Production and Inventory Detail for 20XX T.O.T.E.S Detail of Inverntory Transactions and Production Data for 20XX Actual totes produced during the Year: 620000 totes Actual Cost per Yard s 3.65 Direct Material - Fabric: - Beginning Balance Purchases Available Ending Balance Used Yards of Fabric 32000 155500 187500 30000 157500 - Actual Cost per Yard $ 0.64 Direct Materials - Webbing: Beginning Balance Purchases Available Ending Balance Used Number of Yards 277000 903000 1180000 257000 923000 Finished Goods Inventory: Beginning Balance Totes Completed Available Sold Ending Balance Totes 6000 620000 626000 610000 16000 Direct Labor: Cutting Sewing Printing Actual Total Direct Labor Hours Actual Hours 7910 2580 2570 13060 Actual Rate $ 20.09 per hour $ 20.21 per hour $ 20.09 per hour Manufacturing Overhead: Actual Amount Spent on MOH (see exhibit 3-C) Actual Machine Hours Actual Manufacturing Overhead Rate (4 decimal places) 7514.5 per MH Lab Exhibit 3-C: Selected Income Statement Account Balances at Year End 20XX T.O.T.E.S Selected Income Statement Account Balances at Year End 20xx 610,000 Actual Totes Sold Actual Amount $ 2,799,900 SALES REVENUE COST OF GOODS SOLD COSTS ACTUAL MANUFACTURING OVERHEAD Company Labels Depreciation - Production Equipment Factory Utilities Insurance - Plant Logo Ink Plant Maintenance Supervisor Plant Manager Rent - Plant Building Repairs and Maintenance $ $ $ $ $ $ 3,350 6,900 20,700 11,500 19,500 25,100 52,800 32,300 19,800 38,900 230,850 Thread TOTAL MANUFACTURING OVERHEAD COSTS $ $ SELLING, GENERAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE COSTS Administrative Office Supplies Administrative Staff, e.g. accountant, etc. Adminstrative Payroll and Fringe $ Advertising, Trade Shows, Travel & Entertainment Depreciation - Admin. Furniture & Equipment Equipment Lease - Finished Goods Shipping and Handling $ Executive Salaries $ Freight & Postage - Administrative $ Legal & Professional Insurance - Company Liability $ Rent - Administrative Building Sales Commissions Sales Salaries $ V 3,400 143,400 96,460 38,400 2,300 4,600 182,080 2,200 3,600 25,700 10,800 141,275 12,100 44,150 41,000 751,465 Shipping Shipping Manager TOTAL SALES, GENERAL AND ADMINISTRATION COSTS $ $ Lab 3 - Standard Versus Actual Cost and Quantities FORMULAS MUST BE WRITTEN FOR EACH VARIANCE PRIOR TO CALCULATIONS Hint: Price and Rate Variance calculations are the same. (TAQ (AP-SP) Quantity and efficiency Variance is done in two steps. 1. Calculate Standard Quantity for Actual Activity (Production Level) TSQ - Std Qty per Tote - Actual e totes produced 2. Calculate Quantity Variance (SP)"(TAQS - TSQ) Sales Price Variance (You will need to calculate Actual Selling Price from information on Exhibit 3-C) Fabric: Material Quantity Variance Material Price Variance Webbing: Material Price Variance Material Quantity Variance Cutting: Labor Efficiency Variance Labor Rate Variance Lab 3 - Standard Versus Actual Cost and Quantities Labor Efficiency Variance Sewing: Labor Rate Variance Calcula fcirete price Gant Price Quant TOTA: Labor Efficiency Variante Printing: Labor Rate Variance Rate Effic Rate E Rate Effice TOT Spe Elf TO Manufacturing Overhead (total): Spending (Rate) Variance Efficiency Variance 1. Which ONE Variance is the most significant indicating the company needs to analyze? 2. Do you think the company is using the correct driver for allocating variable manufacturing overhead? Why? Calculate Total Variances for Cost of Goods Sold Adjustment (circle U for Unfavorable or F for Favorable) - Price - Fabric Quantity - Fabric Price - Webbing Quantity - Webbing TOTAL Material Variance $ $ $ $ $ U/F U/F U/F U/F U/F Rate - Cutting Efficiency - Cutting Rate - Sewing Efficiency - Sewing Rate - Printing Efficiency - Printing TOTAL Labor Variance $ $ $ $ $ $ $ U/F U/F U/F U/F U/F U/F U/F $ $ $ U/F U/F Spending Efficiency TOTAL MOH Variance U/F Step 1: Complete the Standard Cost Sheet (Exhibit 3-A) to record standard costs. Lab 1 Company Overview, Exhibit 2-A, and Exhibit 2-B contain data relative to standard costs. o Direct labor efficiency standards must be calculated using information in Exhibit 2-A. o Manufacturing overhead standards per machine-hour appear on Exhibit 2-A. Standard Qty. EXHIBIT 3-A: Standard Cost Sheet Direct Materials (Company Overview) Fabric per tote Standard Cost per yard $ Webbing $. Direct Labor (Exhibit 2-A &Company Overview) Cutting Standard DLH per tote Standard Rate per DLH $ Sewing $ Printing $ Standard Rate Standard MH per tote per MH (PDOHR) Total Manufacturing Overhead (Exhibit 2-4) Total Manufacturing Overhead Company Description and Overview Tonia Odenburg and Tara Evans were life-long friends. One earned a degree in accounting and the other became a nutritionist. Both were accomplished seamstresses were concerned about the impact plastic grocery bags had on the environment and had created reusable grocery bags for their personal use. After numerous compliments on the design and strength of their bags from store clerks and customers, they developed a business plan and started T.O.T.E.S. They called their version of the grocery bag a tote and sold them to grocery stores and small community farms. The company has grown rapidly and is now operating near capacity Current Operations Employees Tonia is the president and Tara is the controller. Both individuals work full time and are salaried. Other employees include: Full-Time Salaried Employees: Plant Manager Plant Mainenance Supervisor Other Administrative Staff (Accountant, Receptionist, Finished Good Warehouse Manager) Hourly Employees: 3 Employee(s) in the cutting department 1 Employee(s) in the sewing department 2 Part-time employee(s) in the printing department The hourly employees are all considered direct labor employees. Historically, the hourly employees earn an average of $20 per hour, including fringe benefits and payroll taxes. All hourly employees work 40 hours each week, except for the part-time employee(s) who works 20 hours each week Materials Each grocery bag requires 1/4 yard of 60 wide fabric and 1-1/2 yards of webbing. The fabric costs $3.63 per yard. Webbing costs $0.65 per yard. Thread is purchased in 500-yard spools and is considered an indirect material. After the totes pass quality control they are silk-screened with a customer's logo and the T.O.T.E.S. label is attached. Both the logo ink and the company labels are indirect materials. Manufacturing Overhead T.O.T.E.S. allocates manufacturing overhead using a plantwide overhead rate based on machine hours in the cutting department. The cutting machines operate 95% of the hours worked by the cutting department employees. The plant operates 50 weeks per year. Inventory T.O.T.E.S. operates on a just-in-time basis in regards to both raw materials and finished goods. Work-in- process inventory is negligible at the end of each month. The company has found that it needs to have 15% of the following month's production requirements on hand at the end of each month in order to meet sales projections. They plan to have 20% of the fabric and 5% of the webbing required for the following month's production on hand at the end of each month. Sales Forecast In the upcoming year, T.O.T.E.S. management forecasted sales of 640,000 totes. Each tote sells for $4.51. Tara estimated annual revenue and expenses based on that level of sales and production. Her estimates are shown on Exhibit 1-A. Exhibit 2-A: Calculate Standard Direct Labor Hours, Machine Hours & Predetermined Overhead Rate T.O.T.E.S. Calculate Standard Costs Forecasted Production per Year 640,000 totes DIRECT LABOR ACTIVITY Cutting Sewing Printing 20 Step 1: Calculate Standard Direct Labor Hours per Tote a. Enter Average number of hours worked per week per employee b. Number of weeks plant operates each year c. Number of employees for each activity d. Total Direct Labor Hours (DLH) per year (a*b*c) e. DLH per tote (Step 1d + # totes produced) round to 4 decimals 40 20 50 50 3 2 L200 2,000 2,000 10.009410.00 310.0031 Step 2: Calculate Estimated Cutting Machine-Hours (MH) per Tote a. Production capacity for one cutting machine b. machine-hours per tote (1+Step2a amount) round to 4 decimals 107.00 Totes/MH MH/tote 0.0093 MH/year Step 3: Calculate Machine-Hours used Per Year a. 95% of Total cutting Direct-Labor Hours (from Step 1d) 5,700 Step 4: Calculate Predetermined Overhead Rate (PDOHR) and Standard MOH per tote a. Total Estimated Manufacturing Overhead (from Exhibit 1-B) 130.800 b. Total machine-hours per year (From Step 3A) 5,700 C. Predetermined Overhead Rate (Step 4a +Step4b) round to 4 decimals 140.4912 MH per MH Standard QTY Standard Cost per Yard $ per tote Exhibit 3-A: Standard Cost Sheet Direct Materials (Company Overview) Fabric $ Webbing Standard Rate Standard DLH per DLH per tote Direct Labor (Exhibit 2-A & Company Overview) Cutting OOO 002 Sewing Printing Standard MH Standard Rate per MH (PDOHR) $ Total Manufacturing Overhead (Exhibit 2-A) Total Manufacturing Overhead per tote Exhibit 3-B: Production and Inventory Detail for 20XX T.O.T.E.S Detail of Inverntory Transactions and Production Data for 20XX Actual totes produced during the Year: 620000 totes Actual Cost per Yard s 3.65 Direct Material - Fabric: - Beginning Balance Purchases Available Ending Balance Used Yards of Fabric 32000 155500 187500 30000 157500 - Actual Cost per Yard $ 0.64 Direct Materials - Webbing: Beginning Balance Purchases Available Ending Balance Used Number of Yards 277000 903000 1180000 257000 923000 Finished Goods Inventory: Beginning Balance Totes Completed Available Sold Ending Balance Totes 6000 620000 626000 610000 16000 Direct Labor: Cutting Sewing Printing Actual Total Direct Labor Hours Actual Hours 7910 2580 2570 13060 Actual Rate $ 20.09 per hour $ 20.21 per hour $ 20.09 per hour Manufacturing Overhead: Actual Amount Spent on MOH (see exhibit 3-C) Actual Machine Hours Actual Manufacturing Overhead Rate (4 decimal places) 7514.5 per MH Lab Exhibit 3-C: Selected Income Statement Account Balances at Year End 20XX T.O.T.E.S Selected Income Statement Account Balances at Year End 20xx 610,000 Actual Totes Sold Actual Amount $ 2,799,900 SALES REVENUE COST OF GOODS SOLD COSTS ACTUAL MANUFACTURING OVERHEAD Company Labels Depreciation - Production Equipment Factory Utilities Insurance - Plant Logo Ink Plant Maintenance Supervisor Plant Manager Rent - Plant Building Repairs and Maintenance $ $ $ $ $ $ 3,350 6,900 20,700 11,500 19,500 25,100 52,800 32,300 19,800 38,900 230,850 Thread TOTAL MANUFACTURING OVERHEAD COSTS $ $ SELLING, GENERAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE COSTS Administrative Office Supplies Administrative Staff, e.g. accountant, etc. Adminstrative Payroll and Fringe $ Advertising, Trade Shows, Travel & Entertainment Depreciation - Admin. Furniture & Equipment Equipment Lease - Finished Goods Shipping and Handling $ Executive Salaries $ Freight & Postage - Administrative $ Legal & Professional Insurance - Company Liability $ Rent - Administrative Building Sales Commissions Sales Salaries $ V 3,400 143,400 96,460 38,400 2,300 4,600 182,080 2,200 3,600 25,700 10,800 141,275 12,100 44,150 41,000 751,465 Shipping Shipping Manager TOTAL SALES, GENERAL AND ADMINISTRATION COSTS $ $ Lab 3 - Standard Versus Actual Cost and Quantities FORMULAS MUST BE WRITTEN FOR EACH VARIANCE PRIOR TO CALCULATIONS Hint: Price and Rate Variance calculations are the same. (TAQ (AP-SP) Quantity and efficiency Variance is done in two steps. 1. Calculate Standard Quantity for Actual Activity (Production Level) TSQ - Std Qty per Tote - Actual e totes produced 2. Calculate Quantity Variance (SP)"(TAQS - TSQ) Sales Price Variance (You will need to calculate Actual Selling Price from information on Exhibit 3-C) Fabric: Material Quantity Variance Material Price Variance Webbing: Material Price Variance Material Quantity Variance Cutting: Labor Efficiency Variance Labor Rate Variance Lab 3 - Standard Versus Actual Cost and Quantities Labor Efficiency Variance Sewing: Labor Rate Variance Calcula fcirete price Gant Price Quant TOTA: Labor Efficiency Variante Printing: Labor Rate Variance Rate Effic Rate E Rate Effice TOT Spe Elf TO Manufacturing Overhead (total): Spending (Rate) Variance Efficiency Variance 1. Which ONE Variance is the most significant indicating the company needs to analyze? 2. Do you think the company is using the correct driver for allocating variable manufacturing overhead? Why? Calculate Total Variances for Cost of Goods Sold Adjustment (circle U for Unfavorable or F for Favorable) - Price - Fabric Quantity - Fabric Price - Webbing Quantity - Webbing TOTAL Material Variance $ $ $ $ $ U/F U/F U/F U/F U/F Rate - Cutting Efficiency - Cutting Rate - Sewing Efficiency - Sewing Rate - Printing Efficiency - Printing TOTAL Labor Variance $ $ $ $ $ $ $ U/F U/F U/F U/F U/F U/F U/F $ $ $ U/F U/F Spending Efficiency TOTAL MOH Variance U/F Step 1: Complete the Standard Cost Sheet (Exhibit 3-A) to record standard costs. Lab 1 Company Overview, Exhibit 2-A, and Exhibit 2-B contain data relative to standard costs. o Direct labor efficiency standards must be calculated using information in Exhibit 2-A. o Manufacturing overhead standards per machine-hour appear on Exhibit 2-A. Standard Qty. EXHIBIT 3-A: Standard Cost Sheet Direct Materials (Company Overview) Fabric per tote Standard Cost per yard $ Webbing $. Direct Labor (Exhibit 2-A &Company Overview) Cutting Standard DLH per tote Standard Rate per DLH $ Sewing $ Printing $ Standard Rate Standard MH per tote per MH (PDOHR) Total Manufacturing Overhead (Exhibit 2-4) Total Manufacturing Overhead 








Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


