please help i got this wrong!

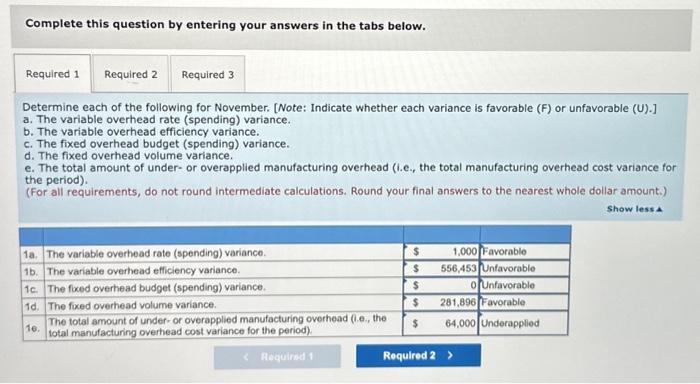
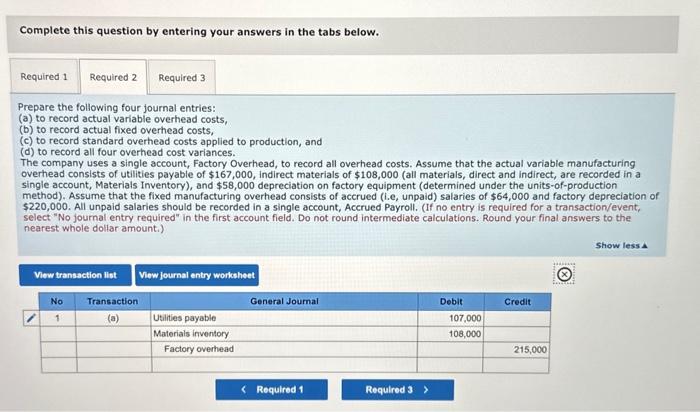
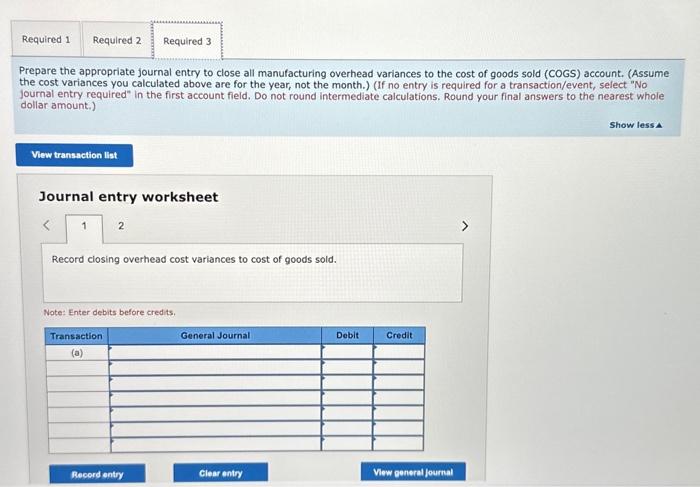
Edney Company employs a standard cost system for product costing. The per-unit standard cost of its product is: The manufacturing overhead rate is based on a normal capacity level of 600,000 direct labor hours. The firm has the following annua manufacturing overhead budget: Edney incurred $434,150 in direct labor cost for 53,900 direct labor hours to manufacture 26,000 units in November. Other costs incurred in November include $284,000 for fixed manufacturing overhead and $333,000 for variable manufacturing overhead. Required: 1. Determine each of the following for November. [Note: Indicate whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).] a. The variable overhead rate (spending) variance. b. The variable overhead efficiency variance. c. The flixed overhead budget (spending) variance. d. The fixed overhead volume variance. e. The total amount of under- or overapplied manufacturing overhead (i.e., the total manufacturing overhead cost variance for the period). 2. Prepare the following four journal entries: (a) to record actual variable overhead costs, (b) to record actual fixed overhead costs, (c) to record standard overhead costs applied to production, and (d) to record all four overhead cost variances. The company uses a single account, Factory Overhead, to record all overhead costs. Assume that the actual variable manufacturing overhead consists of utilities payable of $167,000, indirect materials of $108,000 (all materials, direct and indirect, are recorded in a single account, Materials inventory), and $58,000 depreciation on factory equipment (determined under the units-of-production method). Assume that the fixed manufacturing overhead consists of accrued salaries of $64,000 and factory depreciation of $220,000. All accrued solaries should be recorded in a single account, Accrued Payroll. 3. Prepare the oppropriate journal entry to close all manufacturing overhead variances to the cost of goods sold (COGS) account. (Assume the cost variances you calculated above are for the vear, not the month.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Determine each of the following for November. [Note: Indicate whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).] a. The variable overhead rate (spending) variance. b. The variable overhead efficiency variance. c. The fixed overhead budget (spending) variance. d. The fixed overhead volume variance. e. The total amount of under- or overapplied manufacturing overhead (i.e., the total manufacturing overhead cost variance for the period). (For all requirements, do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Prepare the following four journal entries: (a) to record actual variable overhead costs, (b) to record actual fixed overhead costs, (c) to record standard overhead costs applied to production, and (d) to record all four overhead cost variances. The company uses a single account, Factory Overhead, to record all overhead costs. Assume that the actual variable manufacturing overhead consists of utilities payable of $167,000, indirect materials of $108,000 (all materials, direct and indirect, are recorded in a single account, Materials Inventory), and $58,000 depreciation on factory equipment (determined under the units-of-production method). Assume that the fixed manufacturing overhead consists of accrued (i.e, unpaid) salaries of $64,000 and factory depreciation of $220,000. All unpaid salaries should be recorded in a single account, Accrued Payroll. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Prepare the appropriate journal entry to close all manufacturing overhead variances to the cost of goods sold (COGS) account. (Assume the cost variances you calculated above are for the year, not the month.) (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Show less 4 Journal entry worksheet Record closing overhead cost variances to cost of goods sold. Note: Enter debits before credits. Edney Company employs a standard cost system for product costing. The per-unit standard cost of its product is: The manufacturing overhead rate is based on a normal capacity level of 600,000 direct labor hours. The firm has the following annua manufacturing overhead budget: Edney incurred $434,150 in direct labor cost for 53,900 direct labor hours to manufacture 26,000 units in November. Other costs incurred in November include $284,000 for fixed manufacturing overhead and $333,000 for variable manufacturing overhead. Required: 1. Determine each of the following for November. [Note: Indicate whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).] a. The variable overhead rate (spending) variance. b. The variable overhead efficiency variance. c. The flixed overhead budget (spending) variance. d. The fixed overhead volume variance. e. The total amount of under- or overapplied manufacturing overhead (i.e., the total manufacturing overhead cost variance for the period). 2. Prepare the following four journal entries: (a) to record actual variable overhead costs, (b) to record actual fixed overhead costs, (c) to record standard overhead costs applied to production, and (d) to record all four overhead cost variances. The company uses a single account, Factory Overhead, to record all overhead costs. Assume that the actual variable manufacturing overhead consists of utilities payable of $167,000, indirect materials of $108,000 (all materials, direct and indirect, are recorded in a single account, Materials inventory), and $58,000 depreciation on factory equipment (determined under the units-of-production method). Assume that the fixed manufacturing overhead consists of accrued salaries of $64,000 and factory depreciation of $220,000. All accrued solaries should be recorded in a single account, Accrued Payroll. 3. Prepare the oppropriate journal entry to close all manufacturing overhead variances to the cost of goods sold (COGS) account. (Assume the cost variances you calculated above are for the vear, not the month.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Determine each of the following for November. [Note: Indicate whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).] a. The variable overhead rate (spending) variance. b. The variable overhead efficiency variance. c. The fixed overhead budget (spending) variance. d. The fixed overhead volume variance. e. The total amount of under- or overapplied manufacturing overhead (i.e., the total manufacturing overhead cost variance for the period). (For all requirements, do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Prepare the following four journal entries: (a) to record actual variable overhead costs, (b) to record actual fixed overhead costs, (c) to record standard overhead costs applied to production, and (d) to record all four overhead cost variances. The company uses a single account, Factory Overhead, to record all overhead costs. Assume that the actual variable manufacturing overhead consists of utilities payable of $167,000, indirect materials of $108,000 (all materials, direct and indirect, are recorded in a single account, Materials Inventory), and $58,000 depreciation on factory equipment (determined under the units-of-production method). Assume that the fixed manufacturing overhead consists of accrued (i.e, unpaid) salaries of $64,000 and factory depreciation of $220,000. All unpaid salaries should be recorded in a single account, Accrued Payroll. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Prepare the appropriate journal entry to close all manufacturing overhead variances to the cost of goods sold (COGS) account. (Assume the cost variances you calculated above are for the year, not the month.) (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Show less 4 Journal entry worksheet Record closing overhead cost variances to cost of goods sold. Note: Enter debits before credits