


Please help in answering the following International Trade Policy and Institutions Questions:
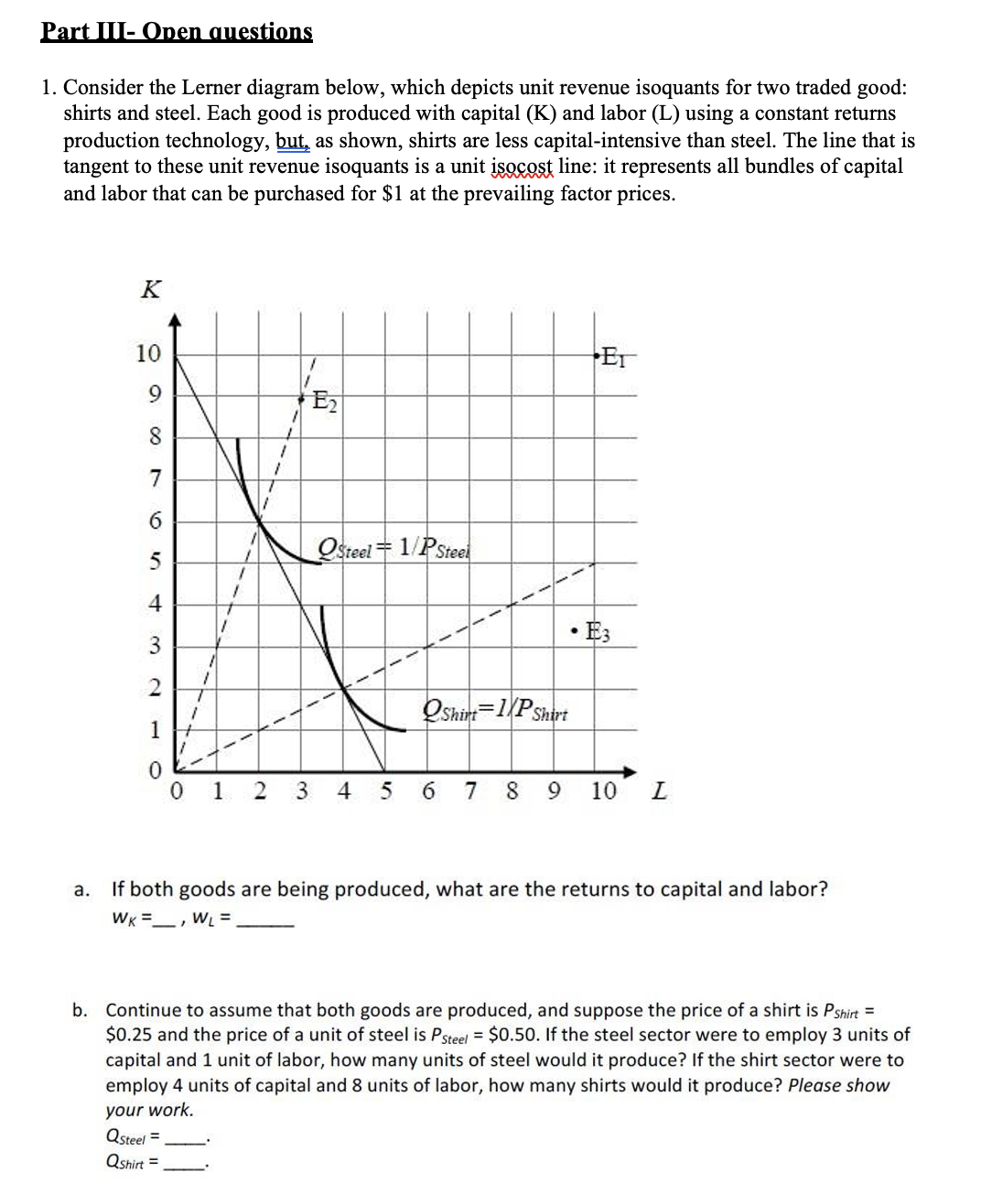
E Il-MII'ICI' Q | (Answer all questions and choose ONE most correct answer) 6. In the HO model with T as the labor-intensive good, an increase in the price of T will lead to (a) technology in the T sector to become more capital intensive. (b) technology in the S sector to become more labor intensive. (c) technology in the S sector to become more capital intensive. (d) Both (a) and (b). (e) Both (a) and (c). 7. According to the factor price equalization theorem, if A is labor abundant, then once trade opens (a) wages and rents should fall in A. (b) wages and rents should rise in A. (c) wages should lii and rents should fall in A. (d) wages should fall and rents should rise in A. (e) None of the above. 8. According to the H0 model, (a) everyone automatically gains from trade. (b) the gainers from trade outnumber the losers from trade. (c) the scarce factor necessarily gains from trade. (d) the abundant factor loses from trade. (e) none of the above. 9. Factor prices are equalized between countries because of (a) free trade. (b) identical technologies. (c) identical preferences. (d) perfect competition. (e) All off the above. 10. In the HO model, with S as the capital-intensive good, a 10% increase in the price of S could induce (a) an increase in the wage rate of 10%, and a fall in the rental rate. (b) a decrease in the wage rate and an increase in the rental rate of less than 10%. (c) an increase in the rental rate of 10%, and a decrease in the wage rate. (d) an increase in the rental rate of more than 10%, and a fall in the wage rate. (e) None of the above. BazLJmeLEalqunr-sm (Indicate if true or false and explain briey- max 3 sentences, if relevant you can add gures andfor numerical examples to your explanation) A) Leontief found that the HO model did not work for the United-States because US exported labor intensive goods (i the US capital/labor ratio for imported goods was larger than that for exported goods). A possible explanation for this paradox is that Leontief ignored the fact that the US imports a variety of products instead of just one and the fact that US labor is highly skilled. B) According to Meg-Samuelson theorem, in the long run, when factors are mobile, an increase in the relative price of a good will increase the real earnings of the factor used intensively in the production of that good. Therefore, according to the WSamuelson theorem, we would expect all workers across the globe to favor limiting trade, since when trade is limited, wages will fall in the labor-abundant country but rise in the capital-abundant country. C) Suppose that the price of shoes (which are labor intensive) has risen by 5%. Then Home wages will rise by more than 5% and the Home rental rates will fall by no more than 5%. D) If: Canada and US produce computers and chemicals using labor and capital, US is capital abundant and Canada is labor abundant, computer production is more labor intensive than chemical production in both countries, Canada and US start trade; Then (according to H0 model): wages of Canadian workers should ri_se and the price of chemicals should fall in the US. E) According to the HO model, international trade for a nation with a relative abundance of skilled labor and a relative scarcity of unskilled labor will tend to widen or aggravate the income disparity between skilled and unskilled workers. F) In the specic-factors model, factors of production that cannot move between industries will gain or lose the most from opening a country to trade. G) The factor of production that is specic to the import and export industry will lose in real terms, as the relative price of the import good and the export good falls. H) The fact that the citizens of Bolivia at the early 20003 could not agree on how to share the gains from exporting natural gas indicates that trade sometimes creates social tension and distributional conicts in trading countries. This is the one of the similar results in the Ricardian model and in the Specic Factor Model. I) In country with agriculture (A) and manufacturing (M) sector, if the wage rate in the agriculture sector is lower than in the manufacturing sector, then labor will migrate to the manufacturing sector, and this will cause both wage and marginal product of labor in the manufacturing sector to decrease. J) In the specic-factor model, a change in the relative price of one good versus another will cause mg; in marginal product and the allocation of labor resources. When the price of good A increases relative to price of good B and labor is mobile, the equilibrium real wage in industry A will rise in terms of good B. Walton: 1. Consider the Lerner diagram below, which depicts unit revenue isoquants for two traded good: shirts and steel. Each good is produced with capital (K) and labor (L) using a constant returns production technology, bJ_.11t as shown, shirts are less capital-intensive than steel. The line that is tangent to these unit revenue isoquants is a unit W line: it represents all bundles of capital and labor that can be purchased for $1 at the prevailing factor prices. pn O OiNUJ-RMQQOOO IEIIHIEIIII II II II II II II II II a. If both goods are being produced, what are the returns to capital and labor? WK =_ : Wt = b. Continue to assume that both goods are produced, and suppose the price of a shirt is PM\" = $0.25 and the price of a unit of steel is P5,\c. Suppose twice the capital and labor described in part (b) were used for steel, but only half the capital and labor described in part {b} were used for shirts. what quantity of steel and shirts would be produced? How much would those quantities be worth? Please provide a briefone sentence explanation of your answer. Qteei = .___- QShirt = - PSteei QSteei' = _. 95m QShirr = d. Suppose the economy's overall endowment of capital and labor is at the point E1. What total amount of each good will the economy produce? Briey explain why the economy will produce this particular combination. Please show your work. QSreei = _- Qshm = . e. If the economy's endowment point had been E2 , what would your answer to part c have been? Om\" = _ , (25,"; = . Please provide a brief one sentence explanation of your answer. f. Fill in the blank: If the economy's endowment point had been E3, which good or goods would be produced? (shirts, steel, both) 3. Fill in the blank: If the endowment were to move from E; to E3, then wax would (rise, fall, remain the same] . Please provide a brief one sentence explanation of your answer. 2. Using a carefully drawn 2x2x2 H0 diagram with Leontief production, demonstrate the effect of an increase in the price of a capital-intensive good on the relative return to labor. (You can draw these by hg copy and paste the gures from my power-points and make appropriate adjustments). Supplement your answer with a one or two sentence explanation of the intuition behind the relationship you demonstrate. 3. Re-draw your diagram from the last question to demonstrate that the wage changes are \"amplied\" with respect to the price changes. Supplement your answer with a one or two sentence explanation of the intuition behind this amplication. 4. Consider the same relative price movement as in problem 3, but now assume the production functions are Cobb Douglas instead of Leontief. Using a new, carefully drawn diagram, show how the relative intensities with which the two industries are produced would change. Supplement your answer with a one or two sentence explanation of the intuition behind these changes in intensity














