Please help me
19 . Price controls in the Florida orange market
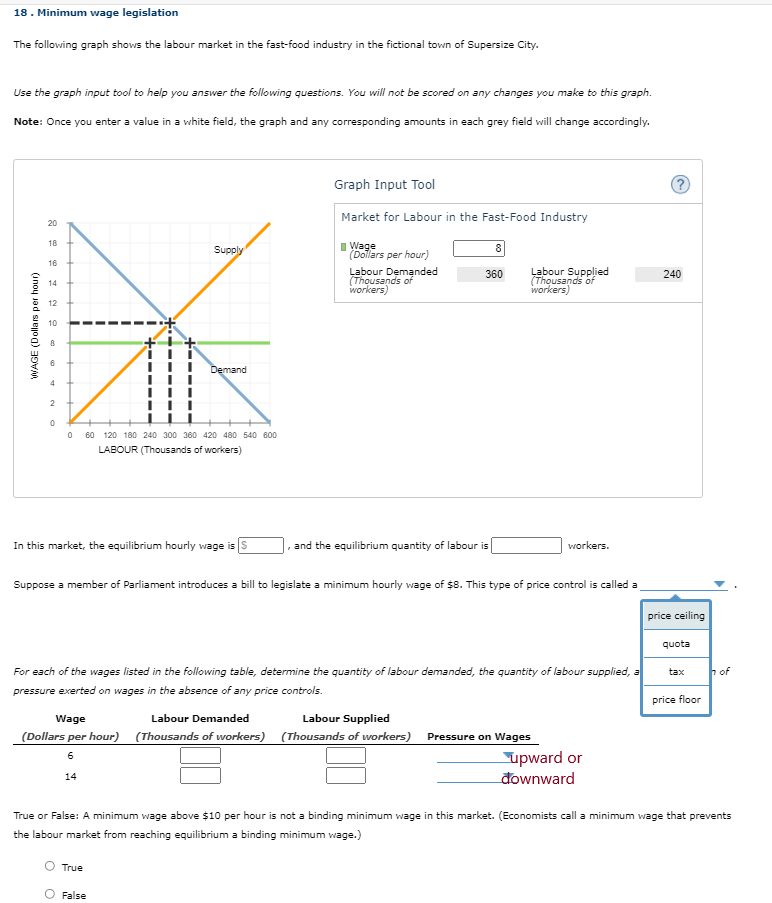
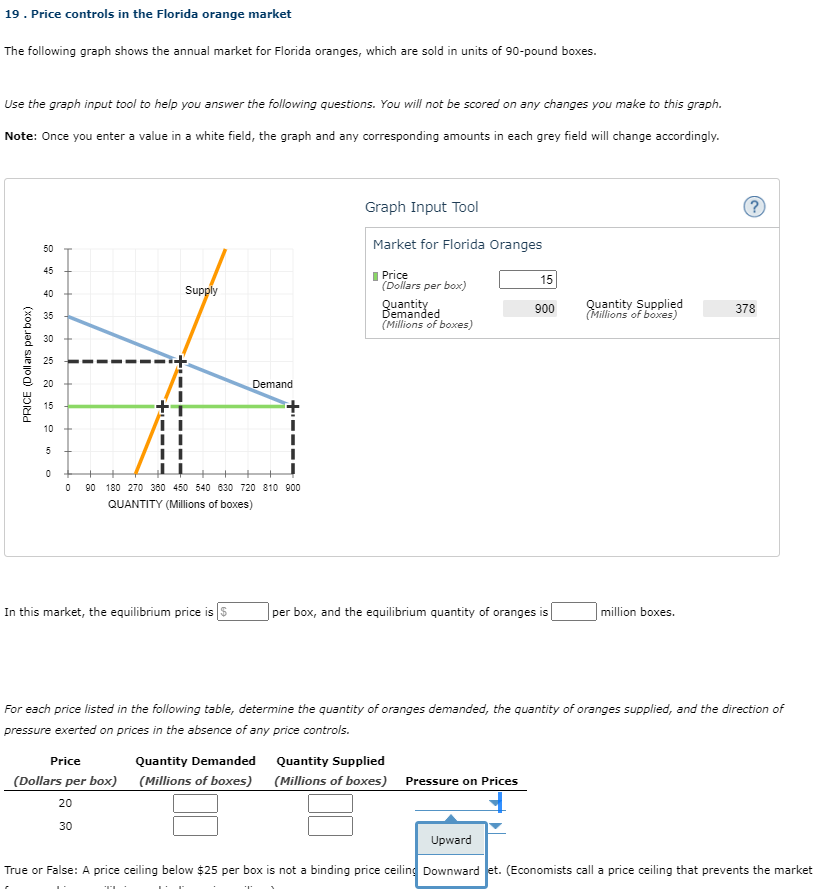
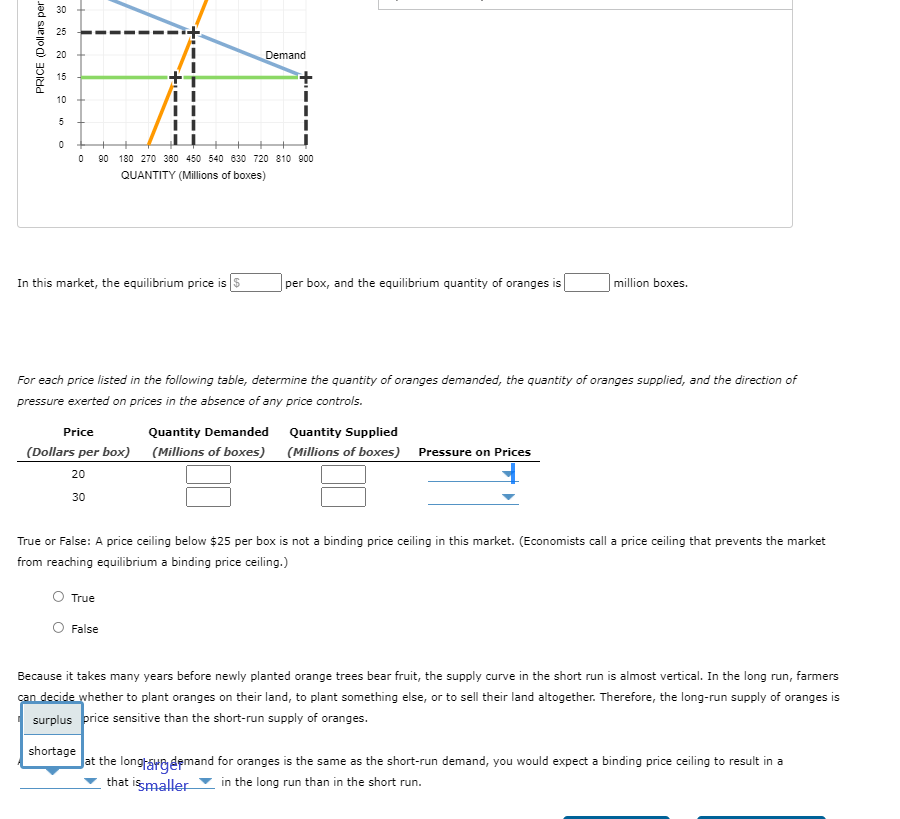
18 . Minimum wage legislation The following graph shows the labour market in the fast-food industry in the fictional town of Supersize City. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be scored on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. Graph Input Tool (? ) Market for Labour in the Fast-Food Industry Supply I Wage (Dollars per hour) Labour Demanded 360 Labour Supplied 240 (Thousands of (Thousands of workers) workers, WAGE (Dollars per hour) Demand 60 120 180 240 300 360 420 480 540 800 LABOUR (Thousands of workers) In this market, the equilibrium hourly wage is |S , and the equilibrium quantity of labour is workers. Suppose a member of Parliament introduces a bill to legislate a minimum hourly wage of $8. This type of price control is called a price ceiling quota For each of the wages listed in the following table, determine the quantity of labour demanded, the quantity of labour supplied, a tax of pressure exerted on wages in the absence of any price controls price floor Wage Labour Demanded Labour Supplied ( Dollars per hour) (Thousands of workers) (Thousands of workers) Pressure on Wages 6 upward or 14 downward True or False: A minimum wage above $10 per hour is not a binding minimum wage in this market. (Economists call a minimum wage that prevents the labour market from reaching equilibrium a binding minimum wage.) True False19 . Price controls in the Florida orange market The following graph shows the annual market for Florida oranges, which are sold in units of 90-pound boxes. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be scored on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. Graph Input Tool (? ) Market for Florida Oranges Price (Dollars per box) 15 Supply Quantity Quantity Supplied Demanded 900 (Millions of boxes) 378 (Millions of boxes) 0 0 6 6 8 8 8 8 8 6 8 PRICE (Dollars perbox) Demand 0 90 180 270 360 450 540 630 720 810 900 QUANTITY (Millions of boxes) In this market, the equilibrium price is $ per box, and the equilibrium quantity of oranges is |million boxes. For each price listed in the following table, determine the quantity of oranges demanded, the quantity of oranges supplied, and the direction of pressure exerted on prices in the absence of any price controls. Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied (Dollars per box) (Millions of boxes) (Millions of boxes) Pressure on Prices 20 30 Upward True or False: A price ceiling below $25 per box is not a binding price ceiling Downward et. (Economists call a price ceiling that prevents the marketPRICE (Dollars per Demand O 90 180 270 360 450 540 630 720 810 900 QUANTITY (Millions of boxes) In this market, the equilibrium price is $ per box, and the equilibrium quantity of oranges is million boxes. For each price listed in the following table, determine the quantity of oranges demanded, the quantity of oranges supplied, and the direction of pressure exerted on prices in the absence of any price controls. Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied ( Dollars per box) (Millions of boxes) (Millions of boxes) Pressure on Prices 20 30 True or False: A price ceiling below $25 per box is not a binding price ceiling in this market. (Economists call a price ceiling that prevents the market from reaching equilibrium a binding price ceiling.) O True O False Because it takes many years before newly planted orange trees bear fruit, the supply curve in the short run is almost vertical. In the long run, farmers can decide whether to plant oranges on their land, to plant something else, or to sell their land altogether. Therefore, the long-run supply of oranges is surplus price sensitive than the short-run supply of oranges. shortage Jat the longraye demand for oranges is the same as the short-run demand, you would expect a binding price ceiling to result in a that issmaller in the long run than in the short run