please help me
And this all the information i got from my teacher, please help me 
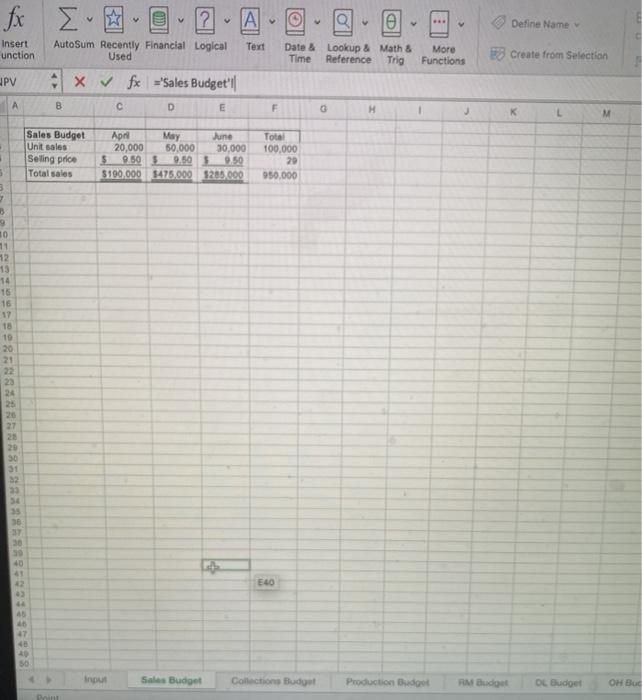
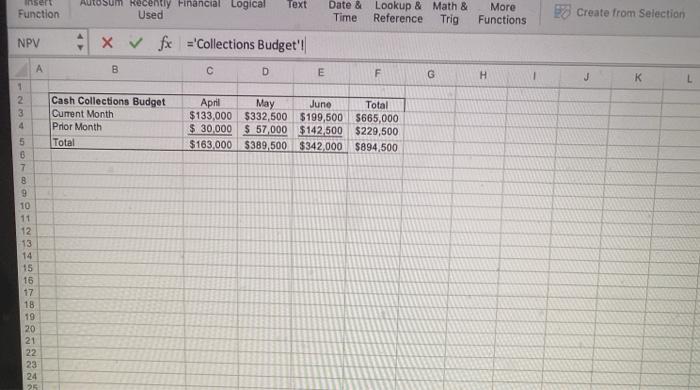
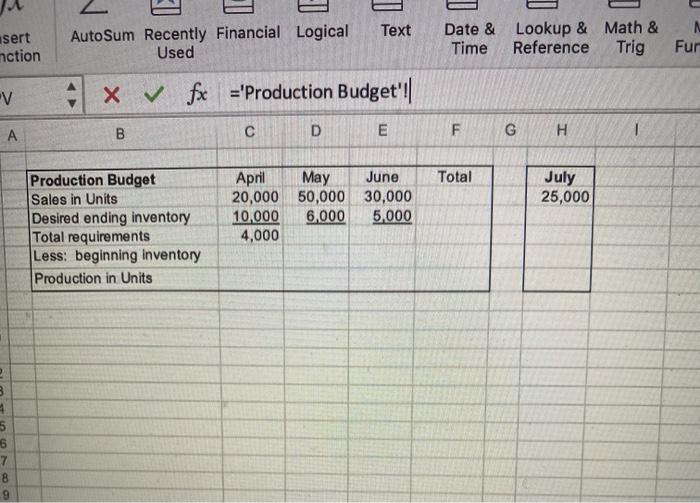
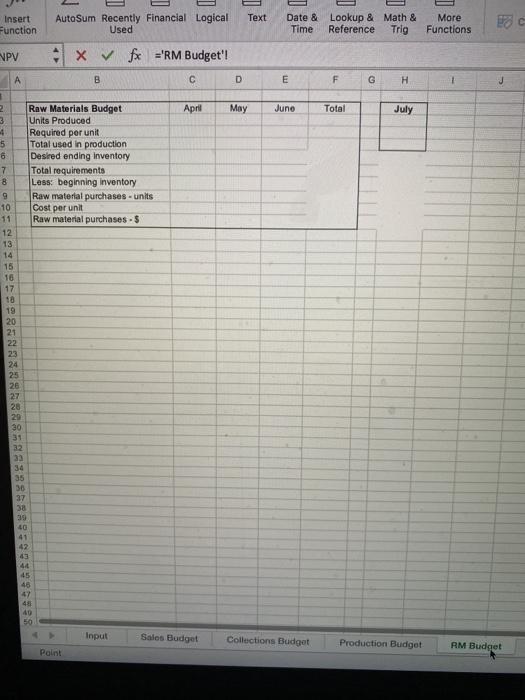
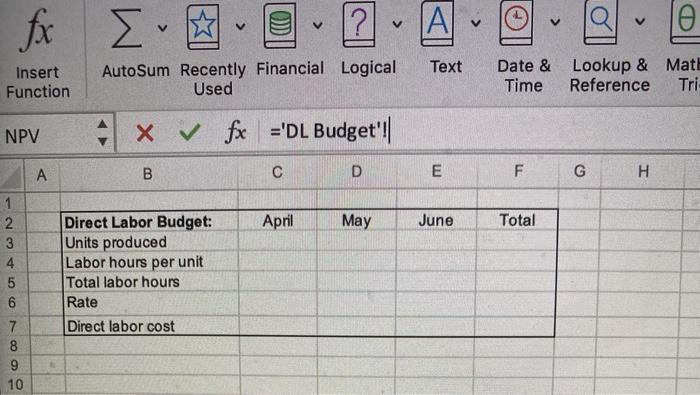
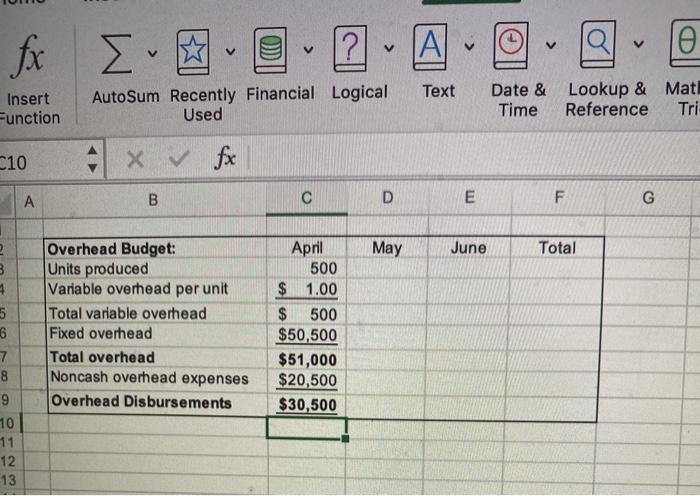

Budgeting Project - Basic Instructions The project should be completed in Excel. When you have finished the project, you need to upload your spreadsheet in the Blackboard assignment link as well as complete the test portion in Blackboard. Make sure your name is on the input's worksheet in the yellow box. Introduction The purpose of this assignment is to let you see the complexity of budgeting and to develop your spreadsheet skills. There is a lot to do here, so get started right away. The Case Patriot Flag Company is a small manufacturing company. They manufacture only American flags. Their product is sold to retail outlets. Stores like Wal-Mart which operate in a close to JIT environment, make frequent orders and expect fast deliveries. The information below pertains to the company's budgeting process. Budited sales in flags (units) are as follows: April May July August 20,000 50,000 30,000 25,000 15,000 June . Each unit sells for $9.50. All sales are on account. The company's collection pattern is: 70% collected the month of sale: 30% collected in the month following. The company desires to have inventory on hand at the end of each month equal to 20 percent of the following month's budgeted sales in units. On March 31, 4,000 units were on hand. Two yards of material are required per flag produced. The company desires to have materials on hand at the end of each month equal to 10 percent of the following month's production needs. The requirement was met on March 31. The material used in production costs $1.00 per yard. One half of the month's purchases is paid for in the month of purchases, the other half is paid for in the following month. No discount terms are available. The accounts payable as of March 31 were $12,000. Each flag requires 3 minutes of labor time to make (.05 hours) and the hourly help is paid $10/hour Variable manufacturing overhead is $1 per unit produced Fixed manufacturing overhead is $50,500 per month including $20,500 in depreciation that is not a current cash outflow. All cash disbursements for manufacturing overhead are paid in the month incurred. Variable selling and administrative expenses are $ 50 per unit sold. Fixed selling and administrative expense is $70,000 per month including $10,000 in depreciation that is not a cash outflow of the current month. All cash disbursements for selling and administrative costs are paid in the month incurred. Cash dividends in the amount of $1,000 are to be paid to shareholders in April. These dividends were declared in March Equipment purchases and payments of $143,700 are scheduled for May and $48,800 for lune. . . . Additionally, Patriot has the following balance sheet as of March 31, 20XX. Assets Liabilities and Equities Cash $40,000 Accounts payable Accounts Receivable 30,000 Notes Payable Raw materials inventory 5,200 Interest payable Finished goods inventory 14,000 Dividend payable Property, plant and equipment, 321000 Common Stock net Total assets $409.200 Retained earnings Total Liabilities and equities $12,000 $0 0 51,000 150,000 196.200 $409.200 The company must maintain a minimum cash balance of $30,000 each month. The cash balance at the beginning of April was $40,000. An open line of credit is available at a local bank, which allows the company to borrow up to $70,000 per quarter. (When preparing a budget the minimum cash balance must ALWAYS be met even if it forecasts cash needs beyond the credit line available. If the available line of credit is insufficient, then alternative arrangements for financing must be made.) All borrowing is done at the beginning of a month, and all repayments are made at the end of a month. Interest is paid monthly on the first of the next month, thus each months interest paid is based on the outstanding borrowings the prior month. The interest rate is 10 percent per year. If there are excess funds above the minimum $30,000 cash at the end of the month, these are used to repay the outstanding loans. When computing interest and repayment watch the number of months the money was borrowed. The Company uses variable costing in its budgeted Income statement and its balance sheet. Requirements 1. Prepare a master budget for the quarter ended June 30 that includes: Sales budget, schedule of expected cash collections, production budget, material purchases budget/schedule of expected cash payments for material, direct labor budget, manufacturing overhead budget, selling and administrative expense budget, cash budget, income statement and balance sheet. (A total of 10 schedules). Each schedule should be on a separate worksheet as appears in your template. There is a template in the assignments link and in the Excel Project folder with an input page you must use All of your spreadsheets must be formula driven from the input tabl This means that EVERY cell should contain either a value referenced from the input worksheet or a formula manually entered the cell using the referenced values or the input values. The tricklest part of the assignment is computing the borrowings. You are expected to create logical formula here. Remember, the borrowings are at the beginning of the month and repayments at the end. If you borrow in January and repay in February, there will be 2 months of interest to be paid (beginning of January to end of February). Interest is paid the first of the next month. Auto Budgeting Project Template Home Insert Draw Page Layout Formulas Data Review View Tell me Share fx A 2 - A - Autour de la cal Te net Date at More Time see the functions Show xx wat o D 4 0 # 1 5 . Botas Belo Sales AH 70.000 150 10.000 30.000 2.600 000 Asset Gan Ace Assen BA 330.000 100 18.00 01 10 115 NOU www INT Me II th A. ON 09 int Pride 14 204 400w Ay 17 1 Rais wa 11 er 2 TON 30 det teger Paths AM Direct w 33 31200 De 0.00 1000 Mertering 1 100 550.000 120.00 Red IN C * M. 140.00 30.000 TON mo Or Owen 3. 51.000 OLD OH Bus Profaget RM Budget Mudget Cash But Budget fx Qe Define Name Insert unction ? TA Auto Sum Recently Financial Logical Text Used + x V fx ='Sales Budget'll c D E Date & Lookup & Math & Time Reference Trig More Functions 3 Create from Selection uPV A B F u M May Sales Budget Unit sales Selling price Total sales April June 20,000 50.000 30,000 $950 $9.50 S 0.50 $190,000 $475,000 $285.000 Tota 100.000 20 950.000 . 5 3 3 9 10 11 12 13 14 16 16 18 19 20 22 24 25 20 27 20 30 31 35 36 30 + 42 E40 45 SO Input Sales Budget Collections Budget Production Budget RM Budget OL Budget OH Bug Autosum Hecently Financial Logical Used Text Function Date & Time Lookup & Math & Reference Trig More Functions o create from Selection NPV fe='Collections Budget' B D E F G H J K L 1 2 3 4 Cash Collections Budget Current Month Prior Month Total April May June Total $133,000 $332,500 $199,500 5665,000 $ 30,000 $ 57,000 $142,500 $229,500 $163,000 $389,500 $342,000 $894,500 5 0 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 95 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 LE 2 Text sert nction AutoSum Recently Financial Logical Used Date & Time Lookup & Math & Reference Trig N Fur -v 4 x fx ='Production Budget'||| B D E F G H Total Production Budget Sales in Units Desired ending inventory Total requirements Less: beginning inventory Production in Units April May June 20,000 50,000 30,000 10,000 6,000 5,000 4,000 July 25,000 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Text Insert Function AutoSum Recently Financial Logical Used Date & Lookup & Math & Time Reference Trig More Functions VPV fx ='RM Budget'! B D E F G H April May June Total July 2 Raw Materials Budget 3 Units Produced 1 Required per unit 5 Total used in production 6 Desired ending inventory 7 Total requirements 8 Less: beginning inventory 9 Raw material purchases - units 10 Cost per unit 11 Raw material purchases. $ 12 13 14 15 16 17 10 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 45 47 45 50 Input Sales Budget Collections Budget Production Budget RM Budget Point V ? fx v v v Text Insert Function AutoSum Recently Financial Logical Used Date & Time Lookup & Mate Reference Tri- NPV x fx ='DL Budget'! B D E F G H April May June Total 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Direct Labor Budget: Units produced Labor hours per unit Total labor hours Rate Direct labor cost ? V fx V AI Text Insert Function AutoSum Recently Financial Logical Used Date & Lookup & Mati Time Reference Tri -10 A B D E F G May June Total 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Overhead Budget: Units produced Variable overhead per unit Total variable overhead Fixed overhead Total overhead Noncash overhead expenses Overhead Disbursements April 500 $ 1.00 $ 500 $50,500 $51,000 $20,500 $30,500 IX vf B D E F April May June Total Selling/Admininstrative Budget Units sold Variable S&A per unit Total Variable S&A Fixed S&A Total S&A Noncash S&A expenses S&A disbursements x fx A B D E F May June April $40,000 Quarter $30,500 Cash Budget: Beginning balance Collections Available balance Disbursements: Direct material prior Direct material current Direct labor Overhead S&A Dividends Equipment purchases Interest Total disbursements Balance before financing Minimum balance Excess (deficiency) Borrowing Accumulated borrowings at beginning of month Repayments Ending balance $30,000 $0 $0 $0 Accumulated Borrowings at end of month: 5 3 B D E Income Statement: Sales Variable Expenses: Manufacturing S&A Contribution margin Fixed Expenses: Manufacturing S&A Operating Income Interest Expense Net Income A B C D E F G H 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Budgeted Balance Sheet Cash Accounts receivable Finished Goods Inventory Raw Material Inventory Equipment Total Assets Accounts payable Notes payable Interest payable Common Stock Retained eamings Total Liabilities & Equity 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Check figures: Total Collections in April: $163,000 Raw Materials Purchases in June: $56,800 S&A Disbursements in May, $110,000 Accumulated Borrowings attche end of June: $46,917 Net Income: $136,224 Total Assets: $558,600




















