




please help me answer the following in a step by step process .the data is already given below
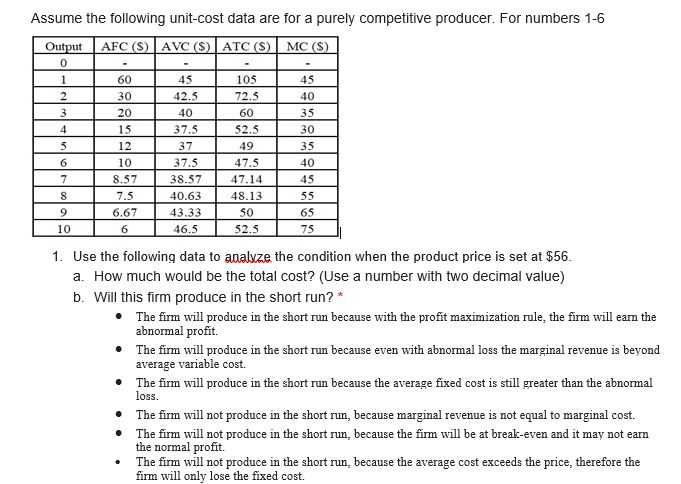
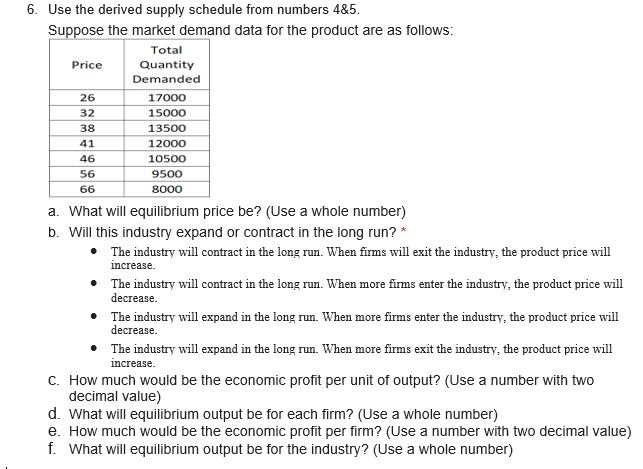
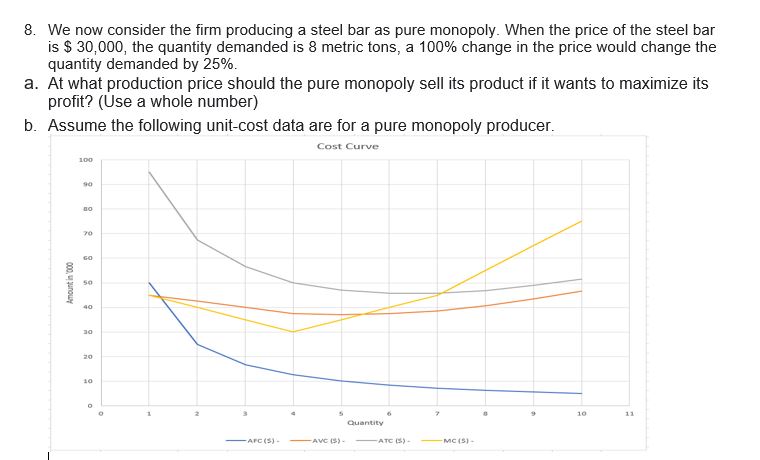
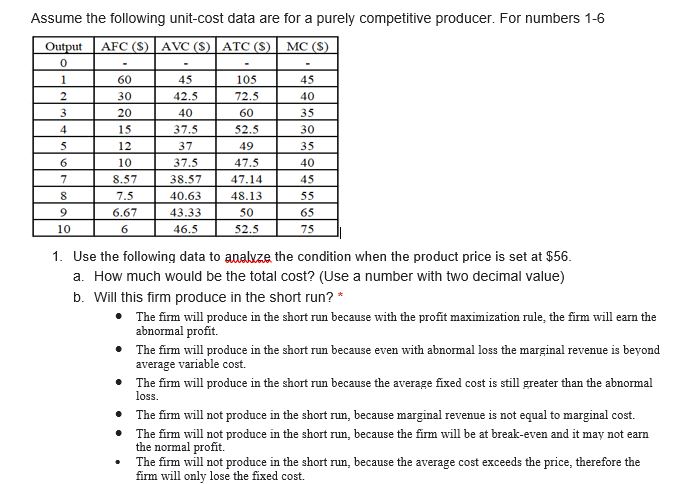
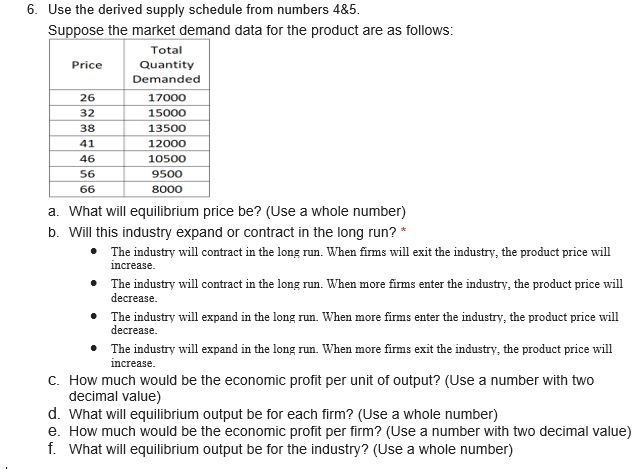
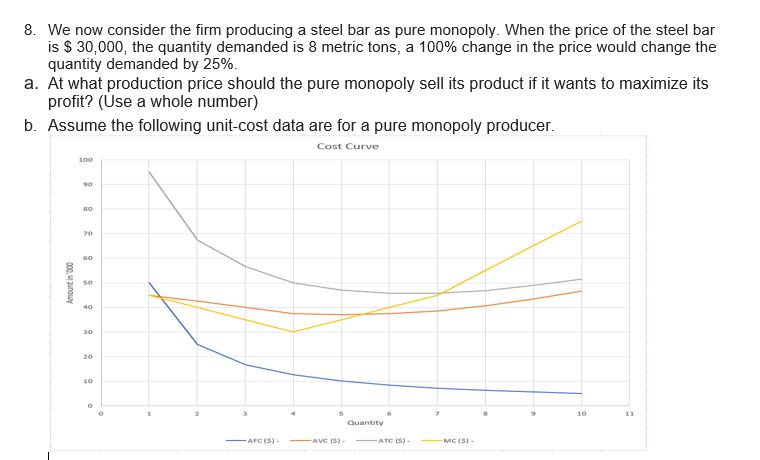
Assume the following unit-cost data are for a purely competitive producer. For numbers 1-6 Output AFC (S) AVC ($) ATC ($) MC ($) 0 60 45 105 45 30 42.5 72.5 40 20 40 60 35 15 37.5 52.5 30 12 37 49 35 10 37.5 47.5 40 8.57 38.57 47.14 45 8 7.5 40.63 48.13 55 6.67 43.33 50 65 10 6 46.5 52.5 75 1. Use the following data to analyze the condition when the product price is set at $56. a. How much would be the total cost? (Use a number with two decimal value) b. Will this firm produce in the short run?* . The firm will produce in the short run because with the profit maximization rule, the firm will earn the abnormal profit. The firm will produce in the short run because even with abnormal loss the marginal revenue is beyond average variable cost. The firm will produce in the short run because the average fixed cost is still greater than the abnormal loss. The firm will not produce in the short run, because marginal revenue is not equal to marginal cost. The firm will not produce in the short run, because the firm will be at break-even and it may not earn the normal profit. The firm will not produce in the short run, because the average cost exceeds the price, therefore the firm will only lose the fixed cost.C. How much would be the total revenue? (Use a number with two decimal value) * d. What will be the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing output? (Use a whole number) * 2. Use the following data to analyze the condition when the product price is set at $41. a. Will this firm produce in the short run? * The firm will produce in the short run because with the profit maximization rule, the firm will earn the abnormal profit. The firm will produce in the short run because even with abnormal loss the marginal revenue is beyond average variable cost. . The firm will produce in the short run because the average fixed cost is still greater than the abnormal loss. The firm will not produce in the short run, because marginal revenue is not equal to marginal cost. The firm will not produce in the short run, because the firm will be at break-even and it may not earn the normal profit. . The firm will not produce in the short run, because the average cost exceeds the price, therefore the firm will only lose the fixed cost. b. How much would be the product price, for the firm to be at a shut down position? (Use a number with two decimal value) * c. What will be the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing output? (Use a whole number) *d. How much would be the economic profit that the firm will realize per unit of output? (Use a number with two decimal value space) * 3. Use the following data to analyze the condition when the product price is set at $32. a. What will be the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing output? (Use a whole number) * b. How much would be the product price, for the firm to be at a break-even position? (Use a number with two decimal value) * C. Will this firm produce in the short run? * The firm will produce in the short run because with the profit maximization rule, the firm will earn the abnormal profit. . The firm will produce in the short run because even with abnormal loss the marginal revenue is beyond average variable cost. . The firm will produce in the short run because the average fixed cost is still greater than the abnormal loss. . The firm will not produce in the short run, because marginal revenue is not equal to marginal cost. . The firm will not produce in the short run, because the firm will be at break-even and it may not earn the normal profit. . The firm will not produce in the short run, because the average cost exceeds the price, therefore the firm will only lose the fixed cost. d. How much would be the economic profit that the firm will realize per unit of output? (Use a number with two decimal value) *4. Construct a shortrun supply schedule iorthe rm and indicate the prot or loss incurred at each output. b. C. When the product price is set at $45, how much would be the economic prot that the rm will realize per unit of output? {Use a number with two decimal yalue} When the product price is set at $55, how many is the quantity supplied by the rm? {Use a whole number} When the product price is set at $45, how many is the quantity supplied by the rm? {Use a whole number} When the product price is set at $55, how much would be the economic prot that the rm will realize per unit of output? {Use a number with two decimal yalue} When the product price is set at $35, how many is the quantity supplied by the rm? {Use a whole number} When the product price is set at $55, how much would be the economic prot that the rm will realize per unit of output? [Use a number with two decimal value} 5. Now assume there are 150D identical rms in this competitive industry; that is, there are 1500 rms, each of which has the same cost data as shown in the rst table. Calculate the industry supply schedule. a. When the product price is set at $45, how many is the quantity supplied by the 15-55 rms? {Use a whole number} h. When the product price is set at see, how many is the quantity supplied by the 15cc rms? {Use a whole number} c. . When the product price is set at $55, how many is the quantity supplied by the 155i] rms? {Use a whole number} 6. Use the derived supply schedule from numbers 4&5. Suppose the market demand data for the product are as follows: Total Price Quantity Demanded 26 17000 32 15000 38 13500 41 12000 46 10500 56 9500 66 8000 a. What will equilibrium price be? (Use a whole number) b. Will this industry expand or contract in the long run? * . The industry will contract in the long run. When firms will exit the industry, the product price will increase. The industry will contract in the long run. When more firms enter the industry, the product price will decrease. . The industry will expand in the long run. When more firms enter the industry, the product price will decrease. The industry will expand in the long run. When more firms exit the industry, the product price will increase. C. How much would be the economic profit per unit of output? (Use a number with two decimal value) d. What will equilibrium output be for each firm? (Use a whole number) e. How much would be the economic profit per firm? (Use a number with two decimal value) f. What will equilibrium output be for the industry? (Use a whole number)T. A rm produces a steel bar. When the price ofthe steel bar is i 3,l}, the r:|uantit;l.lr demanded is 3 metric tons, a \"lillil'h'l change in the price would change the guantitv demanded bv 25%. a. b. What is the total revenue function of the rm? [Use the variable Cl for the quantityr and the variable TR for the total revenue) At what price should the rm sell its product to maximize its total revenue? [Use a whole number} What is the demand function Elf the rm? [Use the variable Q for the quantity demanded and the variable P for the price; no currency; use traclion form for the slope] _ Atwhat production output should the rm produce to maximize its total revenue? [Use a whole number} How much would be the maximum total revenue of the rm? [Use a whole number} 1Illl'hat is the marginal revenue function of the rm? {Use the variable Cl for the qua ntl'rvI and the variable MR for the marginal revenue} _ What is the price function of demand of the rm? {Use the variable (It for the guantltlur demanded and the variable P for the price} _ We now consider the rm producing a steel bar as pure monopoly. When the price of the steel bar is $ 31, the quantityr demanded is 8 metric tons, a t'lt: change in the price would change the quantity demanded by 25%. . At what production price should the pure monopolyr sell its product if it wants to maximize its prot? [Use a whole number} _ Assume the following unitcost data are for a pure monopolyr producer. Cast Curve mo - III - Ia - w - . __ -"'J :41 . MI- mum 111' U I merm- Q4. How much would be the total revenue of the pure monopolyr if he wants to maximize its prot? [Use a whole number} DJL How much would be the maximum prot of the pure monopoly? {Use a whole number} Dill How much would be the total cost of the pure monopolyr if he wants to maximize its prot? (Use a whole number} m much would be the consumers' surplus when the pure monopoly wants to maximize its prot? [Use a whole number} 9,3,, At what production output should the pure monopoly produce it it wants to maximize its prot? [Use a whole number} _ We now assume the rm producing a steel bar is under monopolistic competition. When the price of the steel bar is $ 3D,t}, the quantity demanded is 3 metric tons, a 1GB% change in the price would change the quantity demanded by 25%. The rms xed cost is $45,5. its variable cost in thousands at each level of production are 45, B5, 12D, 15B, 185, 225, 2m, 325, 39D, and 455. a. At what production output should the rm produce in the long run? (Use a whole number} b. How much would be the economic prot of the rm? {Use a whole number} 1:. At what price should the rm sell its product in the long run? {Use a whole number} [1. How much would be the consumers' surplus when the rm produces in the long run? [Use a whole number