Question
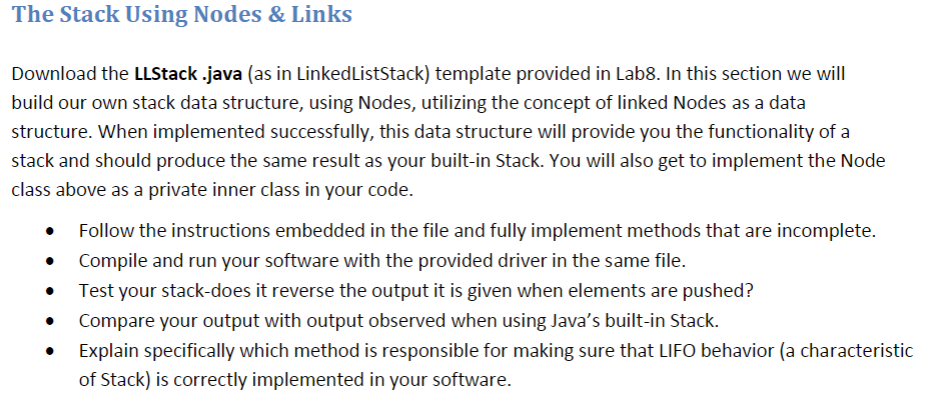
Please help me code the following in: JAVA Please use many COMMENTS Full points will be awarded, thanks in advance! LLStack class: /** * This
Please help me code the following in: JAVA
Please use many COMMENTS
Full points will be awarded, thanks in advance!


 LLStack class:
LLStack class:
/**
* This class will use Nodes to form a linked list. It implements the LIFO
* (Last In First Out) methodology to reverse the input string.
*
**/
public class LLStack {
private Node head;
// Constructor with no parameters for outer class
public LLStack( ) {
// to do
}
// This is an inner class specifically utilized for LLStack class,
// thus no setter or getters are needed
private class Node {
private Object data;
private Node next;
// Constructor with no parameters for inner class
public Node(){
// to do
// to do
}
// Parametrized constructor for inner class
public Node (Object newData, Node nextLink) {
// to do: Data part of Node is an Object
// to do: Link to next node is a type Node
}
}
// Adds a node as the first node element at the start of the list with the specified data.
public void addToStart(Object itemData) {
// to do
// NOTE: the logic here could be implemented in a single line,
// but not required to be a one liner.
}
// Removes the head node and returns true if the list contains at
// least one node. Returns false if the list is empty.
public boolean deleteHead( ) {
// to do
}
// Returns the size of linked list by traversing the list
public int size( ) {
// to do
}
return count;
}
// Finds if there is match for the given object
public boolean contains(Object item) {
// to do
}
// Finds the first node containing the target item, and returns a
// reference to that node. Return null if target not found.
private Node findData(Object target) {
Node current = head;
Object itemAtPosition;
while (current != null) {
itemAtPosition = current.data;
if (itemAtPosition.equals(target))
return current;
current = current.next;
}
return null; // Target not found!
}
public void outputList( ) {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.println(current.data);
current = current.next;
}
}
public String toString() {
String retValue = "";
Node current = head;
while(current != null) {
retValue += current.data.toString() + " ";
current = current.next;
}
return retValue;
}
public boolean isEmpty( ) {
// to do
}
public void clear( ) {
// to do
}
// For two lists to be equal they must contain the same data items in
// the same order. The equals method of T is used to compare data items.
public boolean equals(Object otherObject) {
if (otherObject == null)
return false;
else if(!(otherObject instanceof LLStack))
return false;
else {
LLStack otherList = (LLStack)otherObject;
if (size( )!= otherList.size( ))
return false;
Node position = head;
Node otherPosition = otherList.head;
while (position != null) {
if (!(position.data.equals(otherPosition.data)))
return false;
position = position.next;
otherPosition = otherPosition.next;
}
return true; // objects are the same
}
}
// There is no need to modify the driver
public static void main(String[] args) {
// input data for testing
String target = "Somethings!";
String palindrome = "a man a plan canal panama";
LLStack list = new LLStack( );
// objects to be added to list
Object object1 = (Character) target.charAt(4);
Object object2 = (Character) target.charAt(1);
Object object3 = (Character) target.charAt(2);
Object object4 = (Character) target.charAt(9);
Object object20 = (Character) target.charAt(6); // will not be added to list
// add 4 objects to our linked list
list.addToStart(object1);
list.addToStart(object2);
list.addToStart(object3);
list.addToStart(object4);
// make sure all are added
System.out.println("My list has " + list.size( ) + " nodes.");
// display the newly created list
list.outputList( );
System.out.println("toString = " + list.toString());
// test findData() here
Node itemFound = list.findData(object1);
System.out.println("Item found: " + itemFound.data);
// Test contains() here
if (list.contains(object1))
System.out.println("Object1 found.");
else
System.out.println("There is NO object1.");
if (list.contains(object20))
System.out.println("Object20 found.");
else
System.out.println("There is NO object20.");
// Creating a new linked list by iteration using different input
LLStack linkedList = new LLStack();
for(int i = 0; i
Object object = (Character) palindrome.charAt(i);
linkedList.addToStart(object);
}
// Display your list now
linkedList.outputList();
// More tests; size() and is Empty()
System.out.println("This time my list has " + linkedList.size( ) + " nodes.");
System.out.println("Is our linkedList empty? " + linkedList.isEmpty());
// Creating an Object of different class to compare with Character class
Object mismatchObject = (Integer) Character.getNumericValue(target.charAt(0));
boolean areEqual = linkedList.equals(mismatchObject);
System.out.println("Are the 2 objects equal? " + areEqual);
boolean areEqualAgain = linkedList.equals(linkedList);
System.out.println("Are the 2 objects equal? " + areEqualAgain);
// test deleteHead()
list.deleteHead( );
if (list.contains(object4))
System.out.println("Object4 found.");
else
System.out.println("Object4 has been deleted!");
while (list.deleteHead( )); //Empty loop body
System.out.println("Start of list:");
list.outputList( );
System.out.println("End of list.");
System.out.println("In the begining linkedList has " + linkedList.size() + " nodes");
linkedList.clear();
System.out.println("After testing clear(), linkedList has " + linkedList.size() + " nodes");
}
}
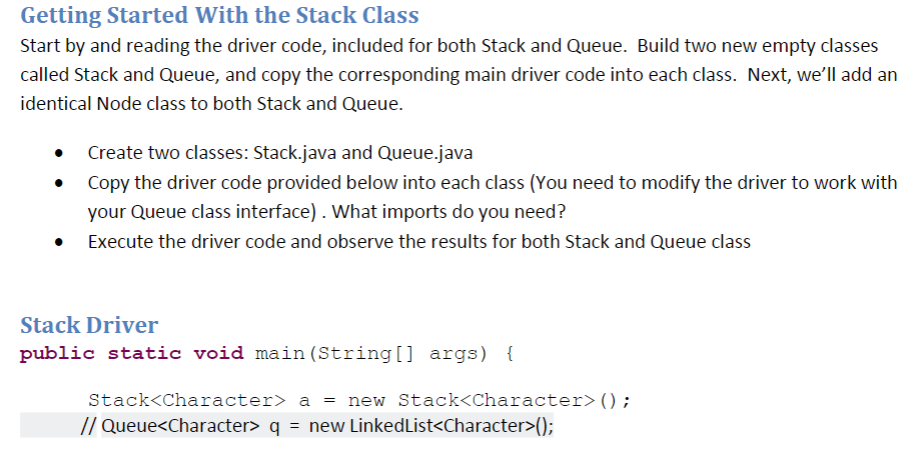
Getting Started With the Stack Class Start by and reading the driver code, included for both Stack and Queue. Build two new empty classes called Stack and Queue, and copy the corresponding main driver code into each class. Next, we'll add an identical Node class to both Stack and Queue. Create two classes: Stack.java and Queue.java Copy the driver code provided below into each class (You need to modify the driver to work with your Queue class interface). What imports do you need? Execute the driver code and observe the results for both Stack and Queue class . Stack Driver public static void main (String[] args) Stack?Character? // QueueStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


