Please help me prepare Consolidated Statements Including Income Statement, Retained Earnings and Balance Sheet. For your information The outstanding of Crandel Company is $450,000 not 425,000.
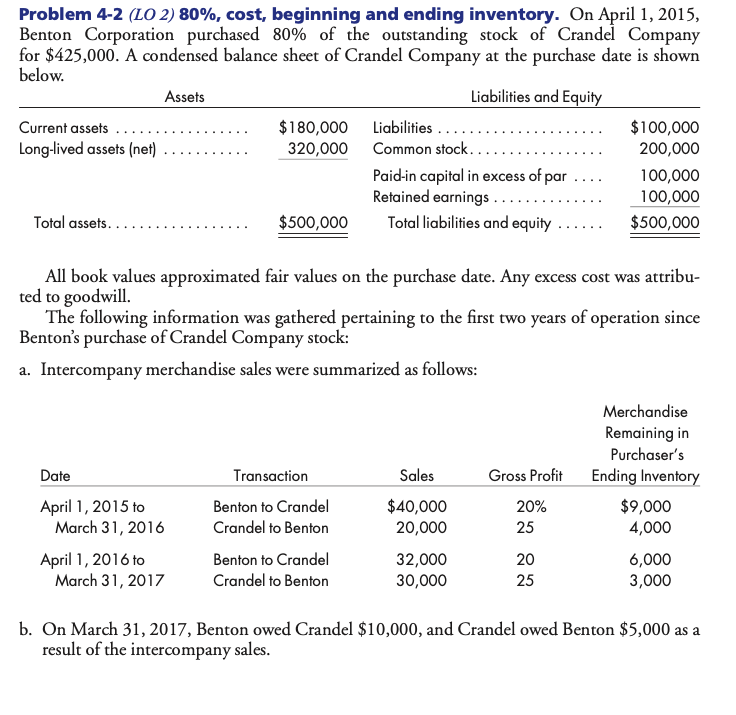
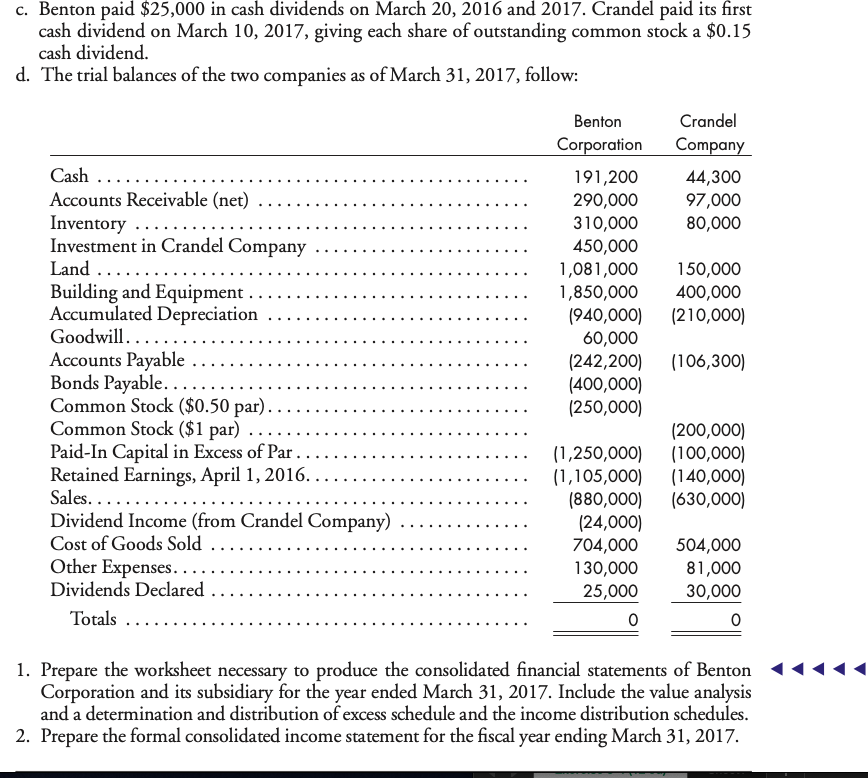
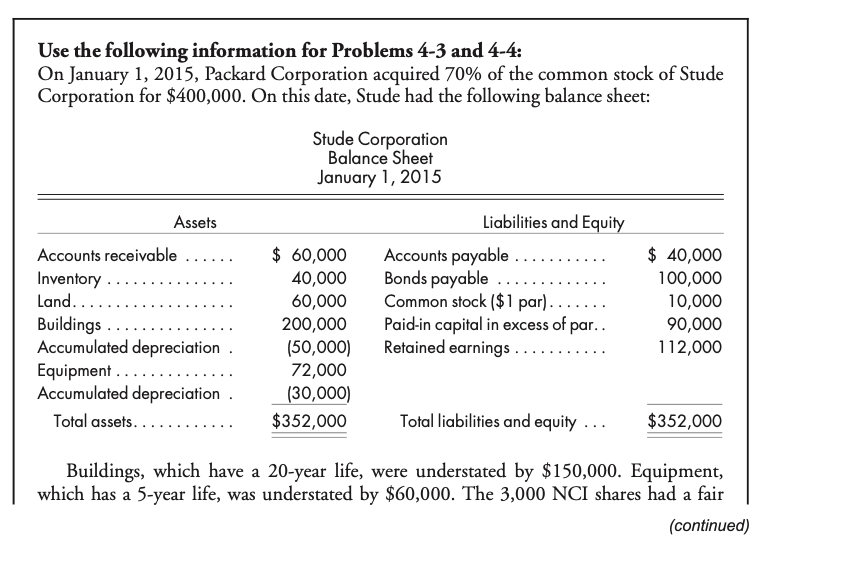
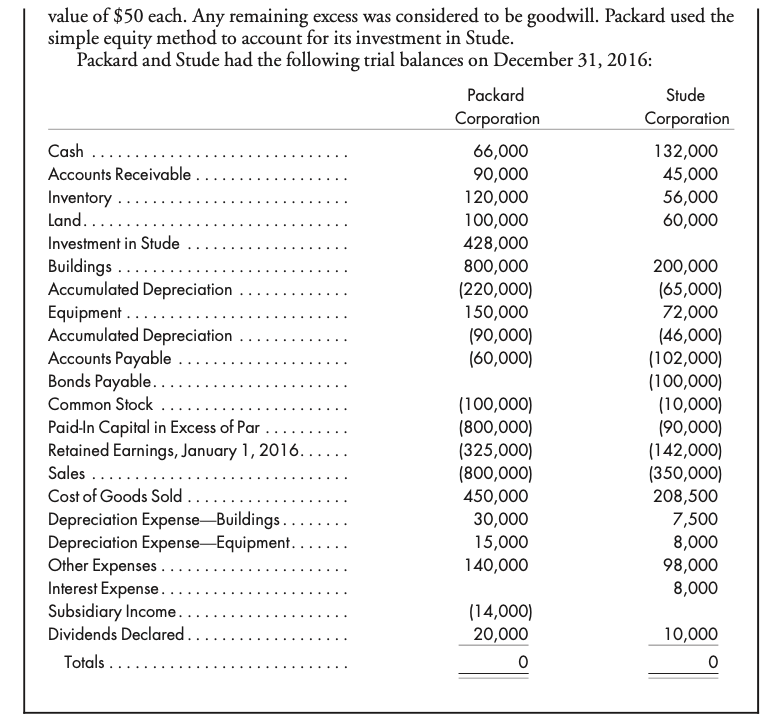
Problem 4-2 (LO 2) 80%, cost, beginning and ending inventory. On April 1, 2015, Benton Corporation purchased 80% of the outstanding stock of Crandel Company for $425,000. A condensed balance sheet of Crandel Company at the purchase date is shown below. Assets Liabilities and Equity Current assets ......... $180,000 Liabilities ... $100,000 Long-lived assets (net) ........... 320,000 Common stock. ... 200,000 Paid-in capital in excess of par .... 100,000 Retained earnings .. 100,000 Total assets......... $500,000 Total liabilities and equity ...... $500,000 All book values approximated fair values on the purchase date. Any excess cost was attribu- ted to goodwill. The following information was gathered pertaining to the first two years of operation since Benton's purchase of Crandel Company stock: a. Intercompany merchandise sales were summarized as follows: Date Transaction Sales Gross Profit April 1, 2015 Merchandise Remaining in Purchaser's Ending Inventory $9,000 4,000 6,000 3,000 20% Benton to Crandel Crandel to Benton 25 April 1, 2015 to March 31, 2016 April 1, 2016 to March 31, 2017 $40,000 20,000 32,000 30,000 20 Benton to Crandel Crandel to Benton 25 b. On March 31, 2017, Benton owed Crandel $10,000, and Crandel owed Benton $5,000 as a result of the intercompany sales. c. Benton paid $25,000 in cash dividends on March 20, 2016 and 2017. Crandel paid its first cash dividend on March 10, 2017, giving each share of outstanding common stock a $0.15 cash dividend. d. The trial balances of the two companies as of March 31, 2017, follow: Crandel Company 44,300 97,000 80,000 L asl . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Benton Corporation 191,200 290,000 310,000 450,000 1,081,000 1,850,000 1940,000) 60,000 (242,200) (400,000) (250,000) 150,000 400,000 (210,000) Cash ...... Accounts Receivable (net) ........ Inventory ....... Investment in Crandel Company Land .... Building and Equipment ....... Accumulated Depreciation .. Goodwill. .................. Accounts Payable ........ Bonds Payable...... Common Stock ($0.50 par)..... Common Stock ($1 par). Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par....... Retained Earnings, April 1, 2016.. Sales......... Dividend Income (from Crandel Company) Cost of Goods Sold . Other Expenses..... Dividends Declared ........ Totals ...................................... (106,300) (200,000) (100,000) (140,000) (630,000) (1,250,000) (1,105,000) (880,000) (24,000) 704,000 130,000 25,000 504,000 81,000 30,000 1. Prepare the worksheet necessary to produce the consolidated financial statements of Benton Corporation and its subsidiary for the year ended March 31, 2017. Include the value analysis and a determination and distribution of excess schedule and the income distribution schedules. 2. Prepare the formal consolidated income statement for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2017. Use the following information for Problems 4-3 and 4-4: On January 1, 2015, Packard Corporation acquired 70% of the common stock of Stude Corporation for $400,000. On this date, Stude had the following balance sheet: Stude Corporation Balance Sheet January 1, 2015 Assets Accounts receivable ...... Inventory .......... Land................... Buildings ....... Accumulated depreciation. Equipment. Accumulated depreciation. Total assets............ $ 60,000 40,000 60,000 200,000 (50,000) 72,000 (30,000) $352,000 Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable ........... Bonds payable ............. Common stock ($1 par)....... Paid-in capital in excess of par.. Retained earnings ........... $ 40,000 100,000 10,000 90,000 112,000 Total liabilities and equity ... $352,000 Buildings, which have a 20-year life, were understated by $150,000. Equipment, which has a 5-year life, was understated by $60,000. The 3,000 NCI shares had a fair (continued) value of $50 each. Any remaining excess was considered to be goodwill. Packard used the simple equity method to account for its investment in Stude. Packard and Stude had the following trial balances on December 31, 2016: Packard Stude Corporation Corporation Cash ....... 66,000 132,000 Accounts Receivable 90,000 45,000 Inventory .. 120,000 56,000 Land. 100,000 60,000 Investment in Stude ...... 428,000 Buildings 800,000 200,000 Accumulated Depreciation ... (220,000) 165,000) Equipment.... 150,000 72,000 Accumulated Depreciation ..... 190,000) (46,000) Accounts Payable ..... 160,000) (102,000) Bonds Payable............... (100,000) Common Stock . (100,000) (10,000) Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par (800,000) 190,000) Retained Earnings, January 1, 2016... (325,000) (142,000) Sales ..... (800,000) (350,000) Cost of Goods Sold ................... 450,000 208,500 Depreciation ExpenseBuildings.. 30,000 7,500 Depreciation Expense-Equipment. 15,000 8,000 Other Expenses .... 140,000 98,000 Interest Expense.. 8,000 Subsidiary Income.. (14,000) Dividends Declared. 20,000 10,000 Totals. Problem 4-2 (LO 2) 80%, cost, beginning and ending inventory. On April 1, 2015, Benton Corporation purchased 80% of the outstanding stock of Crandel Company for $425,000. A condensed balance sheet of Crandel Company at the purchase date is shown below. Assets Liabilities and Equity Current assets ......... $180,000 Liabilities ... $100,000 Long-lived assets (net) ........... 320,000 Common stock. ... 200,000 Paid-in capital in excess of par .... 100,000 Retained earnings .. 100,000 Total assets......... $500,000 Total liabilities and equity ...... $500,000 All book values approximated fair values on the purchase date. Any excess cost was attribu- ted to goodwill. The following information was gathered pertaining to the first two years of operation since Benton's purchase of Crandel Company stock: a. Intercompany merchandise sales were summarized as follows: Date Transaction Sales Gross Profit April 1, 2015 Merchandise Remaining in Purchaser's Ending Inventory $9,000 4,000 6,000 3,000 20% Benton to Crandel Crandel to Benton 25 April 1, 2015 to March 31, 2016 April 1, 2016 to March 31, 2017 $40,000 20,000 32,000 30,000 20 Benton to Crandel Crandel to Benton 25 b. On March 31, 2017, Benton owed Crandel $10,000, and Crandel owed Benton $5,000 as a result of the intercompany sales. c. Benton paid $25,000 in cash dividends on March 20, 2016 and 2017. Crandel paid its first cash dividend on March 10, 2017, giving each share of outstanding common stock a $0.15 cash dividend. d. The trial balances of the two companies as of March 31, 2017, follow: Crandel Company 44,300 97,000 80,000 L asl . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Benton Corporation 191,200 290,000 310,000 450,000 1,081,000 1,850,000 1940,000) 60,000 (242,200) (400,000) (250,000) 150,000 400,000 (210,000) Cash ...... Accounts Receivable (net) ........ Inventory ....... Investment in Crandel Company Land .... Building and Equipment ....... Accumulated Depreciation .. Goodwill. .................. Accounts Payable ........ Bonds Payable...... Common Stock ($0.50 par)..... Common Stock ($1 par). Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par....... Retained Earnings, April 1, 2016.. Sales......... Dividend Income (from Crandel Company) Cost of Goods Sold . Other Expenses..... Dividends Declared ........ Totals ...................................... (106,300) (200,000) (100,000) (140,000) (630,000) (1,250,000) (1,105,000) (880,000) (24,000) 704,000 130,000 25,000 504,000 81,000 30,000 1. Prepare the worksheet necessary to produce the consolidated financial statements of Benton Corporation and its subsidiary for the year ended March 31, 2017. Include the value analysis and a determination and distribution of excess schedule and the income distribution schedules. 2. Prepare the formal consolidated income statement for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2017. Use the following information for Problems 4-3 and 4-4: On January 1, 2015, Packard Corporation acquired 70% of the common stock of Stude Corporation for $400,000. On this date, Stude had the following balance sheet: Stude Corporation Balance Sheet January 1, 2015 Assets Accounts receivable ...... Inventory .......... Land................... Buildings ....... Accumulated depreciation. Equipment. Accumulated depreciation. Total assets............ $ 60,000 40,000 60,000 200,000 (50,000) 72,000 (30,000) $352,000 Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable ........... Bonds payable ............. Common stock ($1 par)....... Paid-in capital in excess of par.. Retained earnings ........... $ 40,000 100,000 10,000 90,000 112,000 Total liabilities and equity ... $352,000 Buildings, which have a 20-year life, were understated by $150,000. Equipment, which has a 5-year life, was understated by $60,000. The 3,000 NCI shares had a fair (continued) value of $50 each. Any remaining excess was considered to be goodwill. Packard used the simple equity method to account for its investment in Stude. Packard and Stude had the following trial balances on December 31, 2016: Packard Stude Corporation Corporation Cash ....... 66,000 132,000 Accounts Receivable 90,000 45,000 Inventory .. 120,000 56,000 Land. 100,000 60,000 Investment in Stude ...... 428,000 Buildings 800,000 200,000 Accumulated Depreciation ... (220,000) 165,000) Equipment.... 150,000 72,000 Accumulated Depreciation ..... 190,000) (46,000) Accounts Payable ..... 160,000) (102,000) Bonds Payable............... (100,000) Common Stock . (100,000) (10,000) Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par (800,000) 190,000) Retained Earnings, January 1, 2016... (325,000) (142,000) Sales ..... (800,000) (350,000) Cost of Goods Sold ................... 450,000 208,500 Depreciation ExpenseBuildings.. 30,000 7,500 Depreciation Expense-Equipment. 15,000 8,000 Other Expenses .... 140,000 98,000 Interest Expense.. 8,000 Subsidiary Income.. (14,000) Dividends Declared. 20,000 10,000 Totals










