please help me

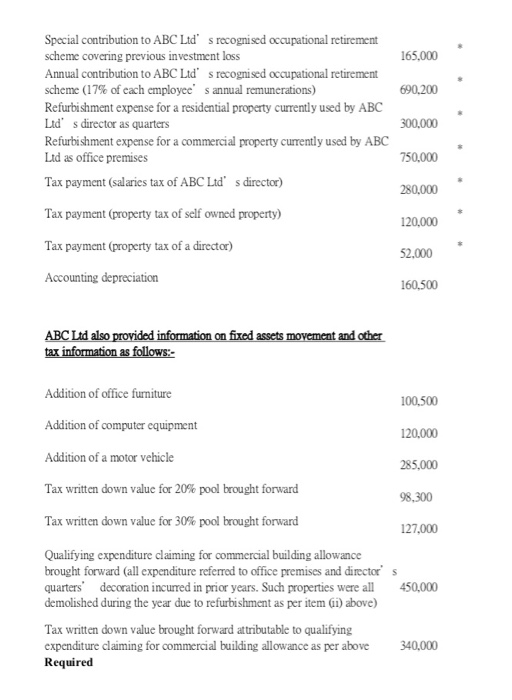
Question 1 (50 marks) ABC Ltd is a computing consulting company with its accounting year ended 31 December. The profit before tax for year ended 31 December 2018 was $5,450,000 after including the following items in its financial statements: Income:- Compensation for early termination of a business contract by a customer 135,000 Share of profits from an associated company 380,000 Exchange gain from daily business related payable balance 18,500 Interest income from loans advanced to employees in HK 7,500 2,400 Interest income from unpledged deposit placed with a local bank Interest income from long outstanding business related receivable balance due from overseas customers 8,600 General bad debt provision written back 18,400 Deposit forfeited by customers due to cancellation of service engagement 120,000 Expenditure:- Interest expense on overdue account payable to an unrelated overseas hardware supplier regarding the purchase of a computer system in prior 3600 year Interest expense on a bank loan from HSBC guaranteed by ABC Ltd's director personally (the loan was exclusively used for ABC Ltd's daily business activities) Interest expense on an unsecured bank loan from Standard Chartered Bank (the loan was exclusively used for the acquisition of certain listed shares for 8000 long term investment purposes) 165.000 690.200 Special contribution to ABC Ltd s recognised occupational retirement scheme covering previous investment loss Annual contribution to ABC Ltd's recognised occupational retirement scheme (17% of each employees annual remunerations) Refurbishment expense for a residential property currently used by ABC Lid s director as quarters Refurbishment expense for a commercial property currently used by ABC Lid as office premises Tax payment (salaries tax of ABC Lid' s director) 300,000 750,000 280,000 Tax payment (property tax of self owned property) 120,000 Tax payment (property tax of a director) 52.000 Accounting depreciation 160,500 ABC Lad also provided information on fixed assets movement and other tax information as follows:- Addition of office furniture 100,500 Addition of computer equipment 120,000 Addition of a motor vehicle 285,000 Tax written down value for 20% pool brought forward 98,300 Tax written down value for 30% pool brought forward 127,000 Qualifying expenditure claiming for commercial building allowance brought forward (all expenditure referred to office premises and directors quarters decoration incurred in prior years. Such properties were all demolished during the year due to refurbishment as per item (1) above) 450,000 Tax written down value brought forward attributable to qualifying expenditure claiming for commercial building allowance as per above Required 340,000 a. Calculation the depreciation allowances for deduction of ABC Ltd for 2018/19 under Part 6 of Inland Revenue Ordinance. (15 marks) Determine the profit tax liabilities of ABC Ltd for year ended 31 December 2018. ((Ignore provisional tax and any tax waiver or tax reductions in your calculation. Assume the taxpayer would not be qualified for the 2-tiered profits tax rate.) (20 marks) c. Explain your treatment of the expenditure with when preparing the tax computation in part (a). (15 marks) Question 2 (30 marks) Mr. Orlando is a US citizen and has been working in the Finance Department of Clever Inc. in Los Angeles since 2012. In April 2018, he visited the Hong Kong office from time to time as the regional financial controller. He also has to travel to other Asian countries on a regular basis to review the financial and related matters. The Hong Kong subsidiary of Clever Inc, did not sign a new employment contract with him but did provide him with administative and support services he needed in carrying out his responsibilities. Mr Orlando continues to work closely with his superior in US on important direction and policy matters. During the year ended 31 March 2019, he visited Hong Kong to discharge his duties on the following dates Date of arrival to Hong Kong 10 May 2018 24 Oct 2018 19 Jan 2019 Date of departure from Hong Kong 5 Jun 2018 2 Nov 2018 11 Feb 2019 During Mr. Orlando's visit to Hong Kong, he stays in a hotel's single standard room at the expense of the Company. For the year ended 31 March 2019 his income received from Clever Inc. is equivalent to HK$2,100,000 and has been credited to his bank account in USA by Clever Inc. Mr Orlando is single, and ordinarily resides in USA with his parents, aged 54 and 64. Required: (a) State and explain the factors which are used by IRD in determining the source of employment and evaluate whether Mr. Orlando's employment should be considered a Hong Kong employment or not. (11 marks) (b) According to IRO, certain exemptions may be available to a taxpayer who is subject to salaries tax. Identify and explain these exemptions if they are applicable to Mr. Orlando (7 marks) (c) Compute the salaries tax liability of Mr. Orlando's tax for the year of assessment 2018/19 based on your discussion of as per part (a) and (b) above. (Ignore provisional tax and tax reduction for the year, if there is any). (12 marks) Question 3 (20 marks) In 2018/19, the following are the highlights of some of the budget proposal resulted in subsequently tax legislation changes: Raising the deduction ceiling for elderly residential care expenses The deduction ceiling for elderly residential care expenses is raised from $92,000 to $100,000 effective from the year of assessment 2018/19. Relaxing the requirement for election of Personal Assessment by married persons Commencing from the year of assessment 2018/19, the requirement for the election of Personal Assessment is relaxed by allowing married persons the option to elect for personal assessment separately. Introducing a tax deduction of qualified premium for eligible health insurance products under the Voluntary Health Insurance Scheme From the year of assessment 2019/20, qualified premium paid for eligible health insurance products under the Voluntary Health Insurance Scheme are tax deductible. The annual tax ceiling of premium for tax deduction is $8,000 per insured person. Implementation details relating to changes of tax bands and marginal tax rates, increasing allowances, raising deduction ceiling and introducing personal disability allowance for the year of assessment 2018/19 Tax concessions under Profits Tax On profits tax, the types of qualified instruments under the qualifying debt instrument scheme are increased. In addition to instruments lodged and cleared by the Central Moneymarkets Unit of the Hong Kong Monetary Authority, debt securities listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange are now also eligible. The scope of tax exemption is also extended from debt instruments with an original maturity of not less than seven years to instruments of any duration. Separately, commencing from the year of assessment 2018/19, capital expenditure incurred by enterprises in procuring eligible efficient building installations and renewable energy devices are allowed for tax deduction in full in one year. Required: Discussed in your own words, what are the arguments behind the changes for taxation legislation listed above? (please comment on all points but your answer should not exceed 1000 words) (20 marks) Question 1 (50 marks) ABC Ltd is a computing consulting company with its accounting year ended 31 December. The profit before tax for year ended 31 December 2018 was $5,450,000 after including the following items in its financial statements: Income:- Compensation for early termination of a business contract by a customer 135,000 Share of profits from an associated company 380,000 Exchange gain from daily business related payable balance 18,500 Interest income from loans advanced to employees in HK 7,500 2,400 Interest income from unpledged deposit placed with a local bank Interest income from long outstanding business related receivable balance due from overseas customers 8,600 General bad debt provision written back 18,400 Deposit forfeited by customers due to cancellation of service engagement 120,000 Expenditure:- Interest expense on overdue account payable to an unrelated overseas hardware supplier regarding the purchase of a computer system in prior 3600 year Interest expense on a bank loan from HSBC guaranteed by ABC Ltd's director personally (the loan was exclusively used for ABC Ltd's daily business activities) Interest expense on an unsecured bank loan from Standard Chartered Bank (the loan was exclusively used for the acquisition of certain listed shares for 8000 long term investment purposes) 165.000 690.200 Special contribution to ABC Ltd s recognised occupational retirement scheme covering previous investment loss Annual contribution to ABC Ltd's recognised occupational retirement scheme (17% of each employees annual remunerations) Refurbishment expense for a residential property currently used by ABC Lid s director as quarters Refurbishment expense for a commercial property currently used by ABC Lid as office premises Tax payment (salaries tax of ABC Lid' s director) 300,000 750,000 280,000 Tax payment (property tax of self owned property) 120,000 Tax payment (property tax of a director) 52.000 Accounting depreciation 160,500 ABC Lad also provided information on fixed assets movement and other tax information as follows:- Addition of office furniture 100,500 Addition of computer equipment 120,000 Addition of a motor vehicle 285,000 Tax written down value for 20% pool brought forward 98,300 Tax written down value for 30% pool brought forward 127,000 Qualifying expenditure claiming for commercial building allowance brought forward (all expenditure referred to office premises and directors quarters decoration incurred in prior years. Such properties were all demolished during the year due to refurbishment as per item (1) above) 450,000 Tax written down value brought forward attributable to qualifying expenditure claiming for commercial building allowance as per above Required 340,000 a. Calculation the depreciation allowances for deduction of ABC Ltd for 2018/19 under Part 6 of Inland Revenue Ordinance. (15 marks) Determine the profit tax liabilities of ABC Ltd for year ended 31 December 2018. ((Ignore provisional tax and any tax waiver or tax reductions in your calculation. Assume the taxpayer would not be qualified for the 2-tiered profits tax rate.) (20 marks) c. Explain your treatment of the expenditure with when preparing the tax computation in part (a). (15 marks) Question 2 (30 marks) Mr. Orlando is a US citizen and has been working in the Finance Department of Clever Inc. in Los Angeles since 2012. In April 2018, he visited the Hong Kong office from time to time as the regional financial controller. He also has to travel to other Asian countries on a regular basis to review the financial and related matters. The Hong Kong subsidiary of Clever Inc, did not sign a new employment contract with him but did provide him with administative and support services he needed in carrying out his responsibilities. Mr Orlando continues to work closely with his superior in US on important direction and policy matters. During the year ended 31 March 2019, he visited Hong Kong to discharge his duties on the following dates Date of arrival to Hong Kong 10 May 2018 24 Oct 2018 19 Jan 2019 Date of departure from Hong Kong 5 Jun 2018 2 Nov 2018 11 Feb 2019 During Mr. Orlando's visit to Hong Kong, he stays in a hotel's single standard room at the expense of the Company. For the year ended 31 March 2019 his income received from Clever Inc. is equivalent to HK$2,100,000 and has been credited to his bank account in USA by Clever Inc. Mr Orlando is single, and ordinarily resides in USA with his parents, aged 54 and 64. Required: (a) State and explain the factors which are used by IRD in determining the source of employment and evaluate whether Mr. Orlando's employment should be considered a Hong Kong employment or not. (11 marks) (b) According to IRO, certain exemptions may be available to a taxpayer who is subject to salaries tax. Identify and explain these exemptions if they are applicable to Mr. Orlando (7 marks) (c) Compute the salaries tax liability of Mr. Orlando's tax for the year of assessment 2018/19 based on your discussion of as per part (a) and (b) above. (Ignore provisional tax and tax reduction for the year, if there is any). (12 marks) Question 3 (20 marks) In 2018/19, the following are the highlights of some of the budget proposal resulted in subsequently tax legislation changes: Raising the deduction ceiling for elderly residential care expenses The deduction ceiling for elderly residential care expenses is raised from $92,000 to $100,000 effective from the year of assessment 2018/19. Relaxing the requirement for election of Personal Assessment by married persons Commencing from the year of assessment 2018/19, the requirement for the election of Personal Assessment is relaxed by allowing married persons the option to elect for personal assessment separately. Introducing a tax deduction of qualified premium for eligible health insurance products under the Voluntary Health Insurance Scheme From the year of assessment 2019/20, qualified premium paid for eligible health insurance products under the Voluntary Health Insurance Scheme are tax deductible. The annual tax ceiling of premium for tax deduction is $8,000 per insured person. Implementation details relating to changes of tax bands and marginal tax rates, increasing allowances, raising deduction ceiling and introducing personal disability allowance for the year of assessment 2018/19 Tax concessions under Profits Tax On profits tax, the types of qualified instruments under the qualifying debt instrument scheme are increased. In addition to instruments lodged and cleared by the Central Moneymarkets Unit of the Hong Kong Monetary Authority, debt securities listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange are now also eligible. The scope of tax exemption is also extended from debt instruments with an original maturity of not less than seven years to instruments of any duration. Separately, commencing from the year of assessment 2018/19, capital expenditure incurred by enterprises in procuring eligible efficient building installations and renewable energy devices are allowed for tax deduction in full in one year. Required: Discussed in your own words, what are the arguments behind the changes for taxation legislation listed above? (please comment on all points but your answer should not exceed 1000 words) (20 marks)