Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
please help me solve all of these questions! the 1st two pictures ks what the whole assognment is based off of! thanks so much Phoenix







please help me solve all of these questions! the 1st two pictures ks what the whole assognment is based off of! thanks so much
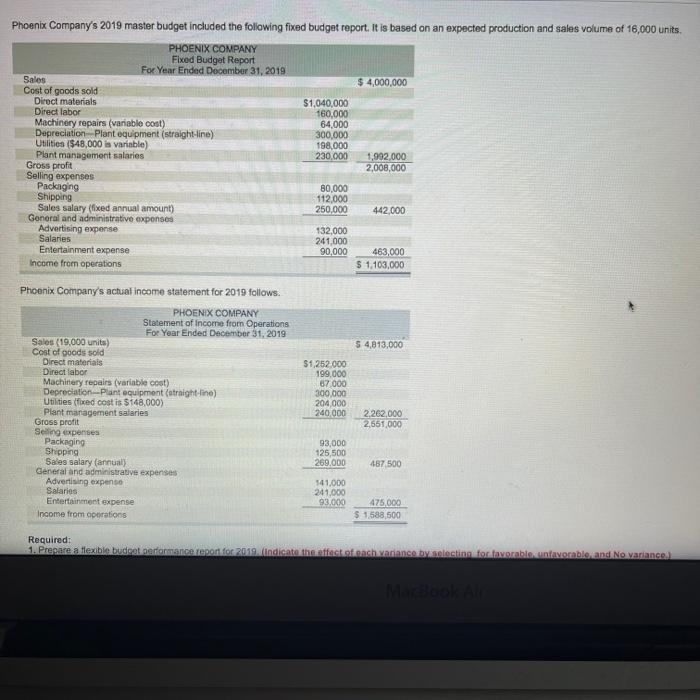
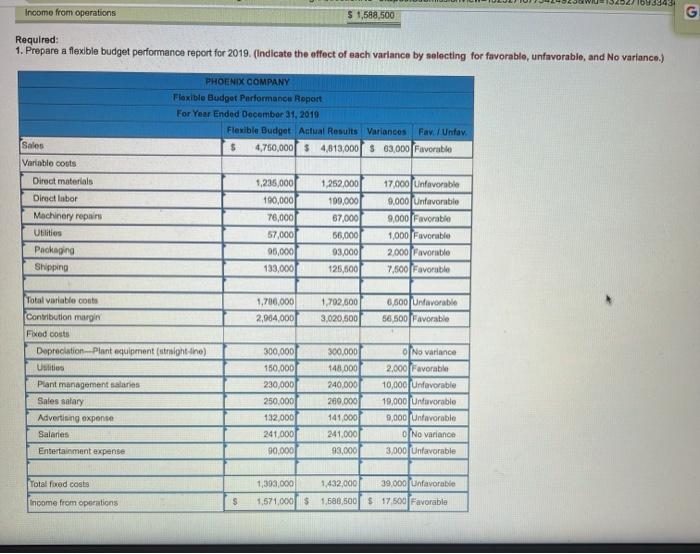
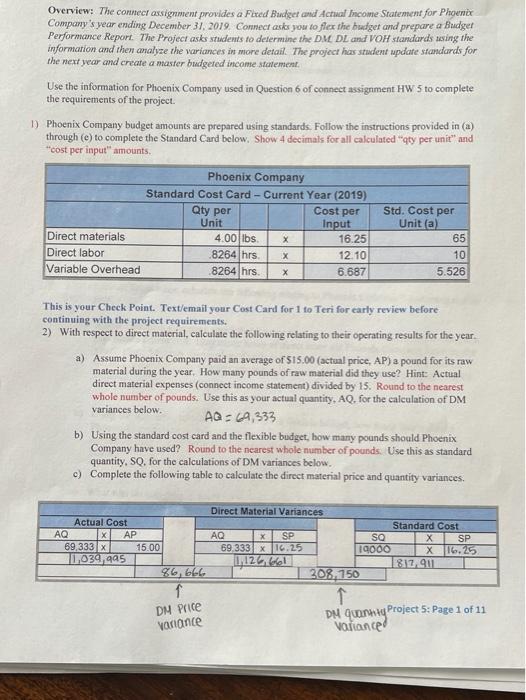
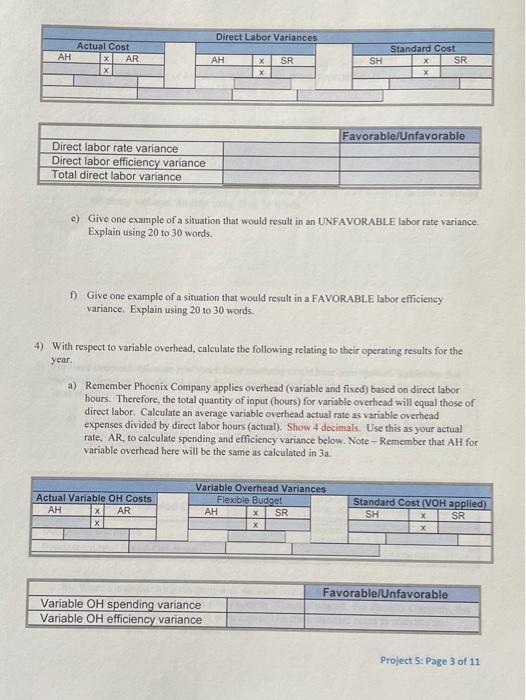
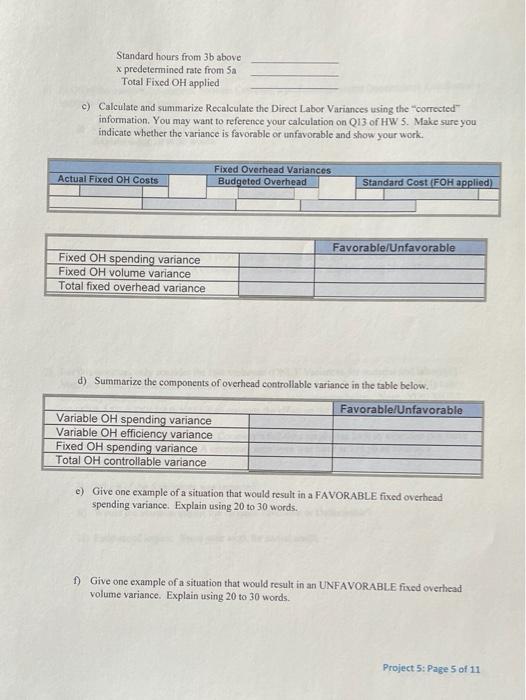
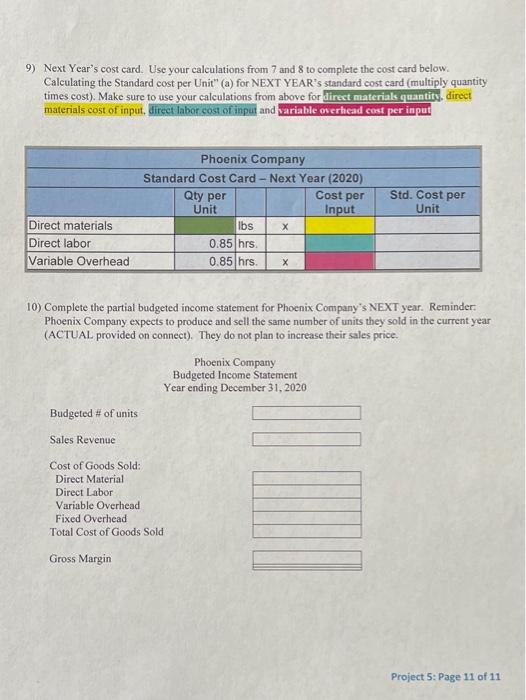
Phoenix Company's 2019 master budget included the following fixed budget report. It is based on an expected production and sales volume of 16,000 units. PHOENIX COMPANY Fixed Budget Report For Year Ended December 31, 2019 Sales $ 4,000,000 $1,040,000 160,000 64,000 300,000 198,000 230,000 1,992,000 2,008,000 Cost of goods sold Direct materials Direct labor Machinery repairs (variable cost) Depreciation Plant equipment (straight line) Utilition ($48,000 is variable) Plant management salaries Gross profit Selling expenses Packaging Shipping Sales salary (fixed annual amount) General and administrative expenses Advertising expense Salaries Entertainment expense Income from operations 80,000 112,000 250,000 442,000 132,000 241,000 90,000 463,000 $ 1,103,000 S 4,813,000 Phoenix Company's actual income statement for 2019 follows. PHOENIX COMPANY Statement of income from Operations For Year Ended December 31, 2019 Sales (19,000 units) Cost of goods sold Direct materials Direct labor Machinery repairs (variable cost) Depreciation Plant equipment straight-line) Utilities (fixed cost is $148,000) Plant management salaries Gross profit Selling expenses Packaging Shipping Sales salary (annual) General and administrative expenses Advertising expenso Salaries Entertainment expense Income from operations $1,252.000 199,000 07.000 300.000 204,000 240.000 2.262.000 2,661,000 93,000 125,500 269.000 487 500 541,000 241.000 93.000 475,000 $ 1588,500 Required: 1. Prepare a flexible budget performance on for 2019 indicate the testach vatanse bylos informeable unfavorable and No variance 10.343 Income from operations $ 1,588,500 G Required: 1. Prepare a flexible budget performance report for 2019. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting for favorable, unfavorable, and No variance.) PHOENIX COMPANY Flexible Budget Performance Report For Year Ended December 31, 2019 Flexible Budget Actual Results Variances Fav. Unfav. $ 4,750,000 $4,813,000 $ 63,000 Favorable Sales Variable costs 1,252.000 Direct materials Direct labor Machinery repairs Utilities Packaging Shipping 1.235,000 190,000 76,000 57,000 96,000 133,000 199,000 67,000 66,000 93,000 125,500 17.000 funfavorable 9.000 Unfavorable 9,000 Favorable 1,000 Favorable 2.000 Favorable 7.500 Favorable 1,700,000 2,964,000 1,702.600 3,020,500 0,500 unfavorable 56,500 Favorable Total variable costs Contribution margin Fixed costs Depreciation Plant equipment (straight-line) Us Plant management salaries Sales salary Advertising expense Salaries Entertainment expense 300,000 150,000 230,000 250.000 132 000 241.000 90,000 300,000 148.000 240.000 269.000 141,000 241,000 93,000 O'No variance 2,000 Favorable 10,000 unfavorable 19,000 (Unfavorable 9,000 (Unfavorable No variance 3,000 Unfavorable Total fored costs 1,393.000 1,571,000 $ 1,432,000 39.000 unfavorable 1,588,500 $ 17.500 Favorable Income from operations $ Overview: The connect assignment provides a Fired Budget and Actual Income Statement for Phoenix Company's year ending December 31, 2019 Connect asks you to flex the budget and prepare a Budget Performance Report. The Project asks students to determine the DM DL and Vow standards using the information and then analyze the variances in more detail. The project has student update standards for the next year and create a master budgeted income statement Use the information for Phoenix Company used in Question 6 of connect assignment HW 5 to complete the requirements of the project. 1) Phoenix Company budget amounts are prepared using standards. Follow the instructions provided in (a) through (c) to complete the Standard Card below. Show 4 decimals for all calculated aty per unit" and "cost per input" amounts Phoenix Company Standard Cost Card-Current Year (2019) Qty per Cost per Unit Input Direct materials 4.00 lbs X 16.25 Direct labor 8264 hrs 12.10 Variable Overhead 8264 hrs X 6.687 Std. Cost per Unita 65 10 5.526 This is your Check Point. Text/email your Cost Card for 1 to Teri for early review before continuing with the project requirements. 2) With respect to direct material, calculate the following relating to their operating results for the year a) Assume Phoenix Company paid an average of 515.00 (actual price, AP) a pound for its raw material during the year. How many pounds of raw material did they use? Hint: Actual direct material expenses (connect income statement) divided by 15. Round to the nearest whole number of pounds. Use this as your actual quantity, AQ, for the calculation of DM variances below. AQ: 69,333 b) Using the standard cost card and the flexible budget, how many pounds should Phoenix Company have used? Round to the nearest whole number of pounds. Use this as standard quantity. So, for the calculations of DM variances below. c) Complete the following table to calculate the direct material price and quantity variances. SP Direct Material Variances Actual Cost Standard Cost AQ X AP AQ x SO X SP 69,333x 15.00 69.333 x 16.25 19000 X16.25 11,034,995 1126 812,911 86,666 208, 750 1 DH quoruty Project 5: Page 1 of 11 Volanced DM Price variance Direct material price variance Direct material quantity variance Total direct material variance 186,666 208 750 1395,416 Favorable/Unfavorable un favorabie Unfavorable Tonfavorable d) Give an example of a situation that would result in a FAVORABLE material price variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. e) Give one an example of a situation that would result in an UN FAVORABLE material quantity variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words 3) With respect to direct labor, calculate the following relating to Phoenix Company's operating results for the year a) Assume Phoenix Company concluded it spent an average of 0.90 hours (Actual) to complete one finished good unit. How many hours of direct labor did Phoenix Company have for the year? Hint: Multiply the number of units produced by 0.90 hours. Round to the nearest whole number of hours. Use this amount as total actual hours, AH, in the calculation of DL variances below 19,00 b) Using the standard cost card (1 above) and the flexible budget, how many hours should Phoenix Company have used for production during the year? Round to the nearest whole number of hours. Use this amount as standard hours, SH, in the calculation of DL variances below. c) What was the company's actual labor rate? Hint: Calculate AR using direct labor expense divided by total direct Inbor hours, AH (calculated in a). Show 4 decimals. Use this as standard rate, AR, in the calculation of DL variances below. d) Complete the following table to calculate the direct labor rate and efficiency variances, Project 5: Page 2 of 11 Direct Labor Variances AH Actual Cost X AR X AH X SR SH Standard Cost x SR X X Favorable/Unfavorable Direct labor rate variance Direct labor efficiency variance Total direct labor variance e) Give one example of a situation that would result in an UNFAVORABLE labor rate variance Explain using 20 to 30 words. Give one example of a situation that would result in a FAVORABLE labor efficiency variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. 4) With respect to variable overhead, calculate the following relating to their operating results for the year. a) Remember Phoenix Company applies overhead (variable and fixed) based on direct labor hours. Therefore, the total quantity of input (hours) for variablc overhead will cqual those of direct labor. Calculate an average variable overhead actual rate as variable overhead expenses divided by direct labor hours (actual). Show 4 decimals. Use this as your actual rate, AR, to calculate spending and efficiency variance below. Note - Remember that AH for variable overhead here will be the same as calculated in 3a. Actual Variable OH Costs AH X AR x Variable Overhead Variances Flexible Budget AH x SR x Standard Cost (VOH applied) SH x SR x Favorable/Unfavorable Variable OH spending variance Variable OH efficiency variance Project 5: Page 3 of 11 Total variable OH variance b) Give one example of a situation that would result in a FAVORABLE variable overhead rate variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. .) Give one example of a situation that would result in an UNFAVORABLE variable overhead efficiency variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. 5) For fixed overhead, calculate how much fixed overhead would have been applied. Remember that overhead (fixed and variable) is applied based on a standard or predetermined rate for a budgeted level of activity a) Calculate portion of the predetermined rate relating to fixed overhead using the table below using budgeted overhead costs and standard hours of labor expected for "PLANNED/BUDGETED" production level. Fixed Overhead Pre-Determined Rate Add Depreciation-Plant equipment fixed Budgeted Fixed Overhead Costs ces and plant management salaries from connect Calculate budgeted 8 of units connect) Budgeted DL hours standard hours per unitin Predetermined Fixed OH Rate Calculate Costs divided by hours b) When a manufacturing company uses standard costing, its overhead is applied based on STANDARD HOURS for the actual number of units produced. For Phoenix Company, this is the standard hours calculated in 3b above. Use these standard houts to calculate the amount of fixed overhead applied below. Project 5: Page 4 of 11 Standard hours from 3b above x predetermined rate from Sa Total Fixed OH applied c) Calculate and summarize Recalculate the Direct Labor Variances using the corrected" information. You may want to reference your calculation on 13 of HW 5. Make sure you indicate whether the variance is favorable or unfavorable and show your work. Actual Fixed OH Costs Fixed Overhead Variances Budgeted Overhead Standard Cost (FOH applied Favorable/Unfavorable Fixed OH spending variance Fixed OH volume variance Total fixed overhead variance d) Summarize the components of overhead controllable variance in the table below. Favorable/Unfavorable Variable OH spending variance Variable OH efficiency variance Fixed OH spending variance Total OH controllable variance c) Give one example of a situation that would result in a FAVORABLE fixed overhead spending variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. f) Give one example of a situation that would result in an UNFAVORABLE fixed overhead volume variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. Project 5: Page 5 of 11 6) In Q6 of the connect assignment, Phoenix Company's performance report (requirement 1) indicated a variance in the sales revenue. a) Give one example of a situation that would result in a FAVORABLE revenue variance, Explain using 20 to 30 words b) Assuming a company DOES NOT change its sales price, give one example of a situation that would result in an UNFAVORABLE revenue variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. 7) For this question, only consider the four variances (ONLY Variances for material and labor) (1) Materials Price Variance, (2) Material Quantity Variance, (3) Labor Rate Variance, and (4) Labor Efficiency Variance. Answer the questions relating to each situation below. Note: YOU MUST CALCULATE A DOLLAR VALUE to estimate the effect on the variance. a) Situation A: One of Phoenix Company's full-time employees took an extended sick leave amounting to 160 hours. A temporary employee was hired at $14.50 an hour as a replacement 1) Which of the 4 variances was impacted? ii) Would the situation impact the variance Favorable or Unfavorable? ii) Estimate of impact. Show your work for partial credit Project 5: Page 6 of 11 b) Situation B: Power outages occurred three times during the year in which all production was shut down for 2 hours the first time, 3 hours the second time, and 1 hour the third time. During these times, 4 workers remained on site, but no work was performed. 1) Which of the 4 variances would this situation impact? ii) Would the situation impact the variance Favorable or Unfavorable? iii) Estimate of impact. Show your work for partial credit. c) Situation C: An order of raw material was received damaged, presumably during shipping. The order contained enough raw material to produce 200 finished goods. Upon inspection, 8% of the raw material was deemed contaminated and not usable. 1) Which of the 4 variances would this situation impact? ii) Would the situation impact the variance Favorable or Unfavorable? iii) Estimate of impact. Show your work for partial credit. d) Situation D: The purchasing department was able to negotiate a S1,200 discount from the supplier for the damaged order from c) above. i) Which of the 4 variances would this situation impact? Project 5: Page 7 of 11 ii) Would the situation impact the variance Favorable or Unfavorable? iii) Estimate of impact. e) Using the information for C and D. do you think purchasing did well with its negotiation of the discount? Explain in 20 to 40 words 8) MAKE A CHOICE !!!!! Do A or B-Do not do both. Review your material variances calculated in 2 above. If your material price variance is FAVORABLE, complete 7A here and SKIP 7B, if your material price variance is UNFAVORABLE, SKIP A here and complete 7B below. A. COMPLETE IF MPV is FAVORABLE or ZERO. Complete this requirement if your material price variance in 2 is favorable or zero. Otherwise, skip and move on to 7B. If you complete A here, DO NOT DO B below. Management wants to make a few changes to its operation for the next year. Assume Phoenix Company plans to produce and sell the same number of units they sold last year (connect-actual units). a. Management believes the lower priced material has contributed to the unfavorable material quantity variance. The purchasing department wants to know what price per pound of raw material they should pay to fully offset the unfavorable material quantity variance they saw last year. Calculate the price. Hint - Use MPV - (SP- AP)AO: Set material price variance to favorable (positive) amount equal to the quantity variance calculated in 2c. Use the SP from standard cost card in 1 and actual quantity of raw material and solve for AP, actual price). Management would like to set this as their standard raw material price per input for next year. Include the amount in NEXT YEAR's standard cost card below in the highlighted cell. Make sure you show your calculations for partial credit. Note - If your quantity variance is also favorable, please contact your instructor for guidance. Project 5: Page 8 of 11 b. The production supervisor is implementing some changes to production that are expected to improve the materials quantity variance. With these changes, the supervisor believes that their unfavorable quantity variance would have been only half (50%) what it was. HINT: Use MQV = (SQ-AQ)SP: Set MQV to 50% of the quantity variance from 20. Use the AQ and SP from 2c and solve for Actual Quantity to achieve the desired variance. This will be total quantity of raw material. Divide this quantity by the number of finished goods units produced/sold to express this as POUNDS PER UNIT (ONE UNIT) of finished goods"Management wants to use this as their new standard for next year. Include this in the standard cost card below for the highlighted square. Make sure you show your calculations for partial credit Note - If your quantity variance is favorable, please contact your instructor for guidance. B. COMPLETE IF MPV is UNFAVORABLE: Complete this requirement if your material price variance in 2 is unfavorable. If you completed A above, DO NOT COMPLETE B here. Management wants to make a few changes to its operation for the next year. Assume for all your calculations that Phoenix Company plans to produce and sell the same number of units they sold last year (connect-actual units). a. The unfavorable material price variance is the result of continually rising prices as set by Phoenix Company's suppliers. Management is it the midst of negotiations with one supplier for a committed price contract if they exclusively supply the company next year. Management would like to set this negotiated price such that last year's material price variance would be half (50%). Calculate the desired price. (Hint: Use MPV = (SP-AP)AQ. Set the MPV equal to 50% of the unfavorable price variance (negative) calculated in 2c (negative for unfavorable). Use the SP from the standard cost card in 1 and the actual quantity of raw material. Solve for AP, actual price). This AP will become next year's standard cost. Include the amount in NEXT YEARS's standard cost card below in the highlighted cell. Make sure you show your calculations for partial credit. Project 5: Page 9 of 11 b. The production supervisor is convinced that the favorable materials quantity variance from last year is because of the high quality of the raw material used for production Because of the new price contract, management is anticipating that quality may suffer and wants to anticipate this impact. Management believes that a 30% decrease to last year's material quantity variance would be acceptable. Calculate the new standard. HINT: Use MOV - (SO-AO)SP: Set MOV to 70% (30% reduced) of the material quantity variance (positive for favorable) from 20. Use the AQ and SP from 2c and solve for Actual Quantity to achieve the desired variance. This will be total quantity of raw material. Divide this quantity by the number of finished goods units produced/sold to express this as POUNDS PER UNIT (ONE UNIT) of finished goods". Management wants to use this as their new standard for next year. Include this in the standard cost card below for the highlighted square. Note - If your MPV and MOV are BOTH favorable or BOTH unfavorable, please contact your instructor for guidance. 8) In the past few years, Phoenix Company has made many changes to their factory production process and have also experienced significant employee turnover. Management believes that operations have been more stable in the most recent year and are representative of future operations. Because of this expected stability, management is proposing standards for direct labor be based on the most current results (Actual quantities and rates from in 3a and 3c). a) A 3% wage increase has been authorized for all direct labor employees. Add the 3% increase to the ACTUAL average labor rate from 3c. This will be the new standard labor rate. Include the amount in the highlighted square in the NEXT YEAR standard cost card. b) The company anticipates the standard direct labor hour will be 0.85 hours per finished good. this is slightly lower than their previous actual average (0.90) because management expects more efficiency given employee experience, etc. c) Overhead costs are expected to increase 2.5% due to inflation. Calculate the new variable overhead standard as 2.5% higher that their most current actual rate (AR calculated in 4s above) Include the amount in the highlighted square in the NEXT YEAR standard cost card. d) Calculate budgeted fixed overhead as 2.5% higher than the previous year's actual. (connect). You will use this amount in the budgeted income statement below. Project 5: Page 10 of 11 9) Next Year's cost card. Use your calculations from 7 and 8 to complete the cost card below. Calculating the Standard cost per Unit" (a) for NEXT YEAR's standard cost card (multiply quantity times cost). Make sure to use your calculations from above for direct materials quantity, direct materials cost of input, direct labor cost of input and variable overhead cost per input Phoenix Company Standard Cost Card - Next Year (2020) Qty per Cost per Unit Input lbs 0.85 hrs 0.85 hrs Std. Cost per Unit Direct materials Direct labor Variable Overhead 10) Complete the partial budgeted income statement for Phoenix Company's NEXT year. Reminder Phoenix Company expects to produce and sell the same number of units they sold in the current year (ACTUAL provided on connect). They do not plan to increase their sales price. Phoenix Company Budgeted Income Statement Year ending December 31, 2020 Budgeted # of units Sales Revenue Cost of Goods Sold: Direct Material Direct Labor Variable Overhead Fixed Overhead Total Cost of Goods Sold Gross Margin Project 5: Page 11 of 11 Phoenix Company's 2019 master budget included the following fixed budget report. It is based on an expected production and sales volume of 16,000 units. PHOENIX COMPANY Fixed Budget Report For Year Ended December 31, 2019 Sales $ 4,000,000 $1,040,000 160,000 64,000 300,000 198,000 230,000 1,992,000 2,008,000 Cost of goods sold Direct materials Direct labor Machinery repairs (variable cost) Depreciation Plant equipment (straight line) Utilition ($48,000 is variable) Plant management salaries Gross profit Selling expenses Packaging Shipping Sales salary (fixed annual amount) General and administrative expenses Advertising expense Salaries Entertainment expense Income from operations 80,000 112,000 250,000 442,000 132,000 241,000 90,000 463,000 $ 1,103,000 S 4,813,000 Phoenix Company's actual income statement for 2019 follows. PHOENIX COMPANY Statement of income from Operations For Year Ended December 31, 2019 Sales (19,000 units) Cost of goods sold Direct materials Direct labor Machinery repairs (variable cost) Depreciation Plant equipment straight-line) Utilities (fixed cost is $148,000) Plant management salaries Gross profit Selling expenses Packaging Shipping Sales salary (annual) General and administrative expenses Advertising expenso Salaries Entertainment expense Income from operations $1,252.000 199,000 07.000 300.000 204,000 240.000 2.262.000 2,661,000 93,000 125,500 269.000 487 500 541,000 241.000 93.000 475,000 $ 1588,500 Required: 1. Prepare a flexible budget performance on for 2019 indicate the testach vatanse bylos informeable unfavorable and No variance 10.343 Income from operations $ 1,588,500 G Required: 1. Prepare a flexible budget performance report for 2019. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting for favorable, unfavorable, and No variance.) PHOENIX COMPANY Flexible Budget Performance Report For Year Ended December 31, 2019 Flexible Budget Actual Results Variances Fav. Unfav. $ 4,750,000 $4,813,000 $ 63,000 Favorable Sales Variable costs 1,252.000 Direct materials Direct labor Machinery repairs Utilities Packaging Shipping 1.235,000 190,000 76,000 57,000 96,000 133,000 199,000 67,000 66,000 93,000 125,500 17.000 funfavorable 9.000 Unfavorable 9,000 Favorable 1,000 Favorable 2.000 Favorable 7.500 Favorable 1,700,000 2,964,000 1,702.600 3,020,500 0,500 unfavorable 56,500 Favorable Total variable costs Contribution margin Fixed costs Depreciation Plant equipment (straight-line) Us Plant management salaries Sales salary Advertising expense Salaries Entertainment expense 300,000 150,000 230,000 250.000 132 000 241.000 90,000 300,000 148.000 240.000 269.000 141,000 241,000 93,000 O'No variance 2,000 Favorable 10,000 unfavorable 19,000 (Unfavorable 9,000 (Unfavorable No variance 3,000 Unfavorable Total fored costs 1,393.000 1,571,000 $ 1,432,000 39.000 unfavorable 1,588,500 $ 17.500 Favorable Income from operations $ Overview: The connect assignment provides a Fired Budget and Actual Income Statement for Phoenix Company's year ending December 31, 2019 Connect asks you to flex the budget and prepare a Budget Performance Report. The Project asks students to determine the DM DL and Vow standards using the information and then analyze the variances in more detail. The project has student update standards for the next year and create a master budgeted income statement Use the information for Phoenix Company used in Question 6 of connect assignment HW 5 to complete the requirements of the project. 1) Phoenix Company budget amounts are prepared using standards. Follow the instructions provided in (a) through (c) to complete the Standard Card below. Show 4 decimals for all calculated aty per unit" and "cost per input" amounts Phoenix Company Standard Cost Card-Current Year (2019) Qty per Cost per Unit Input Direct materials 4.00 lbs X 16.25 Direct labor 8264 hrs 12.10 Variable Overhead 8264 hrs X 6.687 Std. Cost per Unita 65 10 5.526 This is your Check Point. Text/email your Cost Card for 1 to Teri for early review before continuing with the project requirements. 2) With respect to direct material, calculate the following relating to their operating results for the year a) Assume Phoenix Company paid an average of 515.00 (actual price, AP) a pound for its raw material during the year. How many pounds of raw material did they use? Hint: Actual direct material expenses (connect income statement) divided by 15. Round to the nearest whole number of pounds. Use this as your actual quantity, AQ, for the calculation of DM variances below. AQ: 69,333 b) Using the standard cost card and the flexible budget, how many pounds should Phoenix Company have used? Round to the nearest whole number of pounds. Use this as standard quantity. So, for the calculations of DM variances below. c) Complete the following table to calculate the direct material price and quantity variances. SP Direct Material Variances Actual Cost Standard Cost AQ X AP AQ x SO X SP 69,333x 15.00 69.333 x 16.25 19000 X16.25 11,034,995 1126 812,911 86,666 208, 750 1 DH quoruty Project 5: Page 1 of 11 Volanced DM Price variance Direct material price variance Direct material quantity variance Total direct material variance 186,666 208 750 1395,416 Favorable/Unfavorable un favorabie Unfavorable Tonfavorable d) Give an example of a situation that would result in a FAVORABLE material price variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. e) Give one an example of a situation that would result in an UN FAVORABLE material quantity variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words 3) With respect to direct labor, calculate the following relating to Phoenix Company's operating results for the year a) Assume Phoenix Company concluded it spent an average of 0.90 hours (Actual) to complete one finished good unit. How many hours of direct labor did Phoenix Company have for the year? Hint: Multiply the number of units produced by 0.90 hours. Round to the nearest whole number of hours. Use this amount as total actual hours, AH, in the calculation of DL variances below 19,00 b) Using the standard cost card (1 above) and the flexible budget, how many hours should Phoenix Company have used for production during the year? Round to the nearest whole number of hours. Use this amount as standard hours, SH, in the calculation of DL variances below. c) What was the company's actual labor rate? Hint: Calculate AR using direct labor expense divided by total direct Inbor hours, AH (calculated in a). Show 4 decimals. Use this as standard rate, AR, in the calculation of DL variances below. d) Complete the following table to calculate the direct labor rate and efficiency variances, Project 5: Page 2 of 11 Direct Labor Variances AH Actual Cost X AR X AH X SR SH Standard Cost x SR X X Favorable/Unfavorable Direct labor rate variance Direct labor efficiency variance Total direct labor variance e) Give one example of a situation that would result in an UNFAVORABLE labor rate variance Explain using 20 to 30 words. Give one example of a situation that would result in a FAVORABLE labor efficiency variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. 4) With respect to variable overhead, calculate the following relating to their operating results for the year. a) Remember Phoenix Company applies overhead (variable and fixed) based on direct labor hours. Therefore, the total quantity of input (hours) for variablc overhead will cqual those of direct labor. Calculate an average variable overhead actual rate as variable overhead expenses divided by direct labor hours (actual). Show 4 decimals. Use this as your actual rate, AR, to calculate spending and efficiency variance below. Note - Remember that AH for variable overhead here will be the same as calculated in 3a. Actual Variable OH Costs AH X AR x Variable Overhead Variances Flexible Budget AH x SR x Standard Cost (VOH applied) SH x SR x Favorable/Unfavorable Variable OH spending variance Variable OH efficiency variance Project 5: Page 3 of 11 Total variable OH variance b) Give one example of a situation that would result in a FAVORABLE variable overhead rate variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. .) Give one example of a situation that would result in an UNFAVORABLE variable overhead efficiency variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. 5) For fixed overhead, calculate how much fixed overhead would have been applied. Remember that overhead (fixed and variable) is applied based on a standard or predetermined rate for a budgeted level of activity a) Calculate portion of the predetermined rate relating to fixed overhead using the table below using budgeted overhead costs and standard hours of labor expected for "PLANNED/BUDGETED" production level. Fixed Overhead Pre-Determined Rate Add Depreciation-Plant equipment fixed Budgeted Fixed Overhead Costs ces and plant management salaries from connect Calculate budgeted 8 of units connect) Budgeted DL hours standard hours per unitin Predetermined Fixed OH Rate Calculate Costs divided by hours b) When a manufacturing company uses standard costing, its overhead is applied based on STANDARD HOURS for the actual number of units produced. For Phoenix Company, this is the standard hours calculated in 3b above. Use these standard houts to calculate the amount of fixed overhead applied below. Project 5: Page 4 of 11 Standard hours from 3b above x predetermined rate from Sa Total Fixed OH applied c) Calculate and summarize Recalculate the Direct Labor Variances using the corrected" information. You may want to reference your calculation on 13 of HW 5. Make sure you indicate whether the variance is favorable or unfavorable and show your work. Actual Fixed OH Costs Fixed Overhead Variances Budgeted Overhead Standard Cost (FOH applied Favorable/Unfavorable Fixed OH spending variance Fixed OH volume variance Total fixed overhead variance d) Summarize the components of overhead controllable variance in the table below. Favorable/Unfavorable Variable OH spending variance Variable OH efficiency variance Fixed OH spending variance Total OH controllable variance c) Give one example of a situation that would result in a FAVORABLE fixed overhead spending variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. f) Give one example of a situation that would result in an UNFAVORABLE fixed overhead volume variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. Project 5: Page 5 of 11 6) In Q6 of the connect assignment, Phoenix Company's performance report (requirement 1) indicated a variance in the sales revenue. a) Give one example of a situation that would result in a FAVORABLE revenue variance, Explain using 20 to 30 words b) Assuming a company DOES NOT change its sales price, give one example of a situation that would result in an UNFAVORABLE revenue variance. Explain using 20 to 30 words. 7) For this question, only consider the four variances (ONLY Variances for material and labor) (1) Materials Price Variance, (2) Material Quantity Variance, (3) Labor Rate Variance, and (4) Labor Efficiency Variance. Answer the questions relating to each situation below. Note: YOU MUST CALCULATE A DOLLAR VALUE to estimate the effect on the variance. a) Situation A: One of Phoenix Company's full-time employees took an extended sick leave amounting to 160 hours. A temporary employee was hired at $14.50 an hour as a replacement 1) Which of the 4 variances was impacted? ii) Would the situation impact the variance Favorable or Unfavorable? ii) Estimate of impact. Show your work for partial credit Project 5: Page 6 of 11 b) Situation B: Power outages occurred three times during the year in which all production was shut down for 2 hours the first time, 3 hours the second time, and 1 hour the third time. During these times, 4 workers remained on site, but no work was performed. 1) Which of the 4 variances would this situation impact? ii) Would the situation impact the variance Favorable or Unfavorable? iii) Estimate of impact. Show your work for partial credit. c) Situation C: An order of raw material was received damaged, presumably during shipping. The order contained enough raw material to produce 200 finished goods. Upon inspection, 8% of the raw material was deemed contaminated and not usable. 1) Which of the 4 variances would this situation impact? ii) Would the situation impact the variance Favorable or Unfavorable? iii) Estimate of impact. Show your work for partial credit. d) Situation D: The purchasing department was able to negotiate a S1,200 discount from the supplier for the damaged order from c) above. i) Which of the 4 variances would this situation impact? Project 5: Page 7 of 11 ii) Would the situation impact the variance Favorable or Unfavorable? iii) Estimate of impact. e) Using the information for C and D. do you think purchasing did well with its negotiation of the discount? Explain in 20 to 40 words 8) MAKE A CHOICE !!!!! Do A or B-Do not do both. Review your material variances calculated in 2 above. If your material price variance is FAVORABLE, complete 7A here and SKIP 7B, if your material price variance is UNFAVORABLE, SKIP A here and complete 7B below. A. COMPLETE IF MPV is FAVORABLE or ZERO. Complete this requirement if your material price variance in 2 is favorable or zero. Otherwise, skip and move on to 7B. If you complete A here, DO NOT DO B below. Management wants to make a few changes to its operation for the next year. Assume Phoenix Company plans to produce and sell the same number of units they sold last year (connect-actual units). a. Management believes the lower priced material has contributed to the unfavorable material quantity variance. The purchasing department wants to know what price per pound of raw material they should pay to fully offset the unfavorable material quantity variance they saw last year. Calculate the price. Hint - Use MPV - (SP- AP)AO: Set material price variance to favorable (positive) amount equal to the quantity variance calculated in 2c. Use the SP from standard cost card in 1 and actual quantity of raw material and solve for AP, actual price). Management would like to set this as their standard raw material price per input for next year. Include the amount in NEXT YEAR's standard cost card below in the highlighted cell. Make sure you show your calculations for partial credit. Note - If your quantity variance is also favorable, please contact your instructor for guidance. Project 5: Page 8 of 11 b. The production supervisor is implementing some changes to production that are expected to improve the materials quantity variance. With these changes, the supervisor believes that their unfavorable quantity variance would have been only half (50%) what it was. HINT: Use MQV = (SQ-AQ)SP: Set MQV to 50% of the quantity variance from 20. Use the AQ and SP from 2c and solve for Actual Quantity to achieve the desired variance. This will be total quantity of raw material. Divide this quantity by the number of finished goods units produced/sold to express this as POUNDS PER UNIT (ONE UNIT) of finished goods"Management wants to use this as their new standard for next year. Include this in the standard cost card below for the highlighted square. Make sure you show your calculations for partial credit Note - If your quantity variance is favorable, please contact your instructor for guidance. B. COMPLETE IF MPV is UNFAVORABLE: Complete this requirement if your material price variance in 2 is unfavorable. If you completed A above, DO NOT COMPLETE B here. Management wants to make a few changes to its operation for the next year. Assume for all your calculations that Phoenix Company plans to produce and sell the same number of units they sold last year (connect-actual units). a. The unfavorable material price variance is the result of continually rising prices as set by Phoenix Company's suppliers. Management is it the midst of negotiations with one supplier for a committed price contract if they exclusively supply the company next year. Management would like to set this negotiated price such that last year's material price variance would be half (50%). Calculate the desired price. (Hint: Use MPV = (SP-AP)AQ. Set the MPV equal to 50% of the unfavorable price variance (negative) calculated in 2c (negative for unfavorable). Use the SP from the standard cost card in 1 and the actual quantity of raw material. Solve for AP, actual price). This AP will become next year's standard cost. Include the amount in NEXT YEARS's standard cost card below in the highlighted cell. Make sure you show your calculations for partial credit. Project 5: Page 9 of 11 b. The production supervisor is convinced that the favorable materials quantity variance from last year is because of the high quality of the raw material used for production Because of the new price contract, management is anticipating that quality may suffer and wants to anticipate this impact. Management believes that a 30% decrease to last year's material quantity variance would be acceptable. Calculate the new standard. HINT: Use MOV - (SO-AO)SP: Set MOV to 70% (30% reduced) of the material quantity variance (positive for favorable) from 20. Use the AQ and SP from 2c and solve for Actual Quantity to achieve the desired variance. This will be total quantity of raw material. Divide this quantity by the number of finished goods units produced/sold to express this as POUNDS PER UNIT (ONE UNIT) of finished goods". Management wants to use this as their new standard for next year. Include this in the standard cost card below for the highlighted square. Note - If your MPV and MOV are BOTH favorable or BOTH unfavorable, please contact your instructor for guidance. 8) In the past few years, Phoenix Company has made many changes to their factory production process and have also experienced significant employee turnover. Management believes that operations have been more stable in the most recent year and are representative of future operations. Because of this expected stability, management is proposing standards for direct labor be based on the most current results (Actual quantities and rates from in 3a and 3c). a) A 3% wage increase has been authorized for all direct labor employees. Add the 3% increase to the ACTUAL average labor rate from 3c. This will be the new standard labor rate. Include the amount in the highlighted square in the NEXT YEAR standard cost card. b) The company anticipates the standard direct labor hour will be 0.85 hours per finished good. this is slightly lower than their previous actual average (0.90) because management expects more efficiency given employee experience, etc. c) Overhead costs are expected to increase 2.5% due to inflation. Calculate the new variable overhead standard as 2.5% higher that their most current actual rate (AR calculated in 4s above) Include the amount in the highlighted square in the NEXT YEAR standard cost card. d) Calculate budgeted fixed overhead as 2.5% higher than the previous year's actual. (connect). You will use this amount in the budgeted income statement below. Project 5: Page 10 of 11 9) Next Year's cost card. Use your calculations from 7 and 8 to complete the cost card below. Calculating the Standard cost per Unit" (a) for NEXT YEAR's standard cost card (multiply quantity times cost). Make sure to use your calculations from above for direct materials quantity, direct materials cost of input, direct labor cost of input and variable overhead cost per input Phoenix Company Standard Cost Card - Next Year (2020) Qty per Cost per Unit Input lbs 0.85 hrs 0.85 hrs Std. Cost per Unit Direct materials Direct labor Variable Overhead 10) Complete the partial budgeted income statement for Phoenix Company's NEXT year. Reminder Phoenix Company expects to produce and sell the same number of units they sold in the current year (ACTUAL provided on connect). They do not plan to increase their sales price. Phoenix Company Budgeted Income Statement Year ending December 31, 2020 Budgeted # of units Sales Revenue Cost of Goods Sold: Direct Material Direct Labor Variable Overhead Fixed Overhead Total Cost of Goods Sold Gross Margin Project 5: Page 11 of 11 Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


