Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please help me solving this With all these steps I have provided the time all the way at bottom EXPERIMENT 44 Rate of Halogenation of


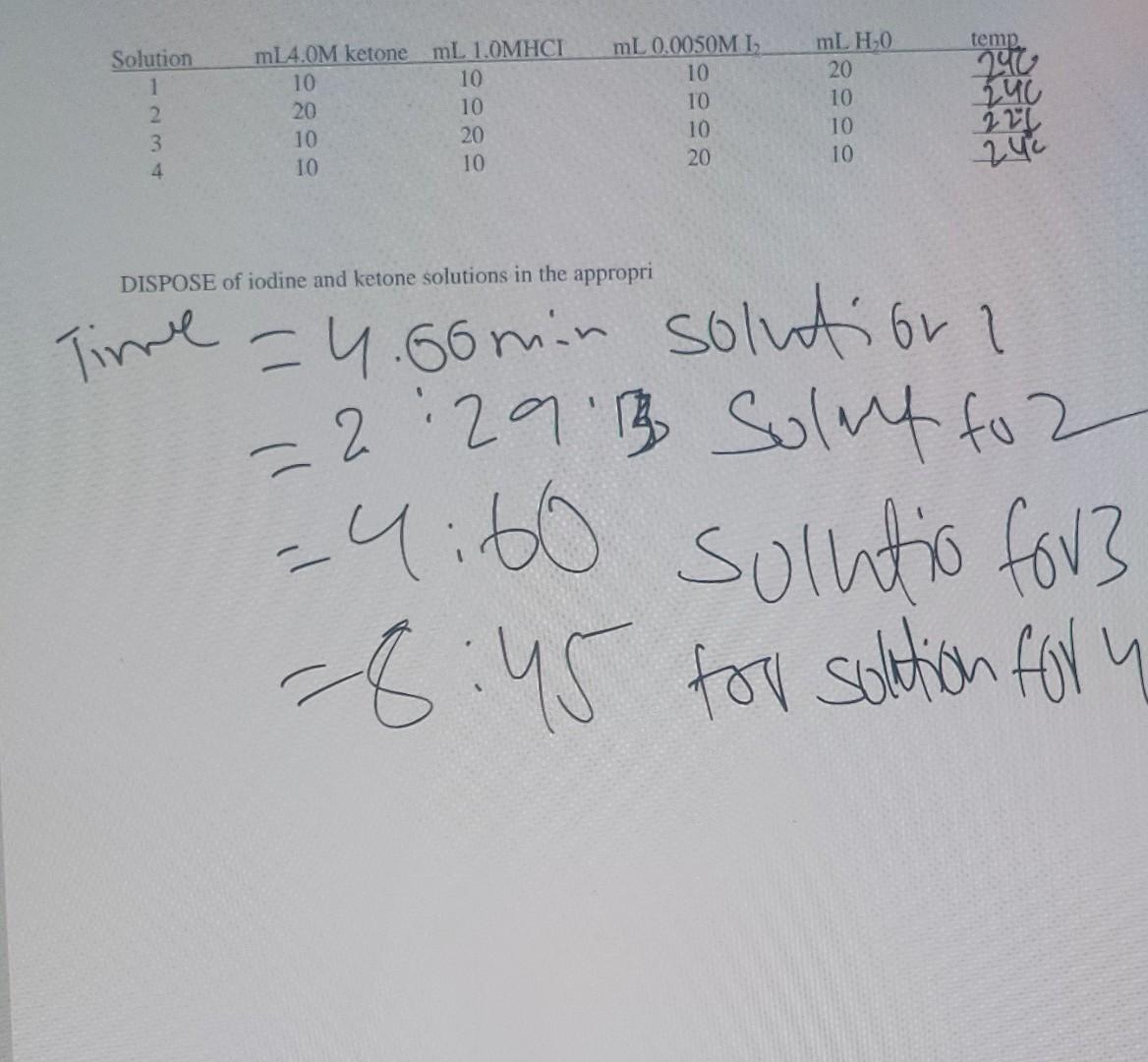
Please help me solving this With all these steps I have provided the time all the way at bottom
EXPERIMENT 44 Rate of Halogenation of a Ketone (Goggles must be worn!!) Thermodynamics is able to predict whether a reaction will occur but it cannot say how long it will take. For the reaction: aA + B C + dD the rate at which the reaction proceeds usually is of the form: rate=k[A].[B]" Normally the rate is monitored as the disappearance of a reactant or as the appearance of a product. The numbers m and n are usually small integers (0, 1, or 2) which represent the orders of the reaction with respect to the concentrations of A and B. The factor k denotes the rate constant for the reaction, and its magnitude usually establishes whether a reaction will occur within a reasonable time. Ketones are compounds which contain the structural group C-C-C The hydrogens on the carbons flanking the carbonyl (C=0) group can be replaced by bromine or iodine, especially in acidic solutions. Using acetone as an example, the reaction with triiodide ion is aqueous solution is: O O 11 H CH3CCH3 + 13 CH3CCHI + 2HI(aq) The rate law for this experiment has the form: Rate=k[ketone]"[H]"[13] (2) The actual value for the rate will be experimentally measured as the loss of a known amount of acetone per time interval: Rate = - A[ketone] (3) At Stock solutions for each reactant will be available. The time as the reaction progresses will be measured as the halogen color (yellow) dissipates. Knowing the [Acetone) which has reacted and the time taken for its disappearance, the rate can be calculated with equation (3). By the relative amounts of reactants and measuring each new rate, information can be found and used to find the orders m, n, and p, equation (4), and finally the rate constant k from equation (2). In addition, if more than one ketone is used, it may be possible to tabulate the class results and compare rate constants for ketones with respect to their molecular structures. Procedure You may work in pairs for this project. Select two regular test tubes, filled with distilled water, they should appear to have identical color when viewed down through the test tubes onto a white piece of paper Pipette 50 mL of each of the following solutions into clean, dry, 100-ml beakers, one solution to a beaker: 4M acetone, IM HC1, and 0.005M 1/ 0.05 M KI, cover each beaker with a watch glass or parafilm. Using a graduated cylinder, measure out 10.0 mL of the 4M acetone solution and pour it into a clean 125 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Next measure out 10.0 mL 1M HCI and add that to the acetone in the flask. Add 20.0 mL distilled H20 to the flask. Drain the graduated cylinder, shaking out any excess water, and then use the cylinder to measure out 10.0 mL 0.005M hi 0.05 M Kl solution. Do not spill the iodine solution on your hands or clothes. Noting the time to 1 second pour the iodine solution into the Erlenmeyer flask and immediately swirl the flask to mix reagents. The presence of iodine will make the contents of the flask appear yellow this will fade as the reaction proceeds. Fill one of the test tubes with mixture and the other, to the same depth with distilled water. Look down the test tubes onto a piece of white paper. Note the time when the iodine color just disappears. Measure the temperature of the solution. Repeat the experiment but use the reacted solution as a reference instead of distilled water. The amount of time of the reactions should agree within 20 seconds. The following sets of solutions are to be studied and temperatures recorded: Solution 1 2 3 4 mL 0.0050ML 10 10 10 temp 240 140 mL4.0M ketonemL 1.0MHCI 10 10 20 10 10 20 10 10 mLHO 20 10 10 10 220 20 240 DISPOSE of iodine and ketone solutions in the appropri Time = 4.60min solution 12:29'3 Sulut to 2 -4:60 solutio for? -8:45 for solution for y uStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


