Question
Please help me with the following question below. (This question has two parts: a and b) You need to read Article 2 Our farmers need
Please help me with the following question below. (This question has two parts: a and b)
You need to read Article 2 ""Our farmers need a better deal": Study
shows true cost of trade barriers to answer questions below. ( I have attached the article below.)
Part (a)
Article 2 specifically mentions: "A NEW AgriFutures Australia-funded study shows that farm subsidies and import barriers abroad lowered Australia's net farm incomes by 15 per cent and reduced its farm exports by 29 per cent."
Use the concept of supply and demand to explain the paragraph above, especially whyfarms subsidiesabroad lowered Australia's net farm income and reduced its farm exports.
Part (b)
Use the concept of supply and demand to explain the paragraph above, especially whyimport barriersabroad lowered Australia's net farm income and reduced its farm exports.
Hint for both Parts (a) and (b): you can assume that the world consists only of two countries: Australia and a country called the Rest of the World. The two countries initially trade freely with each other and Australia exports its farm products to the Rest of the World. Then analyse what happens when the Rest of the World provides a production subsidy to its farmers or impose an import tariff on its imports of Australia's farm products.
(Source:Beef Central, April 20, 2020)
"Our farmers need a better deal": Study shows true cost of trade barriers
A NEW AgriFutures Australia-funded study shows that farm subsidies and import barriers abroad lowered Australia's net farm incomes by 15 per cent and reduced its farm exports by 29 per cent.
The report by Kym Anderson and Ernesto Valenzuela explores the impact of international agriculture subsidies on Australia, a non-subsidising agricultural export country.
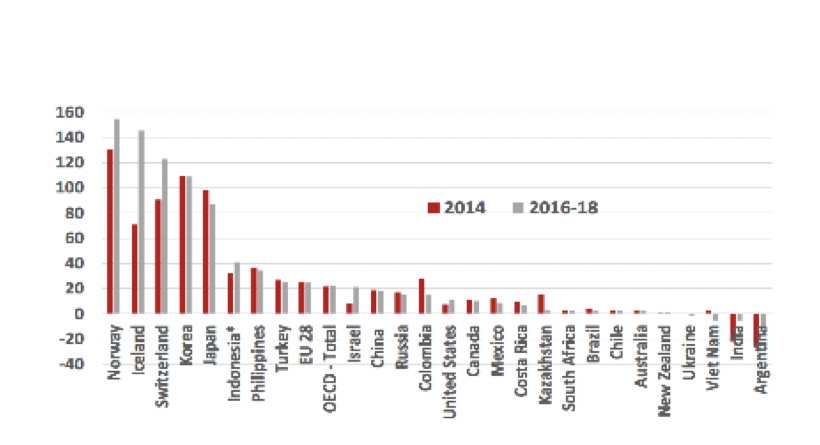
The report shows that in the four years to 2018 the average nominal rate ofassistance to farmers rose for all OECD countries by one-tenth (from 21pc to 23pc), and for the EU28 by slightly more (by one sixth, from 21pc to 25pc), between 2014 and 2016-18.
Aggregate agricultural nominal rate of assistance by country 2014 and 2016-18. (% weighted average using value of production without assistance as weights) *Indonesia refers to 2015 in place of 2016-18.
Source: OECD (2019).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


