Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
please help me with this lab graph must be done in excel and all questions answered please !!!!!! 116 Interactive Workbook for General Chemistry ||
please help me with this lab 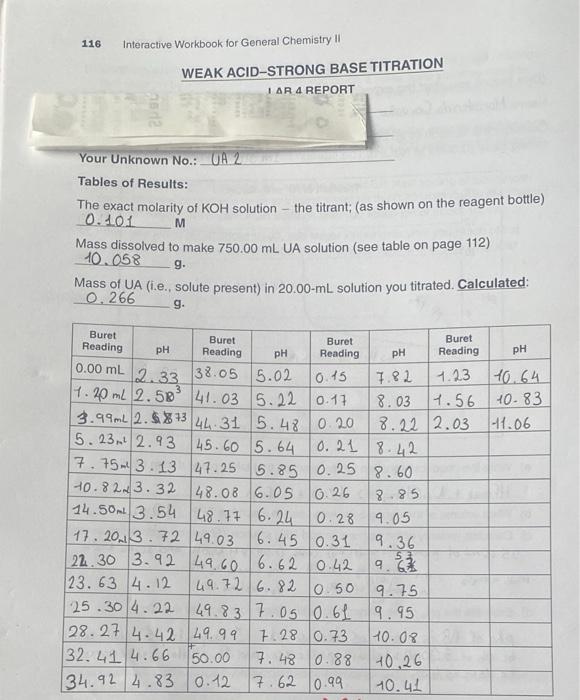
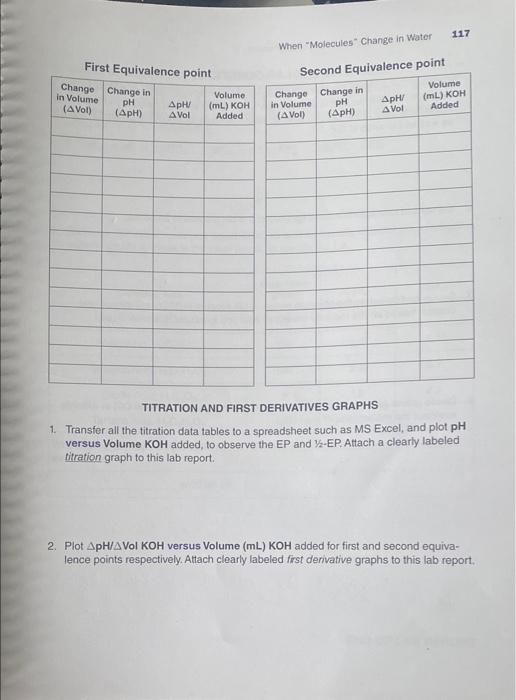

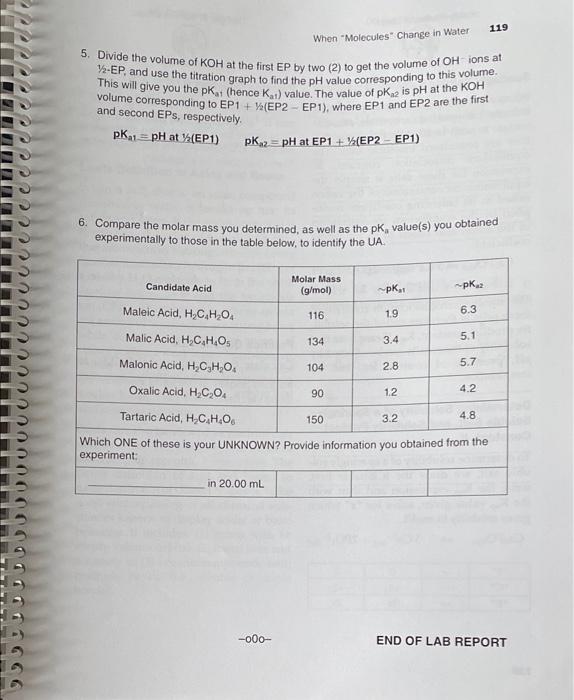
116 Interactive Workbook for General Chemistry || WEAK ACID-STRONG BASE TITRATION IAR A REPORT Your Unknown No.: UA 2 Tables of Results: The exact molarity of KOH solution the titrant; (as shown on the reagent bottle) 0.101 M Mass dissolved to make 750.00 mL UA solution (see table on page 112) 10.058 g. Mass of UA (i.e., solute present) in 20.00-ml solution you titrated. Calculated: 0.266 g. pH pH 12.33 0.45 7.82 6.26 Buret Buret Buret Buret Reading pH Reading pH Reading Reading 0.00 mL 138.05 5.02 1.23 10.64 3 7.40 ml 2.589 41.03 5.22 0.17 8.03 1.56 40.83 3.99mL 2.5%+344 31 5.48 0.20 8.22 2.03 -1.06 15. 23. 2.93 45.60 5.64 10.21 8.42 7.753.13 47.25 5.85 0.25 8.60 H0.82.3.32 148.08 6.05 2.85 14.500 3.54 48.77 6.24 0.28 9.05 17. 2013. 72 49.03 6.45 0.31 9.36 122.30 3.92 49.60 6.62 0.42 . 123.63 4.12 49.72 6.82 To 5o 9.75 125.30/4.22 49.83 7.05 0.61 19.95 28.27 4.42 49.99 7.28 0.73 10.08 132.41 4.66 50.00 7.48 0.88 10,26 134.92 4.83 0.12 7.62 0.99 10.41 lonno 9 117 When "Molecules" Change in Water First Equivalence point Change in Volume (Vol) Change in pH (ApH) Second Equivalence point Change Change in Volume in Volume pH / (mL) KOM (pH) Vol Added Volume (mL) KOH Added pHV A Vol (A Vol) TITRATION AND FIRST DERIVATIVES GRAPHS 1 Transfer all the titration data tables to a spreadsheet such as MS Excel, and plot pH versus Volume KOH added, to observe the EP and Y-EP Attach a clearly labeled titration graph to this lab report, 2. Plot ApH/A VOI KOH versus Volume (mL) KOH added for first and second equiva- lence points respectively, Attach clearly labeled first derivative graphs to this lab report, 118 Interactive Workbook for General Chemistry II POST-LAB QUESTIONS 1. Take the volume (ML) of KOH corresponding to the highest ApH/A VOI KOH as vol- ume KOH used to reach the equivalence point. Given the exact molarity of KOH, and the volume (mL) of the UA you titrated, calculate molarity of UA based on the first EP as well as the second EP 2. Set up and calculate the mass (grams) of the UA present in 20.00 mL. 3. Set up and calculate the absolute moles of UA present in 20.00-ml aliquot you titrated, based on the molarity (mol/L) of acid you found in 02 above. 4. Divide grams (you found in Q2) by the absolute moles (you found in 03) in order to work out the molar mass of your UA 119 When "Molecules" Change in Water 5. Divide the volume of KOH at the first EP by two (2) to get the volume of OH ions at 7-EP, and use the titration graph to find the pH value corresponding to this volume. This will give you the pk (hence Ku) value. The value of pk is pH at the KOH volume corresponding to EP1 + (EP2 EP1), where EP1 and EP2 are the first and second EPs, respectively. pK21=pH at (EP1) pK2=pH at EP1+ (EP2 - EP1) 6. Compare the molar mass you determined, as well as the pk, value(s) you obtained experimentally to those in the table below, to identify the UA Candidate Acid Molar Mass (g/mol) ~pk pk. Maleic Acid, HC H20 116 1.9 6.3 134 3.4 5.1 Malic Acid, H.C.H.O Malonic Acid, H.CH,0. Oxalic Acid, H.C.O. 104 2.8 5.7 90 12 4.2 Tartaric Acid, H.C.H.06 150 3.2 4.8 Which ONE of these is your UNKNOWN? Provide information you obtained from the experiment in 20.00 ml -000- END OF LAB REPORT graph must be done in excel and all questions answered please !!!!!!




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


