Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please help. Not sure what I'm doing wrong. Depreciation Methods Lord Company purchased a machine on January 2, 2019, for $70,000. The machine had an

Please help. Not sure what I'm doing wrong.
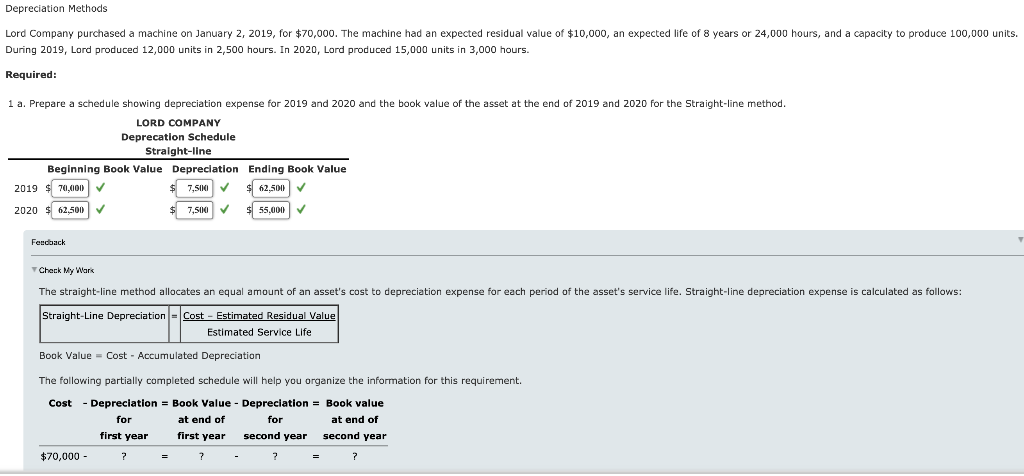
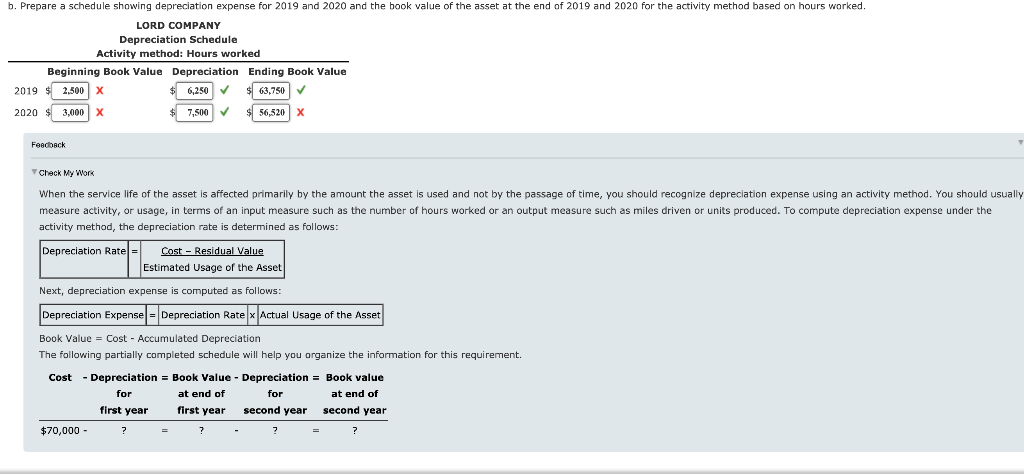
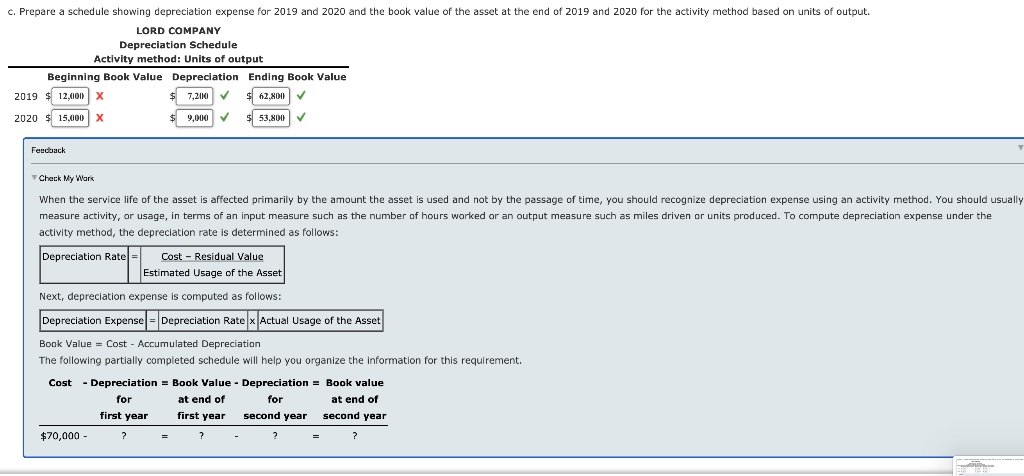
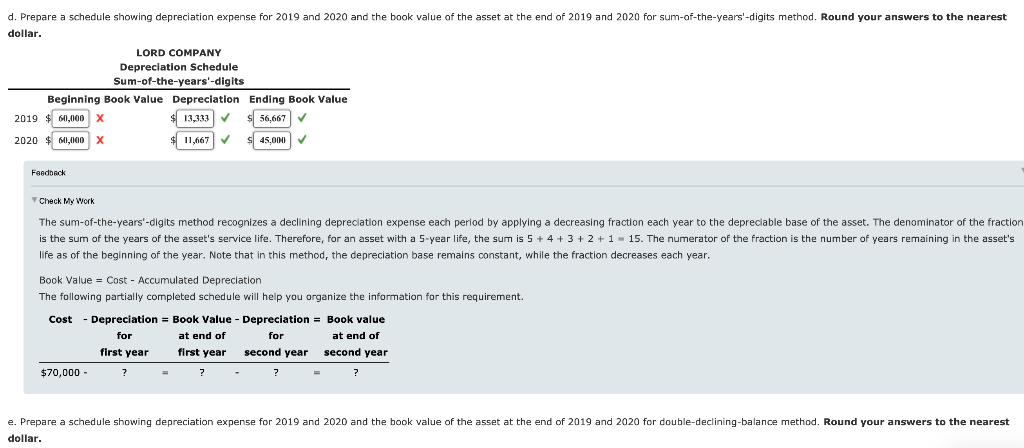
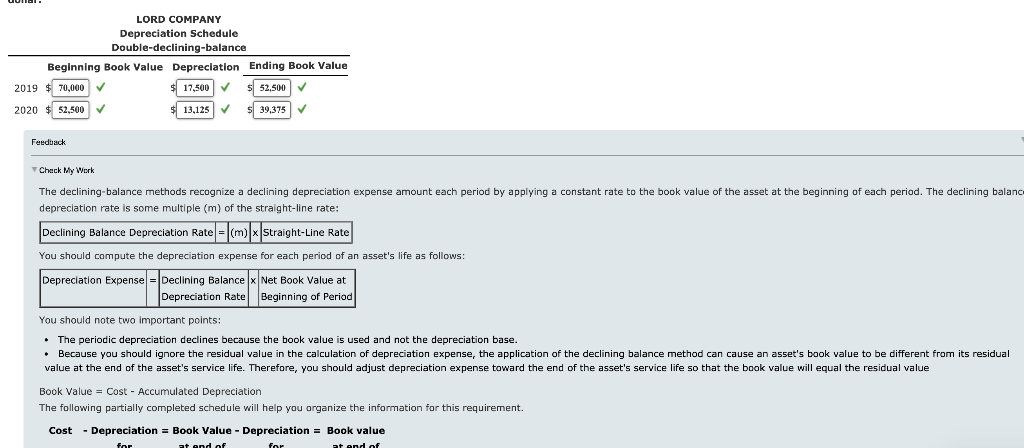
Depreciation Methods Lord Company purchased a machine on January 2, 2019, for $70,000. The machine had an expected residual value of $10,000, an expected life of 8 years or 24,000 hours, and a capacity to produce 100,000 units. During 2019, Lord produced 12,000 units in 2,500 hours. In 2020, Lord produced 15,000 units in 3,000 hours. Required: 1 a. Prepare a schedule showing depreciation expense for 2019 and 2020 and the book value of the asset at the end of 2019 and 2020 for the Straight-line method. LORD COMPANY Deprecation Schedule Straight-line Beginning Book Value Depreciation Ending Book Value 2019 $ 70,000 7,500 62.500 2020 62,500 $ 7,500 $ 55,000 Feedback Check My Wars The straight-line method allocates an equal amount of an asset's cost to depreciation expense for each period of the asset's service life. Straight-line depreciation expense is calculated as follows: Straight-Line Depreciation = Cost - Estimated Residual Value Estimated Service Life Book Value = Cost - Accumulated Depreciation The following partially completed schedule will help you organize the information for this requirement. Cost - Depreciation = Book Value - Depreciation = Book value for at end of for at end of first year first year second year second year $70,000 - b. Prepare a schedule showing depreciation expense for 2019 and 2020 and the book value of the asset at the end of 2019 and 2020 for the activity method based on hours worked. LORD COMPANY Depreciation Schedule Activity method: Hours worked Beginning Book Value Depreciation Ending Book Value 2019 2,500 X 6,250 63,750 2020 3,000 7.500 56,520 X X Feedback Check My Work When the service life of the asset is affected primarily by the amount the asset is used and not by the passage of time, you should recognize depreciation expense using an activity method. You should usually measure activity, or usage, in terms of an input measure such as the number of hours worked or an output measure such as miles driven or units produced. To compute depreciation expense under the activity method, the depreciation rate is determined as follows: Depreciation Ratel Cost - Residual Value Estimated Usage of the Asset Next, depreciation expense is computed as follows: Depreciation Expense = Depreciation Rate x Actual Usage the Asset Book Value = Cost - Accumulated Depreciation The following partially completed schedule will help you organize the information for this requirement. at end of Cost - Depreciation = Book Value - Depreciation = Book value for at end of for first year first year second year second year $70,000 - ? ? ? = 7 output. C. Prepare a schedule showing depreciation expense for 2019 and 2020 and the book value of the asset at the end of 2019 and 2020 for the activity method based on units LORD COMPANY Depreciation Schedule Activity method: Units of output Beginning Book Value Depreciation Ending Book Value 2019 $ 12,000 7,200 $ 62.800 2020 15.000 X $ 9,000 $ 53.800 Feedback Check My Wars When the service life of the asset is affected primarily by the amount the asset is used and not by the passage of time, you should recognize depreciation expense using an activity method. You should usually measure activity, or usage, in terms of an input measure such as the number of hours worked or an output measure such as miles driven or units produced. To compute depreciation expense under the activity method, the depreciation rate is determined as follows: Depreciation Rate = Cost - Residual Value Estimated Usage of the Asset Next, depreciation expense is computed as follows: Depreciation Expense = Depreciation Rate x Actual Usage the Asset Book Value = Cost - Accumulated Depreciation The following partially completed schedule will help you organize the information for this requirement. Cost - Depreciation = Book Value - Depreciation = Book value at end of at end of first year first year second year second year $70,000 - for for ? d. Prepare a schedule showing depreciation expense for 2019 and 2020 and the book value of the asset at the end of 2019 and 2020 for sum-of-the-years'-digits method. Round your answers to the nearest dollar. LORD COMPANY Depreciation Schedule Sum-of-the-years'-digits Beginning Book Value Depreciation Ending Book Value 2019 $ 60,000 X $ 13,333 56,667 2020 60,000 x $ 11,467 $ 45,000 Feedback Check My Work The sum-of-the-years'-digits method recognizes a declining depreciation expense each period by applying a decreasing fraction each year to the depreciable base of the asset. The denominator of the fraction is the sum the years of the asset's service life. Therefore, for an asset with a 5-year life, the sum is 5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1 - 15. The numerator of the fraction is the number of years remaining in the asset's life as of the beginning of the year. Note that in this method, the depreciation base remains constant, while the fraction decreases each year. Book Value = Cost - Accumulated Depreciation The following partially completed schedule will help you organize the information for this requirement. Cost - Depreciation = Book Value - Depreciation = Book value for at end of at end of first year first year second year second year $70,000 - for 7 e. Prepare a schedule showing depreciation expense for 2019 and 2020 and the book value of the asset at the end of 2019 and 2020 for double-declining-balance method. Round your answers to the nearest dollar. LORD COMPANY Depreciation Schedule Double-declining-balance Beginning Book Value Depreciation Ending Book Value $ 17,500 52,500 52,500 13,125 $ 39,375 2019 70,000 2020 Feedback Check My Work The declining-balance methods recognize a declining depreciation expense amount each period by applying a constant rate to the book value of the asset at the beginning of each period. The declining balano depreciation rate is some multiple (m) of the straight-line rate: Declining Balance Depreciation Rate = (m)|x Straight-Line Rate You should compute the depreciation expense for each period of an asset's life as follows: Depreciation Expense = Declining Balance x Net Book Value at Depreciation Rate Beginning of Period You should note two important points: The periodic depreciation declines because the book value is used and not the depreciation base. . Because you should ignore the residual value in the calculation of depreciation expense, the application of the declining balance method can cause an asset's book value to be different from its residual value at the end of the asset's service life. Therefore, you should adjust depreciation expense toward the end of the asset's service life so that the book value will equal the residual value Book Value = Cost - Accumulated Depreciation The following partially completed schedule will help you organize the information for this requirement. Cost - Depreciation = Book Value - Depreciation = Book value nt and of at end of 2. Time-based X methods are appropriate when a company estimates that the service potential of the asset will decline more quickly in the early periods of the asset's useful life. Time-based methods are appropriate when the service life of an asset is affected primarily by the amount the asset is used. FeedbackStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


