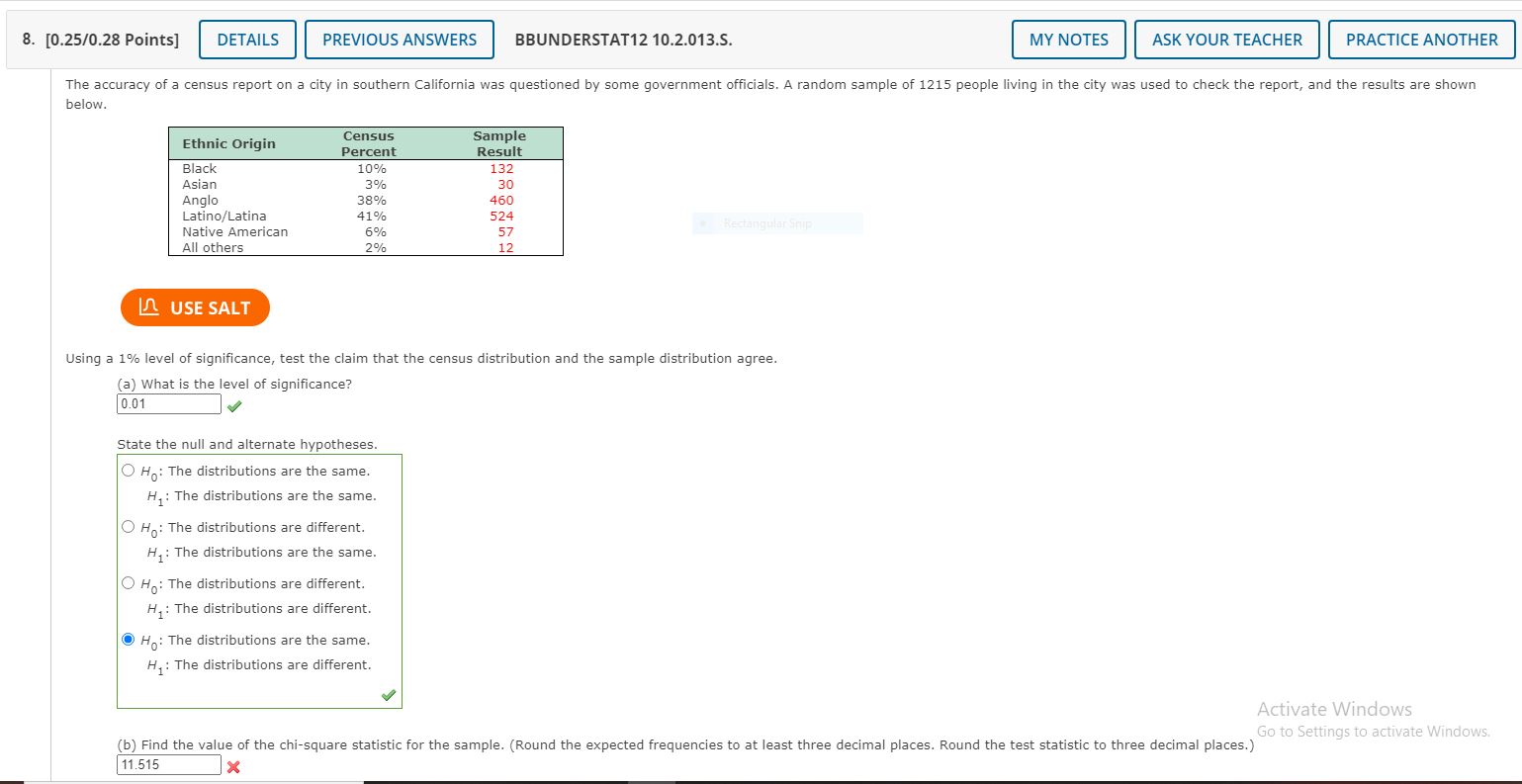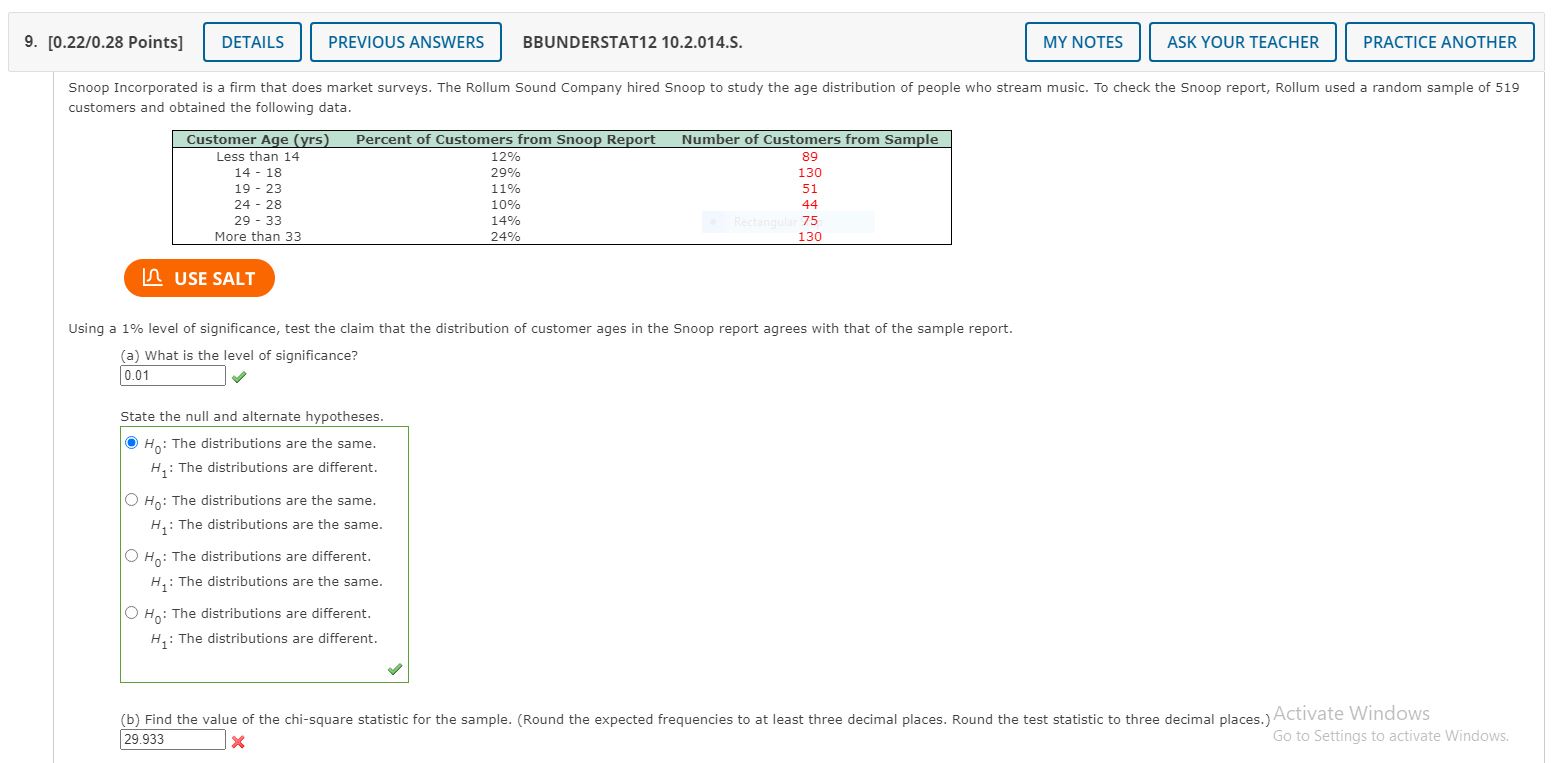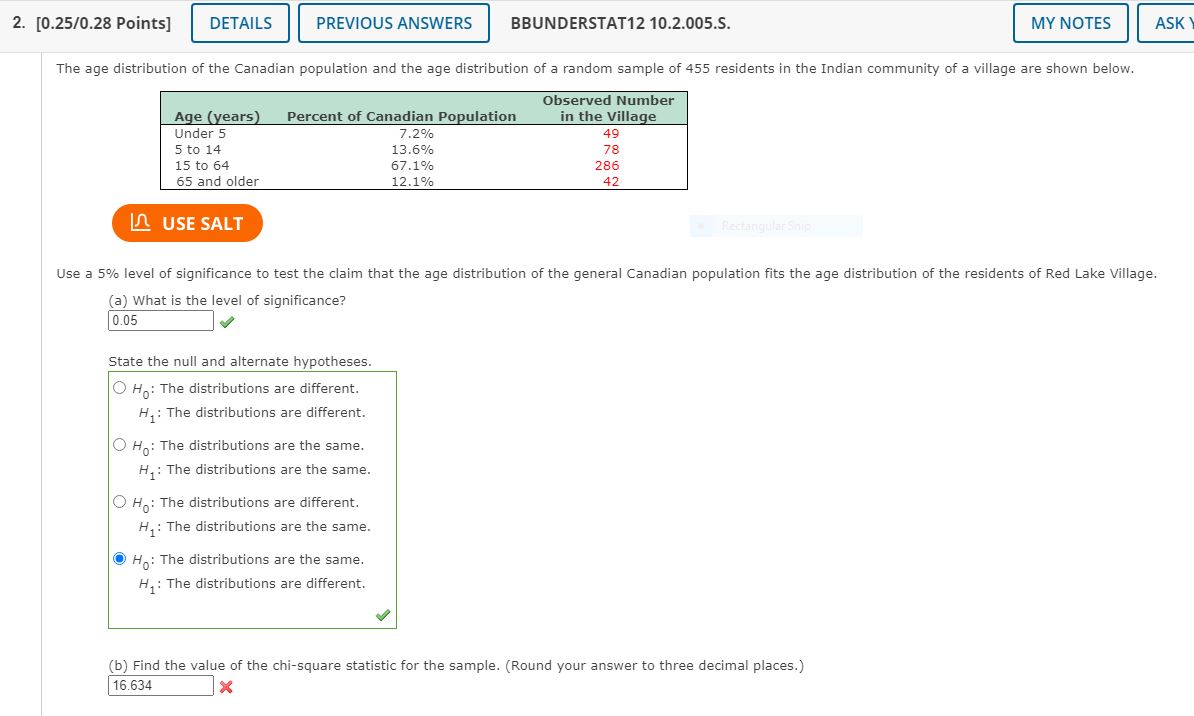
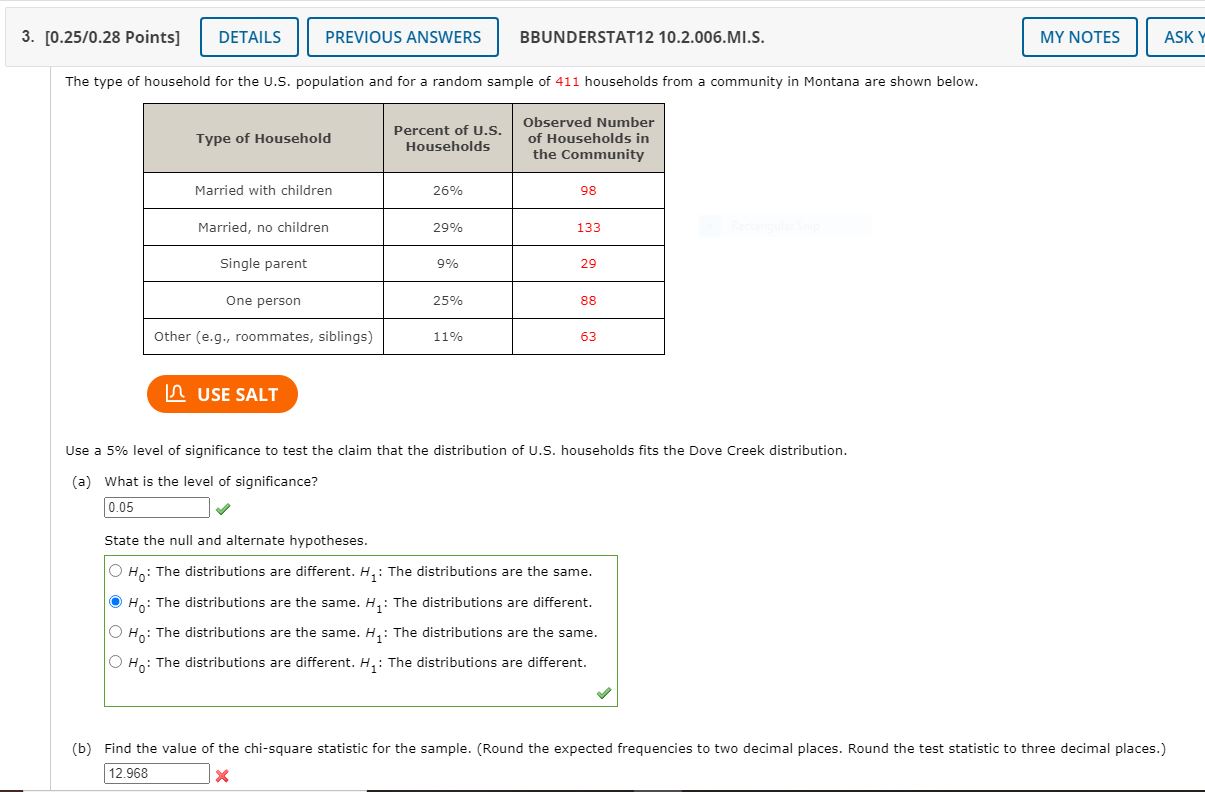

Please help on the wrong questions, AS IN THE PICTURE. thanks
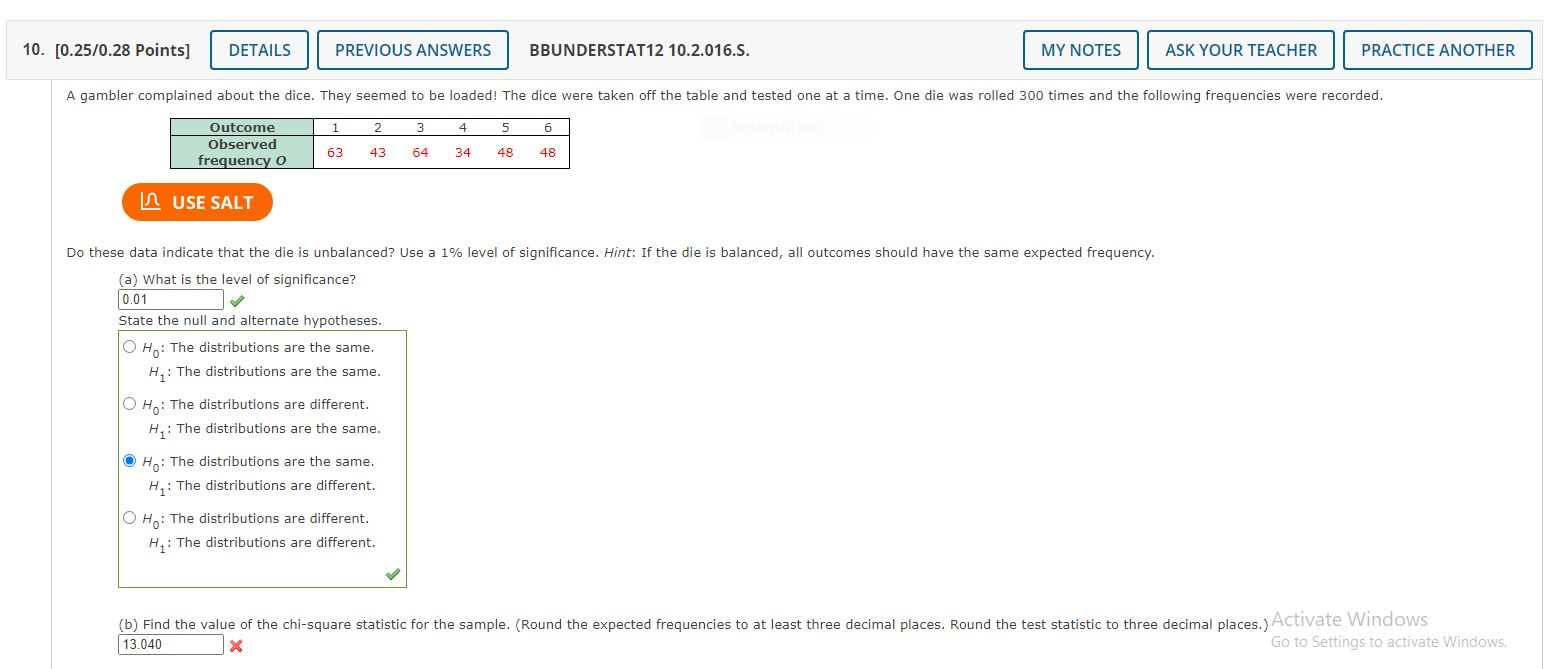
10. [0.251028 Points] PREVIOUSANSWERS BBUNDERSTAT12 10.2.0165. ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER A gambler complained about the dice. They seemed to be loaded! The dice were taken off the table and tested one at a time. One die was rolled 300 times and the following frequencies were recorded 53 43 64 34 48 4B l USE SALT Do these data indicate that the die is unbalanced? Use a 1% level of signicance. Hint: If the die is balanced, all outcomes should have the same expected frequency. (a) What is the ievel of signicance? om State the null and alternate hypotheses. 0 HD: The distributions are the same H1: The distributions are the same. 0 HD: The distributions are different. H1: The distributions are the same. HD: The distributions are the same H1: The distributions are different. 0 HD: The distributions are different. H1: The distributions are different. I inciov-ss (in) Find the vaiue of the chi-square statistic for the sample. (Round the expected frequencies to at least three decimal places. Round the test stau'stic to three decimal placesJACIVJEe 13 040 x L30 to S \f3. [0.25!0.28 Points] DETAILS PREVIOUS ANSWERS BBUNDERSTATIZ 10.2.006.MI.S. MY NOTES | ASK '1' The type of household for the U.S. population and for a random sample of 411 households from a community in Montana are shown below. Married with children 26% 98 Married, no children 29% 133 Single parent 9% 29 ne person 259i) BS Other (e.g., roommates, siblings) 11% 63 I USE SALT Use a 5% level of signicance to test the claim that the distribution of U5. households ts the Dove Creek distribution. (a) What is the level of significance? 0.05 State the null and alternate hypotheses. 0 H0: The distributions are different. H1: The distributions are the same. Q H0: The distributions are the same. H1: The distributions are different. 0 H": The distributions are the same. H1: The distributions are the same. O H": The distributions are different. H1: The distributions are different. I (b) Find the value of the chiisquare statistic for the sample. (Round the expected frequencies to two decimal places. Round the test slatisb'c to three decimal places.) 12.968 X 4. [0.251028 Paints] PREVIOUS ANSWERS EBUNDERSTATi 2 10.2.0015. | ASK YOUR TEAC The types of raw materials used to construct stone tools found at an archaeological site are shown below. A random samote of 1486 stone tools were obtained from a current excavation : Basalt Obsidian 10.6% 158 Welded Tuff 11.4% 184 Pedernal chert 13.1% 198 Other 3.6% 49 IE USE SA 1 Use a 1% level of signicance to test the claim that the regional distribution of raw materials ts the distribution at the current excavation site. (a) What is the level of signicance? um ,p State the nuil and alternate hypotheses. O H\": The distributions are different. H1: The distributions are different. 0 H0: The distributions are the same. H1: The distributions are the same. HQ: The distributions are the same. H1: The distributions are ditferent. 0 H0: The distributions are different. H1: The distributions are the same. I (b) Find the value of the chiisquare statistic for the sample. (Round the expected frequencies to at least three decimai places. Round the test statistic to three decEmal places.) flu 3-293 3' L3: 5. [0.251'028 Points] DETAILS PREVIOUS ANSWERS BBUNDERSTAT'IZ 10.2.0035. MY NOTES | ASK YOUR TE)! The types of browse favored by deer are shown in the following table. Using binoculars, volunteers observed the feeding habits of a random sample of 320 deer Tamed-imn inst-mm aming on "I'hislaimt Sage brush 32% 102 Rabbit brush 38.7%: 13 1 Salt brush 12% 39 Service berry 9.3% 29 Othe! 8% 19 I USE SALT Use a 5% level of significance to test the claim that the natural distribution of browse Fits the deer feeding pattern. (a) What is the level of signicance? 005 State the null and aiternate hypotheses. HD: The distributions are the same. H1: "he distributions are different. 0 HQ: The distributions are different. H1: "he distributions are different. 0 HI]: The distributions are different. H1: The distributiuns are the same. O HD: The distributions are the same. H1: The distributions are the same. J (b) Find the value of the chi-square statistic for the sample. (Round the expected frequencies to at least tthE decimal places. Round the test statistic to three decimal places.) 3.710 x \f6. [0.221028 Points] PREVIOUS ANSWERS BBUNDERSTAT12 10.2.011.M|.S. ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER The Fish and Game Department stocked a lake with sh in the following proportions: 30% catsh, 15% bass, 40% bluegill, and 15% pike. Five years later it sampled the lake to see if the distribution of sh had changed. It found that the 500 sh in the sample were distributed as follows. 116 75 224 85 I USE SALT In the 5-year intenlal, did the distbution of sh change at the 0.05 level? 7. [0.251023 Points] PREVIOUS ANSWERS BBUNDERSTAT12 10.2.0125. ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER The director of library services at a college did a survey of types of books (by subject) in the circulation library. Then she used library records to take a random sample of 888 books checked out last term and classied the books in the sample by subject. The results are Sl'IGWI'I below. Business Humanities 25% 213 Natural Science 20% 226 Social Science 15% 1 10 All other subjects 8% 69 I USES Using a 5% level of signicance, test the claim that the subject distribution of books in the library ts the distribution of books checked out by students. (a) What is the level of signicance? 0,05 State the null and alternate hypotheses. O H\": The distributions are different. H1: The distributions are different. H0: The distributions are the same. H1: The distributions are different. 0 H0: The distributions are different. H1: The distributions are the same. O H\": The distributions are the same. H1: The distributions are the same. \\f 22.445 x (b) Find the value of the chi-square statistic for the sample. (Round the expected frequencies to three decimal places. Round the test statistic to three decimal places.) . ctivate Winclov-rs L'C' .ii' D5 1L 8. [0.25/0.28 Points] DETAILS PREVIOUS ANSWERS BBUNDERSTAT12 10.2.013.S. MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER The accuracy of a census report on a city in southern California was questioned by some government officials. A random sample of 1215 people living in the city was used to check the report, and the results are shown below. Ethnic Origin Census Sample Percent Result Black 10% 132 Asian 3% 30 Anglo 38% 460 Latino/Latina 41% 524 Native American 6% 57 Rectangular Ship All others 2% 12 LA USE SALT Using a 1% level of significance, test the claim that the census distribution and the sample distribution agree. (a) What is the level of significance? 0.01 State the null and alternate hypotheses. O Ho: The distributions are the same. H, : The distributions are the same. O Ho: The distributions are different. H : The distributions are the same. O Ho: The distributions are different. H. : The distributions are different. O Ho: The distributions are the same. H, : The distributions are different. Activate Windows Go to Settings to activate Windows. b) Find the value of the chi-square statistic for the sample. (Round the expected frequencies to at least three decimal places. Round the test statistic to three decimal places.) 11.515 X(b) Find the value of the chi-square statistic for the sample. (Round the expected frequencles to at least three decimal places. Round the test statistic to three decimal places.) 29.933 x Are all the expected frequencies greater than 5? @ Yes 0 No I What sampling distribution will you use? O uniform 0 normal 0 Student's t chisquare I What are the degrees of freedom? 5 u! (c) Estimate the P-value 0f the sample test statistic. O P-value b 0.100 O 0.050