Please help.
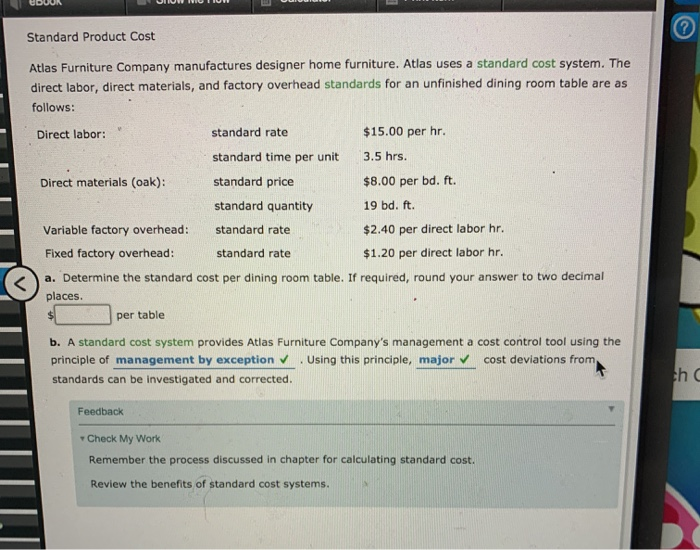
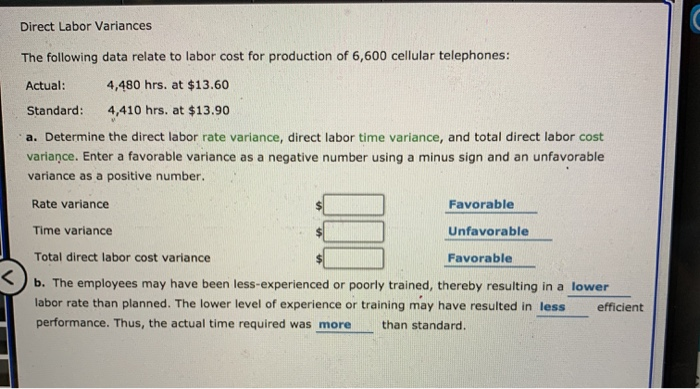
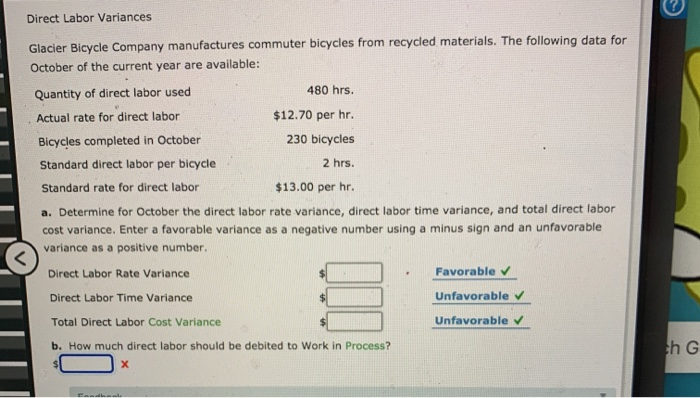
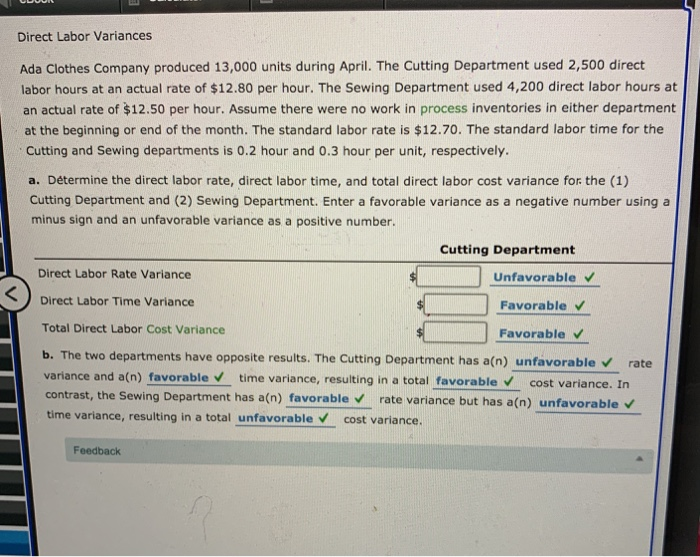
Standard Product Cost Atlas Furniture Company manufactures designer home furniture. Atlas uses a standard cost system. The direct labor, direct materials, and factory overhead standards for an unfinished dining room table are as follows: Direct labor: standard rate $15.00 per hr standard time per unit 3.5 hrs. Direct materials (oak): standard price $8.00 per bd. ft. standard quantity 19 bd. ft. Variable factory overhead: standard rate $2.40 per direct labor hr. Fixed factory overhead: standard rate $1.20 per direct labor hr. a. Determine the standard cost per dining room table. If required, round your answer to two decimal places per table b. A standard cost system provides Atlas Furniture Company's management a cost control tool using the principle of management by exception . Using this principle, major cost deviations from standards can be investigated and corrected. th Feedback Check My Work Remember the process discussed in chapter for calculating standard cost. Review the benefits of standard cost systems. Direct Materials Variances Actual: The following data relate to the direct materials cost for the production of 2,100 automobile tires: 60,000 lbs. at $1.85 per lb. Standard: 58,200 lbs. at $1.90 per lb. a. Determine the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. Direct Materials Price Variance Favorable Direct Materials Quantity Variance Unfavorable Total Direct Materials Cost Variance Unfavorable b. The direct materials price variance should normally be reported to the Purchasing Department When lower amounts of direct materials are used because of production efficiencies, the variance would be reported to the Production Supervisor . When the favorable use of raw materials is caused by the purchase of higher-quality raw materials, the variance should be reported to the Purchasing Department Feedback Direct Labor Variances The following data relate to labor cost for production of 6,600 cellular telephones: Actual: 4,480 hrs. at $13.60 Standard: 4,410 hrs. at $13.90 a. Determine the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. Rate variance Favorable Time variance Unfavorable Total direct labor cost variance Favorable b. The employees may have been less-experienced or poorly trained, thereby resulting in a lower labor rate than planned. The lower level of experience or training may have resulted in less efficient performance. Thus, the actual time required was more than standard. Direct Labor Variances Glacier Bicycle Company manufactures commuter bicycles from recycled materials. The following data for October of the current year are available: Quantity of direct labor used 480 hrs. Actual rate for direct labor $12.70 per hr. Bicycles completed in October 230 bicycles Standard direct labor per bicycle 2 hrs. Standard rate for direct labor $13.00 per hr. a. Determine for October the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. Direct Labor Rate Variance Favorable Direct Labor Time Variance Unfavorable Total Direct Labor Cost Variance Unfavorable b. How much direct labor should be debited to Work in Process? th G X Direct Labor Variances Ada Clothes Company produced 13,000 units during April. The Cutting Department used 2,500 direct labor hours at an actual rate of $12.80 per hour. The Sewing Department used 4,200 direct labor hours at an actual rate of $12.50 per hour. Assume there were no work in process inventories in either department at the beginning or end of the month. The standard labor rate is $12.70. The standard labor time for the Cutting and Sewing departments is 0.2 hour and 0.3 hour per unit, respectively. a. Determine the direct labor rate, direct labor time, and total direct labor cost variance for the (1) Cutting Department and (2) Sewing Department. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. Cutting Department Direct Labor Rate Variance Unfavorable Direct Labor Time Variance Favorable Total Direct Labor Cost Variance Favorable b. The two departments have opposite results. The Cutting Department has a(n) unfavorable rate variance and a(n) favorable time variance, resulting in a total favorable cost variance. In contrast, the Sewing Department has a(n) favorable rate variance but has a(n) unfavorable time variance, resulting in a total unfavorable cost variance, Feedback