Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please help, where did I go wrong. Thank you Skye's earnings per share last year were $3.75. The common stock sells for $60.00, last year's
Please help, where did I go wrong. Thank you
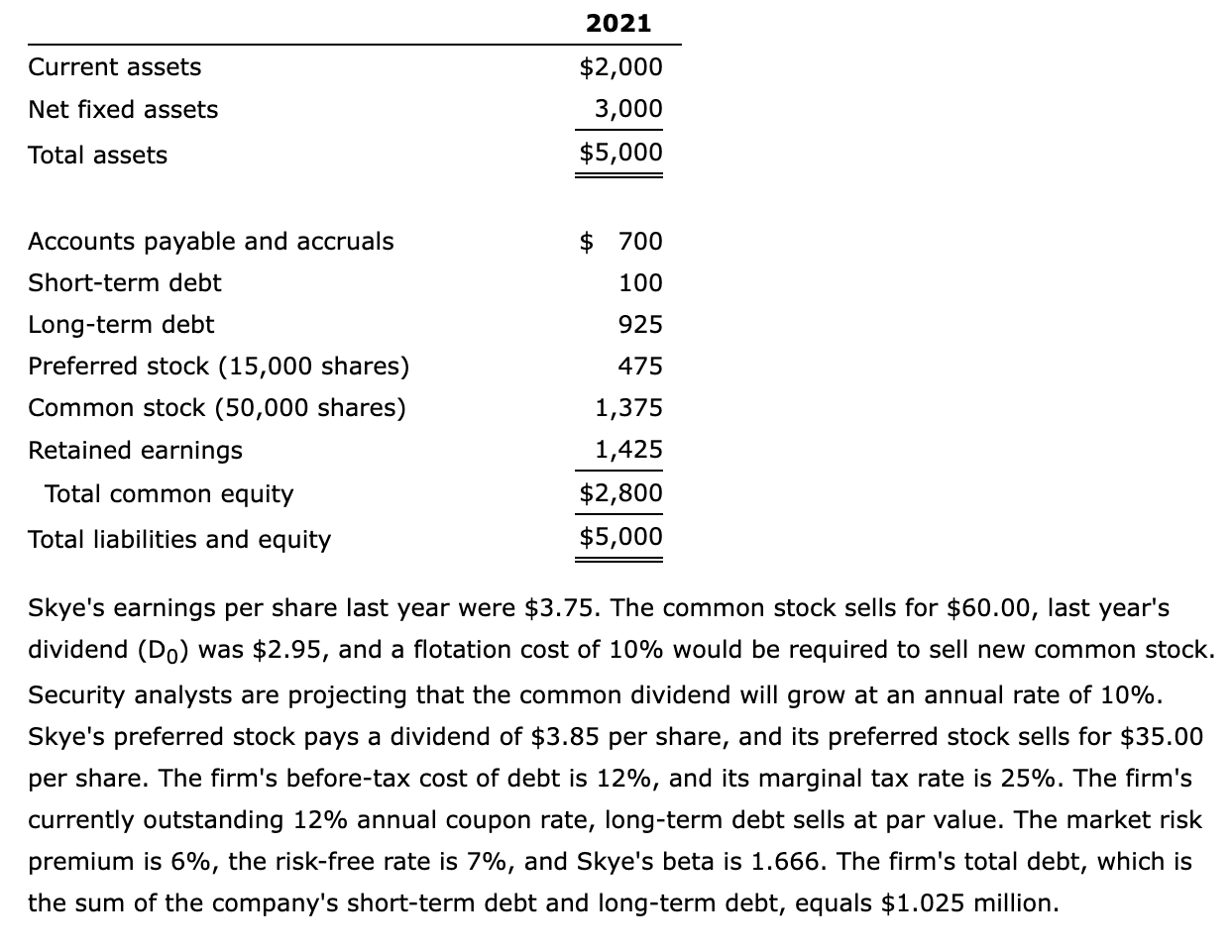
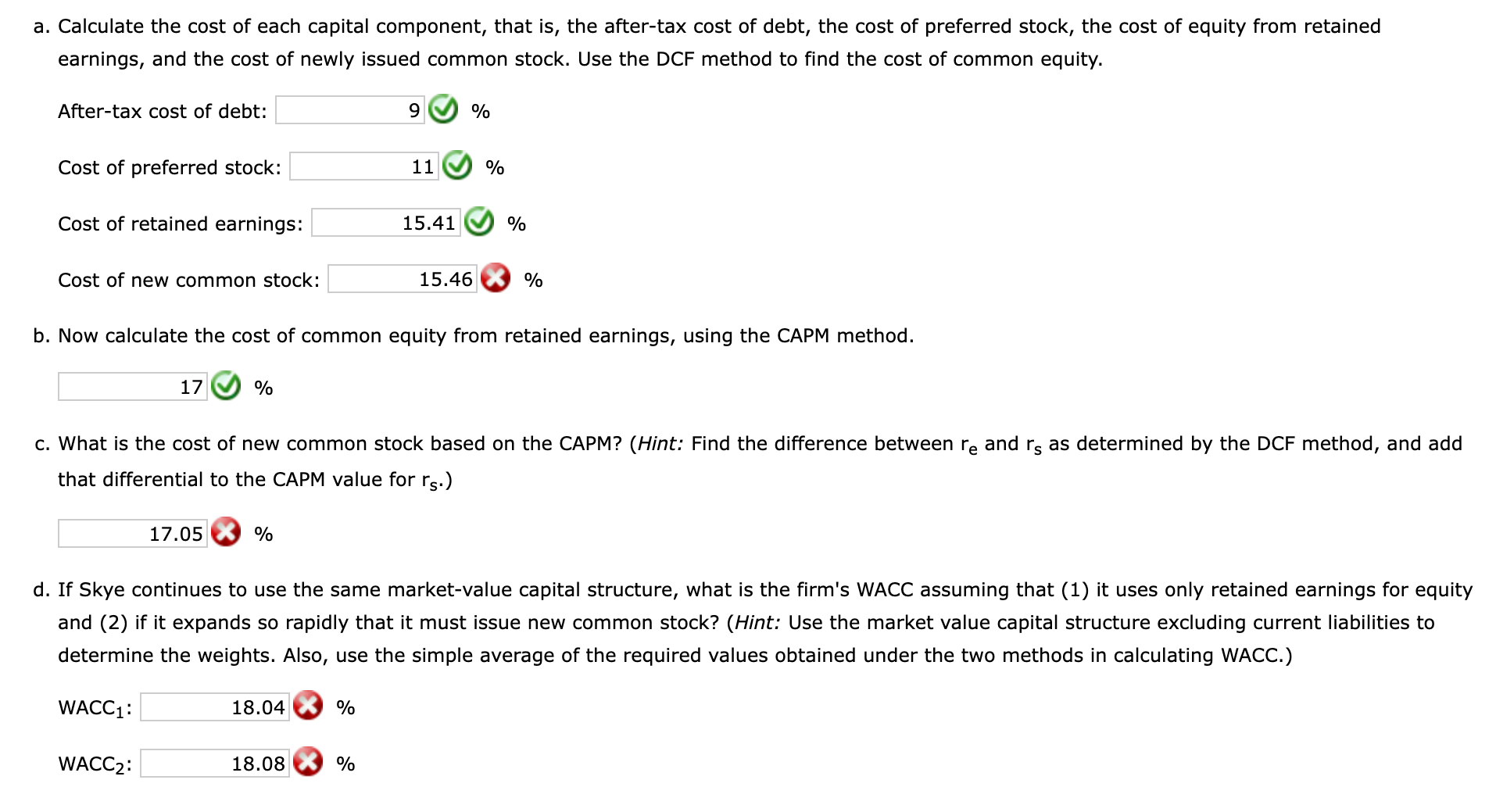
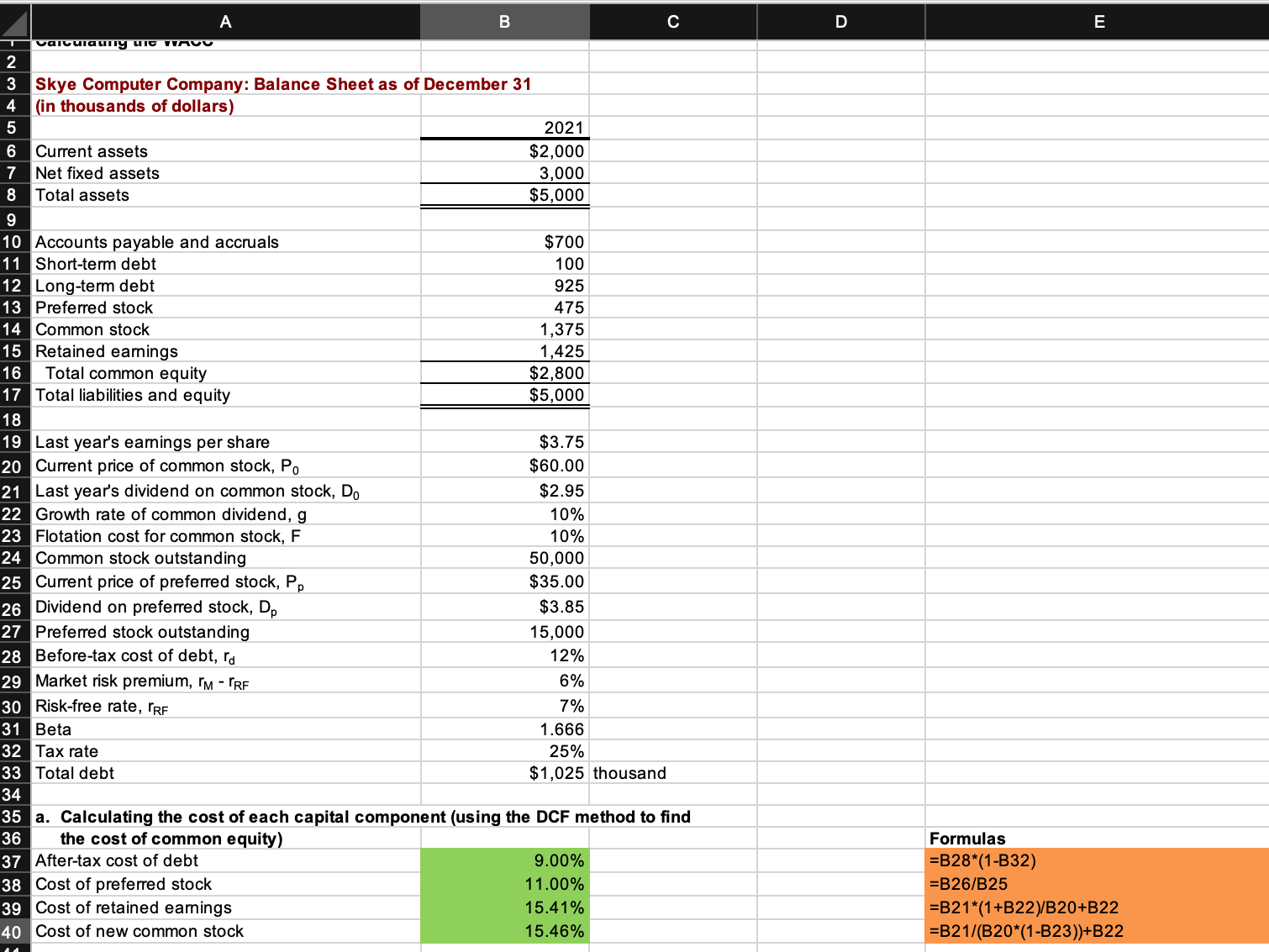
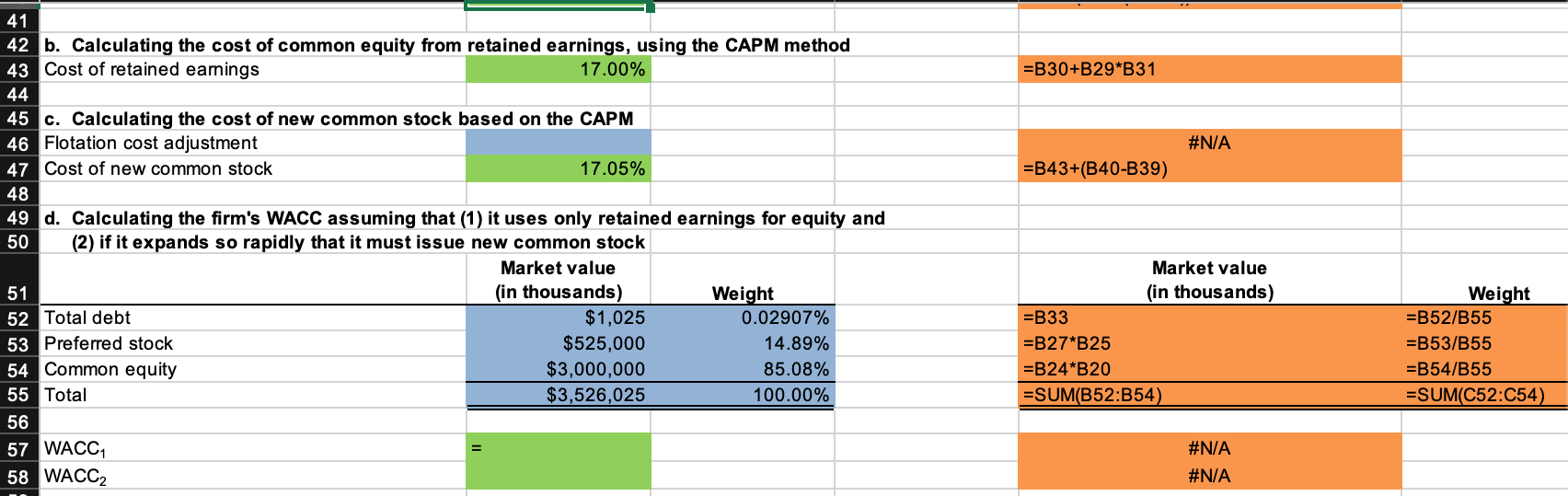 Skye's earnings per share last year were $3.75. The common stock sells for $60.00, last year's dividend (D0) was $2.95, and a flotation cost of 10% would be required to sell new common stock. Security analysts are projecting that the common dividend will grow at an annual rate of 10%. Skye's preferred stock pays a dividend of $3.85 per share, and its preferred stock sells for $35.00 per share. The firm's before-tax cost of debt is 12%, and its marginal tax rate is 25%. The firm's currently outstanding 12% annual coupon rate, long-term debt sells at par value. The market risk premium is 6%, the risk-free rate is 7%, and Skye's beta is 1.666 . The firm's total debt, which is the sum of the company's short-term debt and long-term debt, equals $1.025 million. a. Calculate the cost of each capital component, that is, the after-tax cost of debt, the cost of preferred stock, the cost of equity from retained earnings, and the cost of newly issued common stock. Use the DCF method to find the cost of common equity. After-tax cost of debt: % Cost of preferred stock: % Cost of retained earnings: % Cost of new common stock: 3% b. Now calculate the cost of common equity from retained earnings, using the CAPM method. % c. What is the cost of new common stock based on the CAPM? (Hint: Find the difference between re and rs as determined by the DCF method, and add that differential to the CAPM value for rs.) % d. If Skye continues to use the same market-value capital structure, what is the firm's WACC assuming that (1) it uses only retained earnings for equity and (2) if it expands so rapidly that it must issue new common stock? (Hint: Use the market value capital structure excluding current liabilities to determine the weights. Also, use the simple average of the required values obtained under the two methods in calculating WACC.) WACC 1 : % WACC 2 : % Skye Computer Company: Balance Sheet as of December 31 (in thousands of dollars) Current assets Net fixed assets Total assets Accounts payable and accruals Short-term debt Long-term debt Preferred stock Common stock Retained earnings Total common equity Total liabilities and equity Last year's earnings per share Current price of common stock, P0 Last year's dividend on common stock, D0 Growth rate of common dividend, g Flotation cost for common stock, F Common stock outstanding Current price of preferred stock, Pp Dividend on preferred stock, Dp Preferred stock outstanding Before-tax cost of debt, rd Market risk premium, rMrRF Risk-free rate, rRF Beta Tax rate Total debt \begin{tabular}{r} 2021 \\ \hline$2,000 \\ 3,000 \\ \hline$5,000 \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{r} \hline \hline$700 \\ 100 \\ 925 \\ 475 \\ 1,375 \\ 1,425 \\ \hline$2,800 \\ \hline$5,000 \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} $3.75 $60.00 $2.95 10% 10% 50,000 $35.00 $3.85 15,000 12% 6% 7% 1.666 25% $1,025 thousand a. Calculating the cost of each capital component (using the DCF method to find the cost of common equity) After-tax cost of debt Cost of preferred stock Cost of retained earnings Cost of new common stock 9.00% Formulas 11.00% =B28(1B32) =B26/B25 =B21(1+B22)/B20+B22 =B21/(B20(1B23))+B22 41 42 b. Calculating the cost of common equity from retained earnings, using the CAPM method 43 Cost of retained earnings 44 45 46 c. Calculating the cost of new common stock based on the CAPM Flotation cost adjustment Cost of new common stock 17.05% = B43+(B40-B39) d. Calculating the firm's WACC assuming that (1) it uses only retained earnings for equity and (2) if it expands so rapidly that it must issue new common stock Market value (in thousands) Weight \begin{tabular}{|c|} \hline \begin{tabular}{l} Market value \\ (in thousands) \end{tabular} \\ \hline= =B33 \\ \hline=B27B25 \\ \hline=B24B20 \\ \hline= =SUM(B52:B54) \\ \hline \#N/A \\ \hline \#N/A \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|lrr} \hline Total debt & $1,025 & 0.02907% \\ \hline Preferred stock & $525,000 & 14.89% \\ \hline Common equity & $3,000,000 & 85.08% \\ \hline Total & $3,526,025 & 100.00% \\ \hline \end{tabular} =B30+B29B31 48 49 50 \begin{tabular}{l|rr|} \hline & \begin{tabular}{c} Market value \\ (in thousands) \end{tabular} & \multicolumn{1}{|c|}{ Weight } \\ \hline Total debt & $1,025 & 0.02907% \\ \hline Preferred stock & $525,000 & 14.89% \\ Common equity & $3,000,000 & 85.08% \\ \hline Total & $3,526,025 & 100.00% \\ \hline WACC 1 & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|c|c|} \hline \begin{tabular}{l} Market value \\ (in thousands) \end{tabular} & Weight \\ \hline= =B33 & = =B52/B55 \\ \hline=B27B25 & =B53/B55 \\ \hline=B24B20 & =B54/B55 \\ \hline= SUM(B52:B54) & = SUM(C52:C54) \\ \hline \end{tabular} WACC2
Skye's earnings per share last year were $3.75. The common stock sells for $60.00, last year's dividend (D0) was $2.95, and a flotation cost of 10% would be required to sell new common stock. Security analysts are projecting that the common dividend will grow at an annual rate of 10%. Skye's preferred stock pays a dividend of $3.85 per share, and its preferred stock sells for $35.00 per share. The firm's before-tax cost of debt is 12%, and its marginal tax rate is 25%. The firm's currently outstanding 12% annual coupon rate, long-term debt sells at par value. The market risk premium is 6%, the risk-free rate is 7%, and Skye's beta is 1.666 . The firm's total debt, which is the sum of the company's short-term debt and long-term debt, equals $1.025 million. a. Calculate the cost of each capital component, that is, the after-tax cost of debt, the cost of preferred stock, the cost of equity from retained earnings, and the cost of newly issued common stock. Use the DCF method to find the cost of common equity. After-tax cost of debt: % Cost of preferred stock: % Cost of retained earnings: % Cost of new common stock: 3% b. Now calculate the cost of common equity from retained earnings, using the CAPM method. % c. What is the cost of new common stock based on the CAPM? (Hint: Find the difference between re and rs as determined by the DCF method, and add that differential to the CAPM value for rs.) % d. If Skye continues to use the same market-value capital structure, what is the firm's WACC assuming that (1) it uses only retained earnings for equity and (2) if it expands so rapidly that it must issue new common stock? (Hint: Use the market value capital structure excluding current liabilities to determine the weights. Also, use the simple average of the required values obtained under the two methods in calculating WACC.) WACC 1 : % WACC 2 : % Skye Computer Company: Balance Sheet as of December 31 (in thousands of dollars) Current assets Net fixed assets Total assets Accounts payable and accruals Short-term debt Long-term debt Preferred stock Common stock Retained earnings Total common equity Total liabilities and equity Last year's earnings per share Current price of common stock, P0 Last year's dividend on common stock, D0 Growth rate of common dividend, g Flotation cost for common stock, F Common stock outstanding Current price of preferred stock, Pp Dividend on preferred stock, Dp Preferred stock outstanding Before-tax cost of debt, rd Market risk premium, rMrRF Risk-free rate, rRF Beta Tax rate Total debt \begin{tabular}{r} 2021 \\ \hline$2,000 \\ 3,000 \\ \hline$5,000 \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{r} \hline \hline$700 \\ 100 \\ 925 \\ 475 \\ 1,375 \\ 1,425 \\ \hline$2,800 \\ \hline$5,000 \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} $3.75 $60.00 $2.95 10% 10% 50,000 $35.00 $3.85 15,000 12% 6% 7% 1.666 25% $1,025 thousand a. Calculating the cost of each capital component (using the DCF method to find the cost of common equity) After-tax cost of debt Cost of preferred stock Cost of retained earnings Cost of new common stock 9.00% Formulas 11.00% =B28(1B32) =B26/B25 =B21(1+B22)/B20+B22 =B21/(B20(1B23))+B22 41 42 b. Calculating the cost of common equity from retained earnings, using the CAPM method 43 Cost of retained earnings 44 45 46 c. Calculating the cost of new common stock based on the CAPM Flotation cost adjustment Cost of new common stock 17.05% = B43+(B40-B39) d. Calculating the firm's WACC assuming that (1) it uses only retained earnings for equity and (2) if it expands so rapidly that it must issue new common stock Market value (in thousands) Weight \begin{tabular}{|c|} \hline \begin{tabular}{l} Market value \\ (in thousands) \end{tabular} \\ \hline= =B33 \\ \hline=B27B25 \\ \hline=B24B20 \\ \hline= =SUM(B52:B54) \\ \hline \#N/A \\ \hline \#N/A \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|lrr} \hline Total debt & $1,025 & 0.02907% \\ \hline Preferred stock & $525,000 & 14.89% \\ \hline Common equity & $3,000,000 & 85.08% \\ \hline Total & $3,526,025 & 100.00% \\ \hline \end{tabular} =B30+B29B31 48 49 50 \begin{tabular}{l|rr|} \hline & \begin{tabular}{c} Market value \\ (in thousands) \end{tabular} & \multicolumn{1}{|c|}{ Weight } \\ \hline Total debt & $1,025 & 0.02907% \\ \hline Preferred stock & $525,000 & 14.89% \\ Common equity & $3,000,000 & 85.08% \\ \hline Total & $3,526,025 & 100.00% \\ \hline WACC 1 & & \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|c|c|} \hline \begin{tabular}{l} Market value \\ (in thousands) \end{tabular} & Weight \\ \hline= =B33 & = =B52/B55 \\ \hline=B27B25 & =B53/B55 \\ \hline=B24B20 & =B54/B55 \\ \hline= SUM(B52:B54) & = SUM(C52:C54) \\ \hline \end{tabular} WACC2 Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


