PLEASE HELP WITH ALL
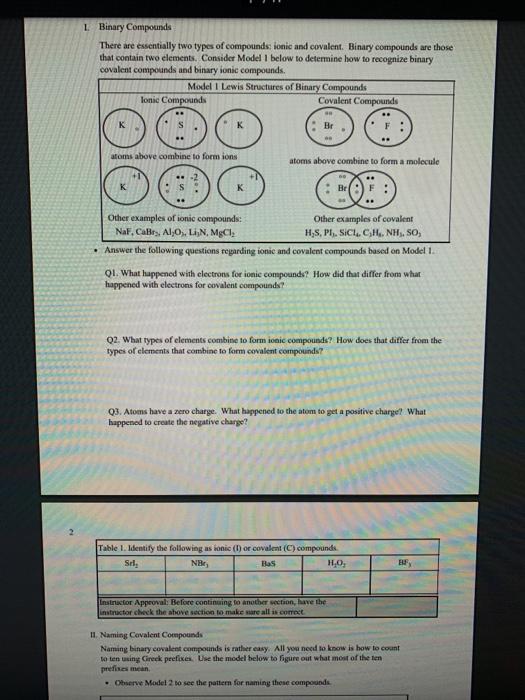
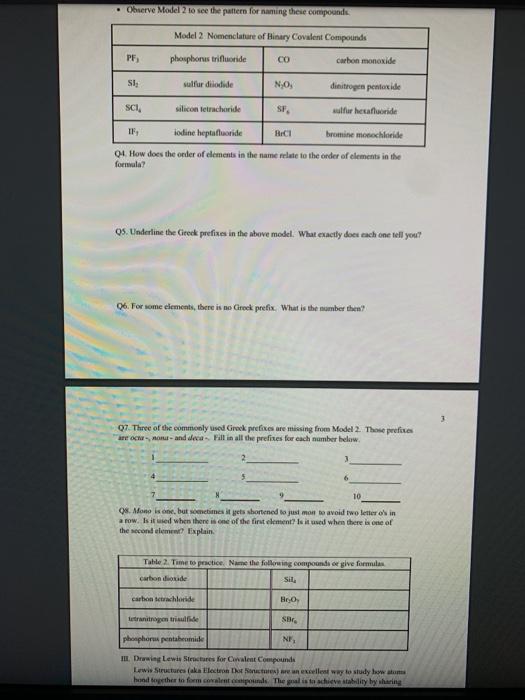
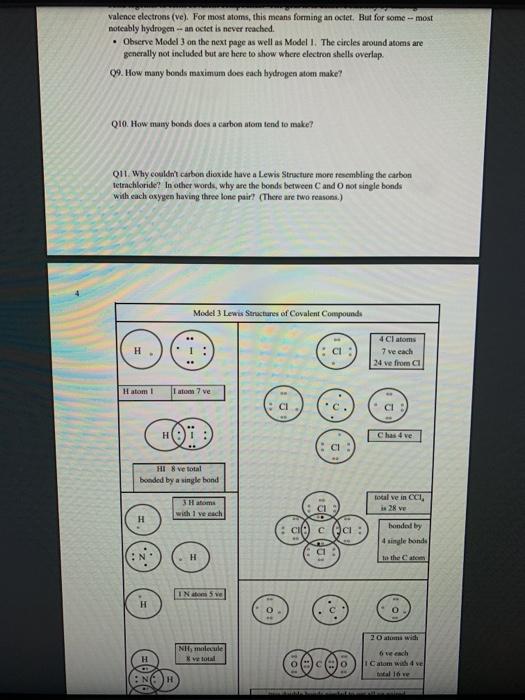
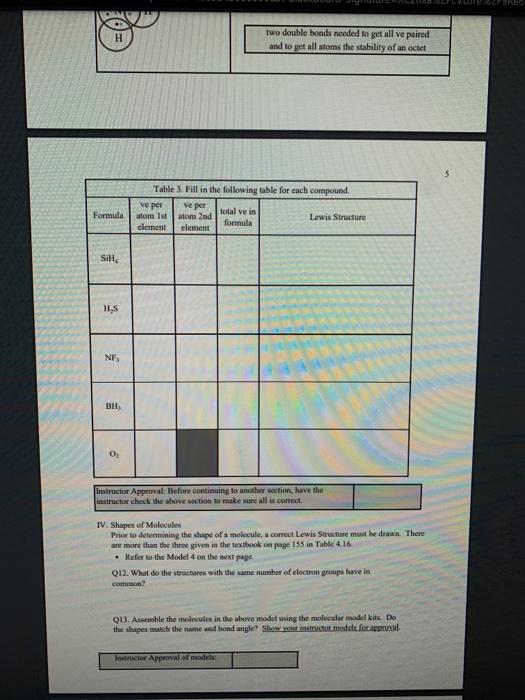
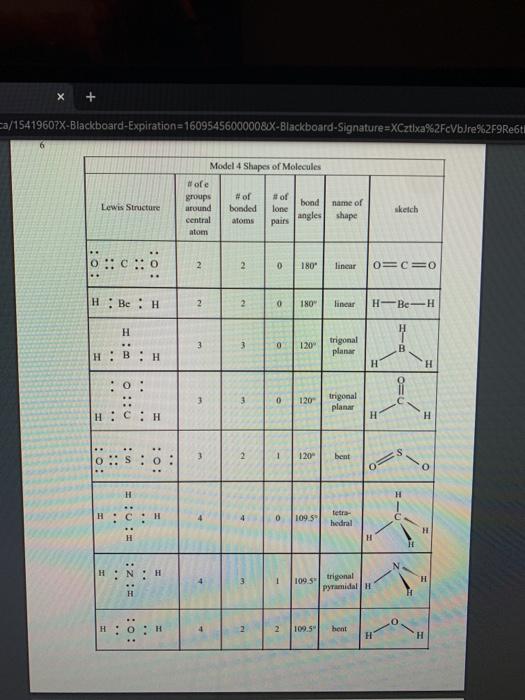
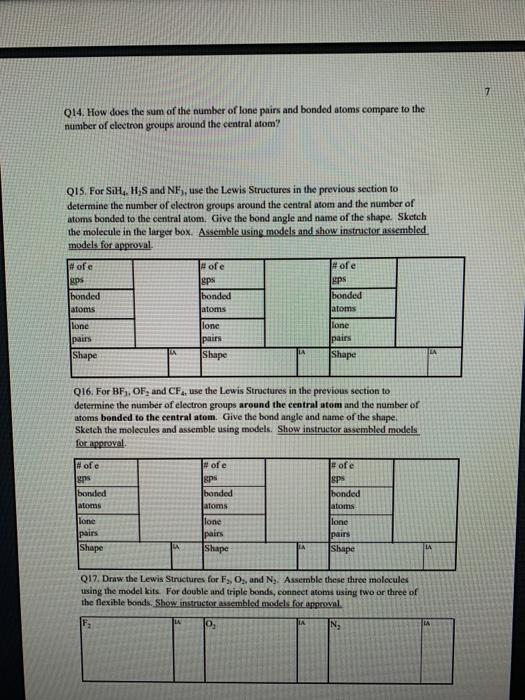
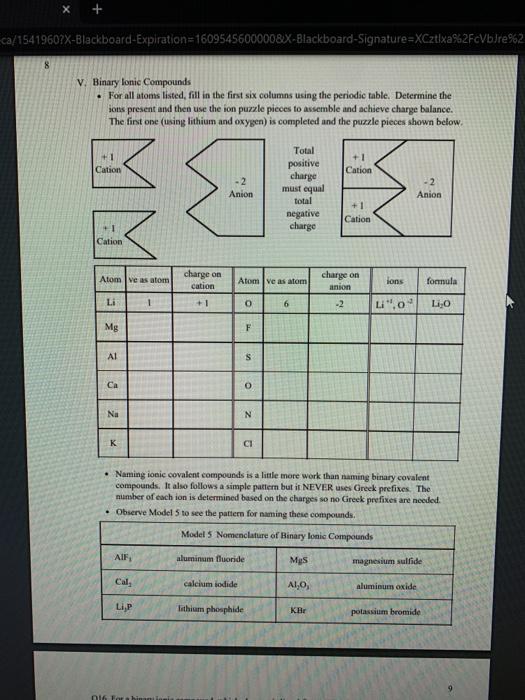
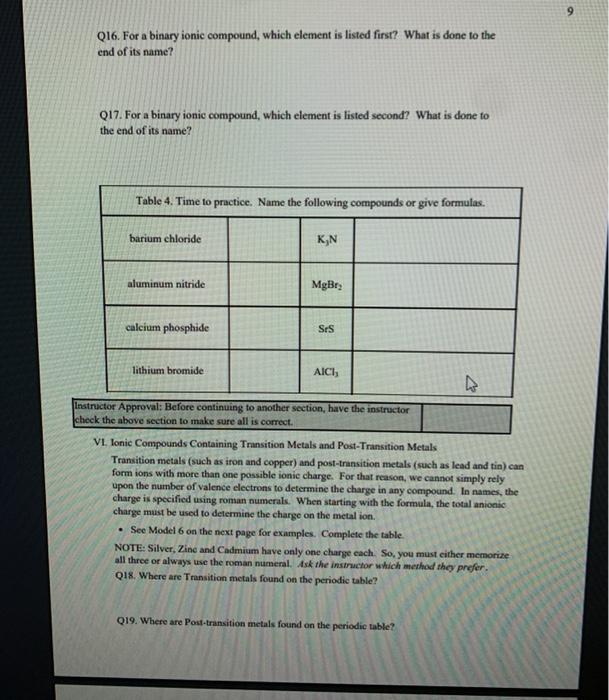
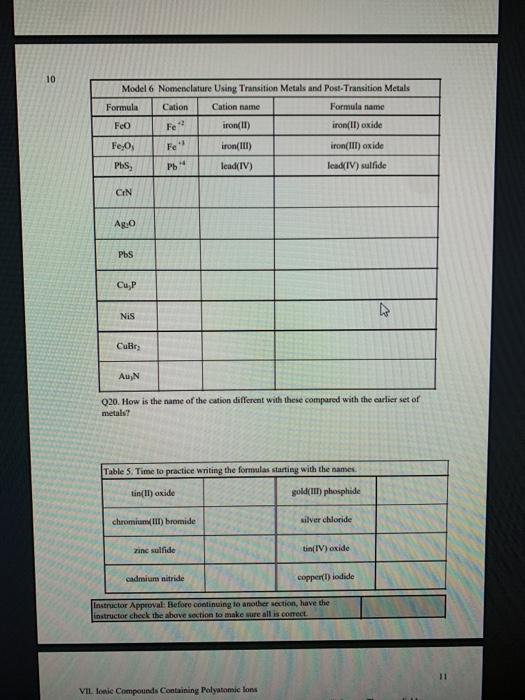
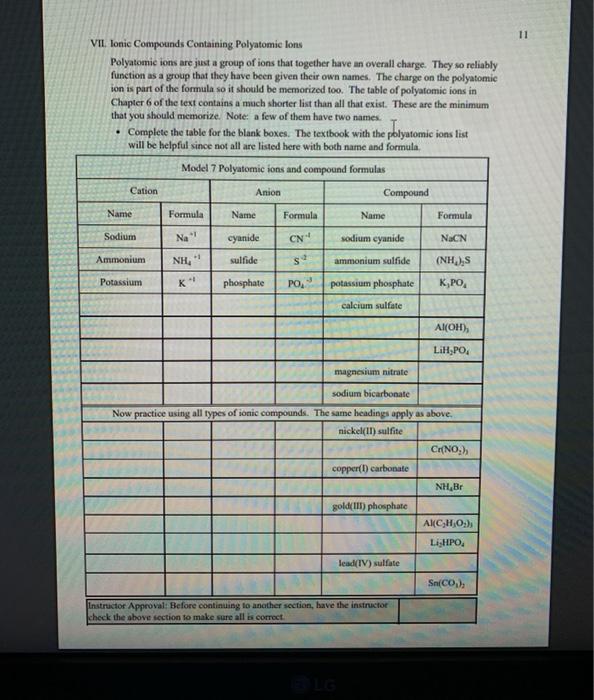
1 Binary Compounds There are essentially two types of compounds ionic and covalent. Binary compounds are those that contain two elements. Consider Model I below to determine how to recognize binary covalent compounds and binary ionic compounds. Model I Lewis Structures of Binary Compounds lonic Compounds Covalent Compounds Hr . F : .. atoms above combine to form ions atoms above combine to form a molecule Br .. Other examples of ionic compounds: Other examples of covalent NaF, Cars, Al, Li,N, Mg, H,S,PISICI. CH. NH, SO, Answer the following questions regarding ionic and covalent compounds based on Model 1. QI. What happened with electrons for ionic compounds? How did that differ from what happened with electrons for covalent compounds? Q2. What types of elements combine to form ionic compounds? How does that differ from the types of elements that combine to form covalent compounds? Q3. Atoms have a zero charge. What happened to the atom to get a positive charge! What happened to create the negative charge? Table 1. Identify the following as bonic (D) or covalent (C) compounds Bas HO, Sels NB BE Instinc for Approval: Before continuing to another section, have the Instructor check the above section to make sure all is correct 11 Naming Covalent Compounds Naming binary covalent compounds is rather easy. All you need to know is how to count to ten using Cireck prefixes. Use the model below to figure out what most of the ten prefinemen . Observe Model 2 to see the patter for naming these compounds Observe Model 2 to see the pattern for naming these compounds Model 2 Nomenclature of Binary Covalent Compounds PF phosphorus trifluoride CO carbon monoxide SI, wulfur diodide N.o dinitrogen penioride SCI silicon tetrachorride SF. wulfur hecafloride IF lodine heptafluoride BrCI bromine monochloride 1. How does the order of elements in the name relate to the order of elements in the formula? OS. Underline the Greek prefixes in the above model. What exactly does each one tell you? 06. For some elements, there is no Grock prefix. What is the number them? Q7. Three of the commonly used Greek prefixes are missing from Model 2. These profiles are octo and deca - Fill in all the prefixes for each number helow. 4 10 8. Moto is one, but onctimes it gets shortened to just mon to avoid iwo letters in a row. Is it used when there is one of the first element? Is it used when there is one of the second element? Explain. Table 2. Time to practice Name the following compounds or give formulas carbon dioxide Sil carbon tetrachloride SB phophorus pentaemide NE II Dwig Lewis Stres for Calent Compounds Luis Structures (aka Llectro Detran excellent way to study walom hand other to form owalent compounds. The pal is to achieved by sharing valence electrons (ve). For mostatoms, this means forming an octet. But for some most nofcably hydrogen -- an octet is never reached. . Observe Model 3 on the next page as well as Model 1. The circles around atoms are generally not included but are here to show where electron shells overlap. 09. How many bonds maximum does each hydrogen atom make? Q10. How muy bonds does a carbon atom tend to make? 011. Why couldn't carbon dioxide have a Lewis Structure more resembling the carbon tetrachloride? In other words, why are the bonds between Cando not single bonds with each oxygen having three lone pair! There are two reasons.) Model 3 Lewis Structures of Covalent Compounds H 4 Clatom 7 ve each 24 ve from a Hatom! 7 ve HO": Chas 4 ve :C: HI 8 ve total bonded by a single band 3 Home with 1 ve each talve in CCL ja 2 ve bonded by 4 single hands to the Cat IN 5 NH, molecule votal H 6 ve each Catom wid 4 ye total 10 two double bonds needed to get all ve paired and to get all atoms the stability of an octet 5 Table 3. Fill in the following table for each compound ve per ve per total ve in atom ist atom 2nd formula Lewis Structure element element Formula SiH Hs NFS BH 0 Instructor Approval Before continuing to another section, have the instructor check the above section to make sure all is correct IV. Shapes of Molecules Prior to determining the shape of a molecule, a correct Lewis Structure must be drawn. There are more than the three given in the textbook on page 155 in Table 4.16 . Refer to the Model 4 on the next page. Q12. What do the structures with the same number of electron groups have in Q13. Assemble the molecules in the above medel using the molecular model kitu Do the shapes match the name and bond angleShow your instructor model for ipproval Intructor Approval of models -a/15419607X-Blackboard-Expiration=16095456000008.X-Blackboard-Signature - XCztixa%2FcVbJre%2F9Reti Model 4 Shapes of Molecules ofe groups bond around name of bonded lone central angles shape atoms pairs atom of Lewis Structure sketch :: 2 2 0 180 O=C=O H: Be : H 2 2 0 180" linear HBH H H 3 3 0 120 trigonal planar B H: B H H : 0 o=U 3 0 120 trigonal planar H:CH H H 120 S: 10: O H H H : 0 109.5 tetra hedral H H Ht N H: N1 || 1 1095 H trigonal pyramidal H HOH 2 109.5" bent H 7 Q14. How does the sum of the number of lone pairs and bonded atoms compare to the number of electron groups around the central atom? QIS. For SiH.H S and NF), use the Lewis Structures in the previous section to determine the number of electron groups around the central atom and the number of atoms bonded to the central atom. Give the bond angle and name of the shape. Sketch the molecule in the larger box. Assemble using models and show instructor assembled models for approval ofe ofe ofe gps sps eps bonded bonded bonded atoms atoms atoms lone lone lone pairs pairs Shape Shape Shape pairs LA Q16. For BF, OF, and CF, use the Lewis Structures in the previous section to determine the number of electron groups around the central atom and the number of atoms bonded to the central atom. Give the bond angle and name of the shape. Sketch the molecules and assemble using models. Show instructor assembled models for approval #ofe #ofe sps bonded atoms lone pairs Shape ofe 8P bonded atoms sps bonded atoms lone pairs Shape lone pairs Shape LA Q17. Draw the Lewis Structures for F, Os, and N, Assemble these three molecules using the model kits. For double and triple bonds, connect atoms using two or three of the flexible bonds. Show instructor assembled models for approval LA 0, LA ILA X + ca/15419607X-Blackboard-Expiration=1609545600000&X-Blackboard-Signature=XCztxa%2FcV bre%2 8 V. Binary lonic Compounds . For all atoms listed, fill in the first six columns using the periodic table. Determine the sons present and then use the ion puzzle pieces to assemble and achieve charge balance. The first one (using lithium and oxygen) is completed and the puzzle pieces shown below +1 +1 Cation Cation - 2 Anion Total positive charge must equal total negative charge -2 Anion + 1 Cation Cation Atom ve as atom Atom ve as atom charge on anion ions charge on cation +1 formula Li 1 0 6 -2 LI". LO Mg F AI S Ca O N Na K CI Naming ionic covalent compounds is a little more work than naming binary covalent compounds. It also follows a simple pattern but it NEVER uses Greek prefixes. The number of each ion is determined based on the charges so no Greek prefixes are needed Observe Model 5 to see the pattern for naming these compounds. Model 5 Nomenclature of Binary lonic Compounds AIF aluminum fluoride Mys magnesium sulfide Cal, calcium iodide ALO, aluminum oxide LIP lithium phosphide r potassium bromide Fabi 9 Q16. For a binary ionic compound, which element is listed first? What is done to the end of its name? Q17. For a binary ionic compound, which element is listed second? What is done to the end of its name? Table 4. Time to practice. Name the following compounds or give formulas. barium chloride KN aluminum nitride MgBry calcium phosphide Srs lithium bromide AICI, Instructor Approval: Before continuing to another section, have the instructor check the above section to make sure all is correct. VI. Ionic Compounds Containing Transition Metals and Post-Transition Metals Transition metals (such as iron and copper) and post-transition metals (such as lead and tin) can form ions with more than one possible ionic charge. For that reason, we cannot simply rely upon the number of valence electrons to determine the charge in any compound. In names, the charge is specified using roman numerals. When starting with the formula, the total anionic charge must be used to determine the charge on the metal ion. See Model 6 on the next page for examples. Complete the table NOTE: Silver, Zinc and Cadmium have only one charge each. So, you must either memorize all three or always use the roman numeral. Ask the instructor which method they prefer. Q18. Where are Transition metals found on the periodic table? Q19. Where are Post-transition metals found on the periodic table? 10 Model 6 Nomenclature Using Transition Metals and Post-Transition Metals Formula Cation Cation name Formula name Feo Fe iron(IT) iron(II)oxide FeO3 Fe iron(III) iron(III)oxide Pbs Pb 4 lead(IV) lead(TV) sulfide CIN Ag.0 Pbs Cu,P Nis Cuary Au N 020. How is the name of the cation different with these compared with the earlier set of metals Table 5. Time to practice writing the formulas starting with the names tin(l)oxide gold(III) phosphide chromium(III) bromide silver chloride zinc sulfide tin(IV) oxide Cadmium nitride copper(1) jodide Instructor Approval: Before continuing to another section, have the Instructor check the above section to make sure all is correct VIL lonic Compounds Containing Palyatomic lons 11 VII. Ionic Compounds Containing Polyatomic fons Polyatomic ions are just a group of ions that together have an overall charge. They so reliably function as a group that they have been given their own names. The charge on the polyatomic ion is part of the formula so it should be memorized too. The table of polyatomic ions in Chapter 6 of the text contains a much shorter list than all that exist. These are the minimum that you should memorize. Note: a few of them have two names. Complete the table for the blank boxes. The textbook with the polyatomic ions list will be helpful since not all are listed here with both name and formula Model 7 Polyatomic ions and compound formulas Cation Anion Compound Name Formula Name Formula Name Formula Sodium Na cyanide CN sodium eyanide NaCN -1 Ammonium NH, sulfide so ammonium sulfide (NH4)2S Potassium K phosphate -5 . potassium phosphate K,PO calcium sulfate Al(OH), LiH,PO magnesium nitrate sodium bicarbonate Now practice using all types of sonic compounds. The same headings apply as above. nickel(II) sulfite CHNO.) copper(t) carbonate NH, Br gold(II) phosphate Al(C,H,O:) LiHPO lead(IV) sulfate Sn(CO) Instructor Approval: Before continuing to another section, have the instructor check the above section to make sure all is correct