Please help with answering all Q's
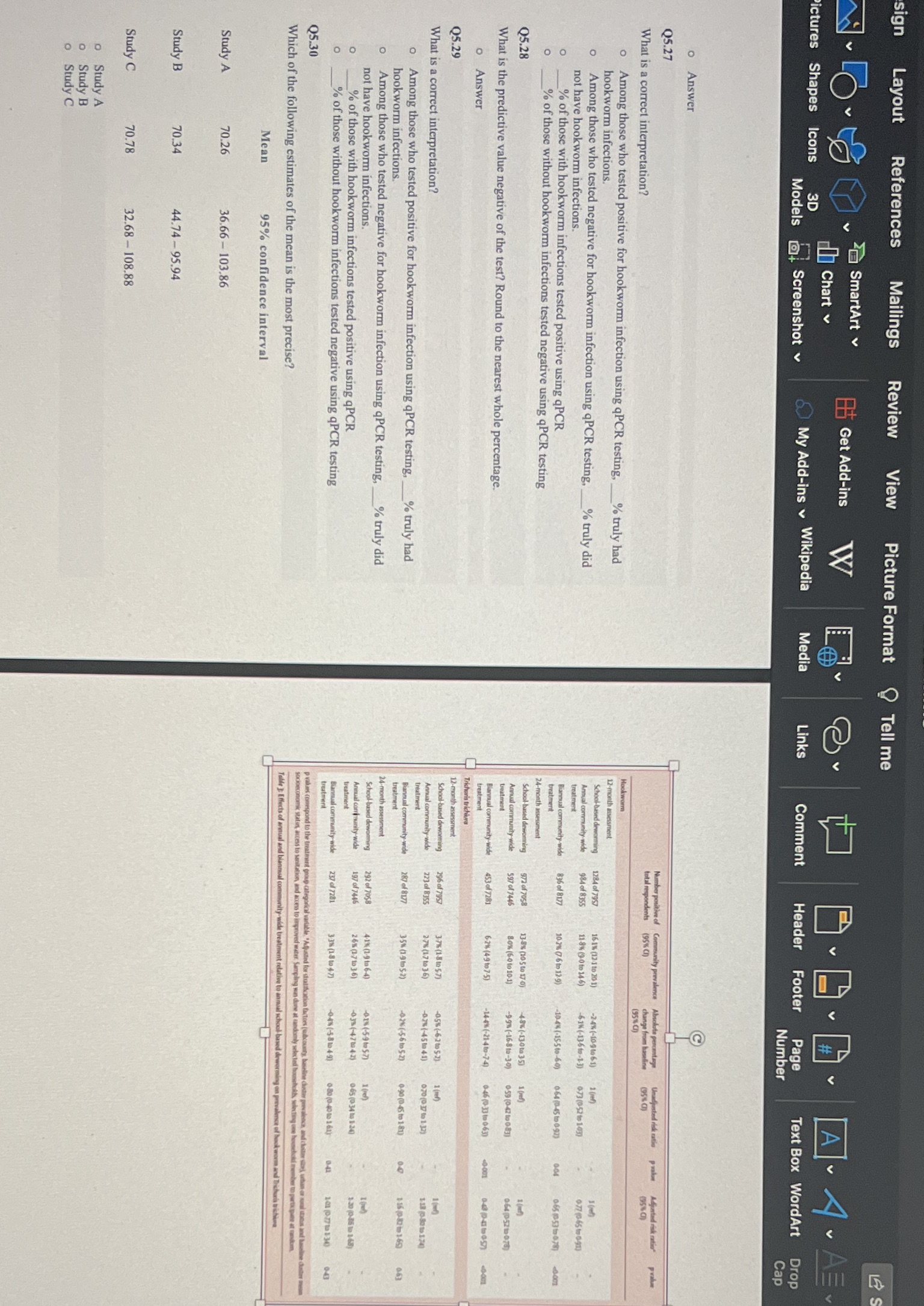
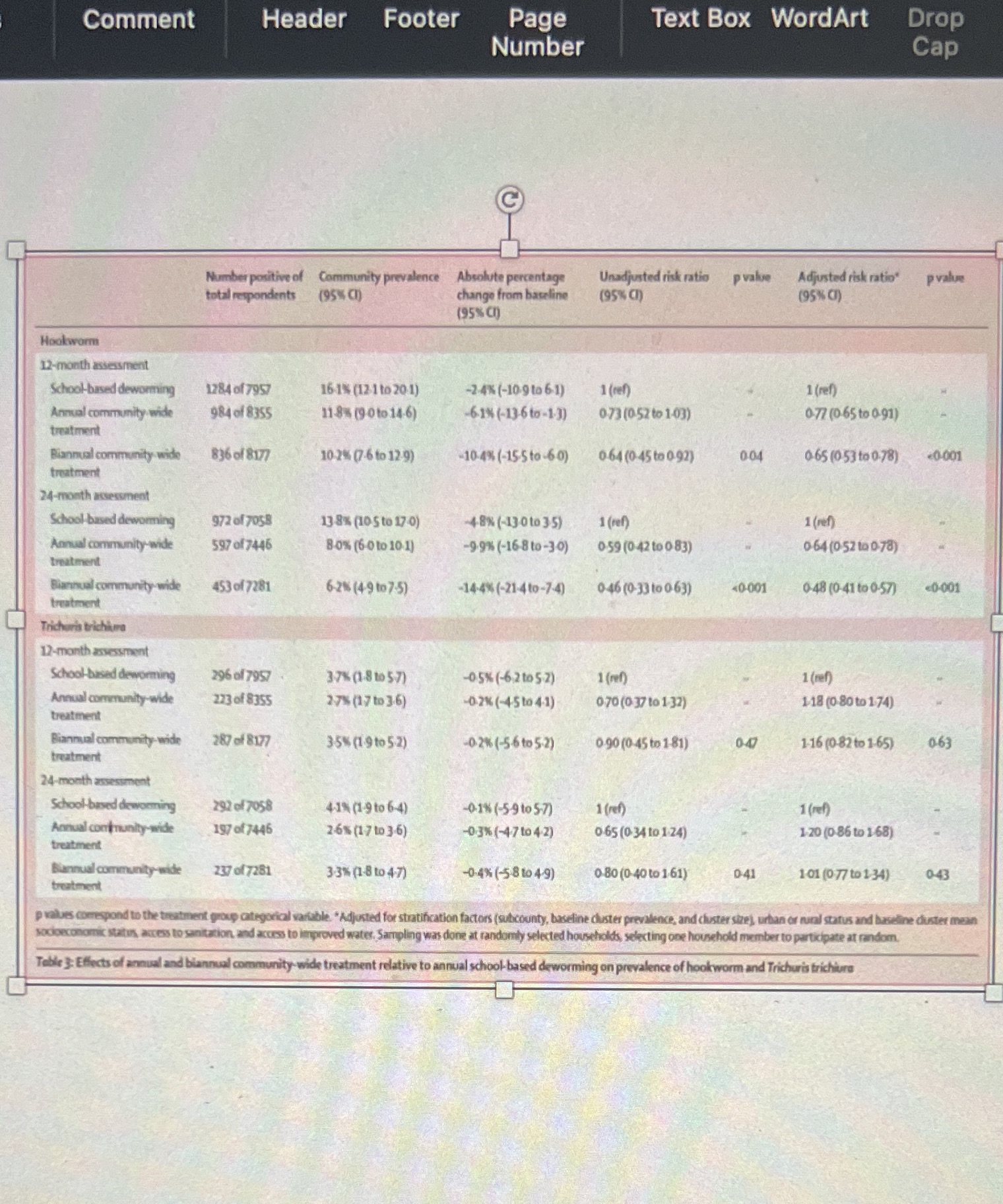
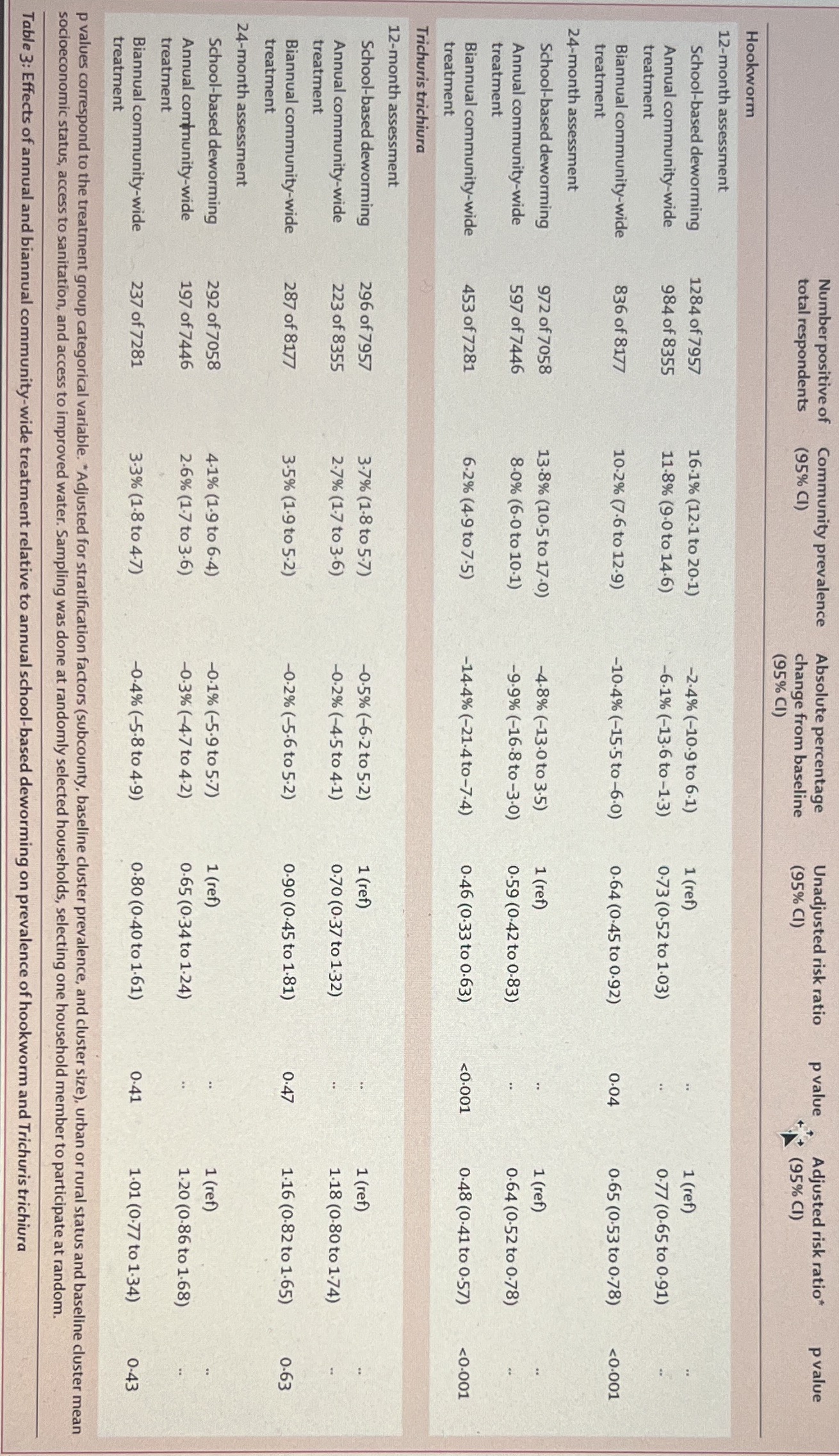
Hookworm No hookworm Total Suppose the investigators decided to perform a follow-up qPCR study on the stool samples to detect Q5.10 Using Table 3, fill in the 2x2 table below using data from the 24-month assessment. hookworm. Questions 5.23-27 refer to the table below, which contains data from a hypothetical study that Pooled data Annual community-wide treatment 4025 4121 performed the qPCR test and then compared the results to the clinical diagnosis of hookworm. For the. Hookworm No hookworm infection Total purpose_of this problem, we will consider clinical diagnosis to the "gold standard" method that can truly School-based deworming distinguish between individuals who are or are not infected with hookworm. 199 1036 1235 Annual community-wide treatment No shoes Diagnosed hookworm School-based deworming C Hookworm No hookworm Total Total qPCR Test 526 121 647 o What value is A? Annual community-wide treatment 501 2824 3325 F 3904 3975 05.11 597 o What value is B? School-based deworming 5050 5823 Total 1025 4622 Q5.12 Use the data to examine whether wearing shoes is a relative scale effect modifier by comparing the What is the sensitivity of the test? Round to the nearest whole percentage. Enter only a number. For o What value is C? observed vs. expected joint RRs. example, if your answer is 100%, enter 100 in the box. 5.13 . First, calculate the observed RR O ANSWER: o What value is D? Q5.18 Then, calculate the expected RR Q5.23 Q5.14 Q5.19 Then, determine if effect measure modification is present on the relative/multiplicative scale. What is a correct interpretation? o Yes o What value is E? No o Among those who tested positive for hookworm infection using qPCR testing, % truly had hookworm infections. 5.15 o Among those who tested negative for hookworm infection using qPCR testing, % truly did What value is F? 25.20 not have hookworm infections. % of those with hookworm infections tested positive using qPCR testing The study used the Kato-Katz microscopy technique instead of the newer, more sensitive qPCR % of those without hookworm infections tested negative using qPCR testing Q5.16 Using the 2x2 table above, calculate the unadjusted ("crude") risk ratio of hookworm infection in technique. Which of the following biases could be introduced by using a diagnostic with imperfect Q5.24 this study. Do not round intermediate steps. Only round the final answer to the nearest hundredth. sensitivity in this study? Select all that apply. Final answer: What is the specificity of the test? Round to the nearest whole percentage. o Differential misclassification of exposure Q5.17 One route of transmission for hookworm is by walking barefoot in contaminated soil. In a Differential misclassification of disease o Answer Nondifferential misclassification of exposure hypothetical scenario, say investigators realized that some communities tended to wear shoes and other Nondifferential misclassification of disease 25.25 communities tended not to wear shoes. The investigators then assessed whether shoe-wearing by Q5.21 What is a correct interpretation? communities was a potential effect measure modifier of the association between annual community-wide Since the study used the Kato-Katz microscopy technique instead of the newer, more sensitive qPCR . Among those who tested positive for hookworm infection using qPCR testing, % truly had treatment and hookworm infection, In addition to the pooled data above, the investigators stratified the technique, how would the estimates be affected? hookworm infections. o data based on shoe-wearing: Among those who tested negative for hookworm infection using qPCR testing, _% truly did Biased away from null (overestimated) not have hookworm infections. o Biased towards null (underestimated) % of those with hookworm infections tested positive using qPCR Shoes Unbiased % of those without hookworm infections tested negative using qPCR testing Q5.22 5.26 What is the predictive value positive of the test? Round to the nearest whole percentage.sign Layout References Mailings Review View Picture Format Tell me 2SmartArt Get Add-ins A Chart Pictures Shapes Icons 3D a Screenshot v Media Links Models My Add-ins v Wikipedia Comment Header Footer Page Text Box WordArt Drop Number Cap Answer Q5.27 Number positive of Community prevalence Absolute percentage Unadjusted rick ratio pxalor Adjusted risk ratio" pratime What is a correct interpretation? atal responder (95 () (95% () (95% () Among those who tested positive for hookworm infection using qPCR testing, % truly had Hookworm O hookworm infections. 2-month assessment School-bused deworming 1284 of 7957 161% (17 1 to 20 1) -2-4% (-109 to 61) 1 (ref) Among those who tested negative for hookworm infection using qPCR testing, % truly did Annual community-wide 984 of 8355 11-8% (9 0 to 14 6) -61% (-136to-13) 673 (052 to 103) 077 10.65 to 897) not have hookworm infections. treatment % of those with hookworm infections tested positive using qPCR Biannual community-wide 836 of 8177 10.7% ( 6 to 12:9) -10.4% (-15 5to-60) 064 10-45 to 0 92) 004 06510536078) 6401 % of those without hookworm infections tested negative using qPCR testing treatment 5.28 School- based deworming 972 of 7058 13:8% (20 5 to 17 0) 48% (-130 to 35) 1 (ref) Annual community-wide $97 of 7446 80% (60 to 101) -9 9% (-16-8 to-30) 0:59 (0-47 10 083) 064 105210 073) What is the predictive value negative of the test? Round to the nearest whole percentage. treatment Biannual community-wide 453 of 7281 6-21 (4-9 1075) -14-4% (-21:4 to-74) 046 (0-33 to 063) 4:001 o Answer Trkcharis trichdura Q5.29 2-month assessment School-based deworming 296 of 7957 3:7% (1.8 1057) -05% (-67to 5-2) 160 What is a correct interpretation? Annual community-wide 723 of B355 275 (17 10 3 6) -078 (-45 10 41) o Among those who tested positive for hookworm infection using qPCR testing, % truly had Biannual community-wide 287 of 8177 35% (19to52) -024(-5-6to52) 0-90(0-45 to 181) 1:16 10-82 to 169) 063 hookworm infections. O Among those who tested negative for hookworm infection using qPCR testing, % truly did 4-month assessment not have hookworm infections. School-based deworming 292 of 7058 4 1% (1.9 to 6-4) - IN(-59 to57) tad1 Annual contrunity-wide 197 of 7446 26% (17 to 36) -03%(471043) % of those with hookworm infections tested positive using qPCR 0 65 (0 34 to 130) 1:20 (0-36 10 168) treatment oo % of those without hookworm infections tested negative using qPCR testing Biannual community wide 237 of 7281 3 38 (18 6047) -0-48(-38104-9) 0 80 (0-40 10 161) 041 101 (07710 130 043 treatment Q5.30 vader's comespond to the treatment group categorical variable. "Adjusted for stratiha socioeconomic statin, access to sanitation, and access to improved Which of the following estimates of the mean is the most precise? able 3: Effects of annual and biannual com A worm and Dichuris bisbing Mean 95% confidence interval Study A 70.26 36.66 - 103.86 Study B 70.34 44.74 -95.94 Study C 70.78 32.68 - 108.88 O Study A o Study B o Study CComment Header Footer Page Text Box WordArt Drop Number Cap Number positive of Community prevalence Absolute percentage Unadjusted risk ratio pvalue Adjusted risk ratio' pvalue total respondents (95% CD) change from baseline (95% () (95% CI) (95% CD) Hookworm 12-month assessment School-based deworming 1284 of 7957 16-1% (12 1 to 201) -2-4% (-10.9 to 6-1) 1 (ref) 1 (ref) Annual community wide 984 of 8355 11-8% (9 0 to 14-6) 61% (-13-6 to-1-3) 073 (0.52 to 1-03) 0.72 (0-65 to 0.91) treatment Biannual community wide 836 of 8177 10.2% (7-6 to 12-9) -10-4% (-15-5 to-60) 064 (0 45 to 0.92) 0:04 065 (053 to 0.78) #0-601 treatment 24-month assessment School-based deworming 972 of 7058 13:8% (10 5 to 17 0) 48% (-13 0 to 35) 1 (ref) 1 (ref) Annual community-wide 597 of 7446 8-0% (6 0 to 10.1) -9:9% (-16-8 to-30) 0:59 (0-42 to 0 83) 064 (0 52 to 0.78) treatment annual community wide 453 of 7281 6-2% (49 to7-5) -14-4% (-21-4to-7-4) 046 (0-33 to 0-63) 40:001 0-48 (0-41 to 0-57) 0-001 Trichuris trichia 12-month assessment School-based deworming 296 of 7957 37% (1-8 10 5-7) -05% (-6.2to 5 2) 1 (ref) 1 (ref) Annual community-wide 273 of 8355 278 (17 to 3.6) -0.2% (-45 to 4.1) 070 (0 37 to 1 32) 1 18 (0.80 to 1 74) treatment annual community-wide 287 of 8177 3-5% (1:9 to 5-2) -0.2% (-5-6 to 5-2) 0 90 (0-45 to 181) 0-47 1-16 (0-82 to 1-65) 063 treatment 24-month asses School-based dewor 292 of 7058 4 1% (1-9 to 6-4) -0:1% (-5-9to 5-7) 1 (ref) 1 (ref) Annual community-wide 197 of 7446 26% (17 to 3-6) -0:3% (-47 to 4.2) 0-65 (0 34 to 1:24) 1:20 (0 86 to 1 68) treatment annual community-wide 237 of 7281 3:3% (1-8 to 4-7) -0-4% (-5 8 to 4 9) 0-80 (0-40 to 1 61) 0-41 1 01 (0 77 to 1 34) 0-43 p wales correspond to the treats it group categorical variable. "Adjusted for stratification factors (subcounty, baseline cluster prevalence, and cluster size), urban or rural status and baseline cluster mean mic staitin, access to sanitation and access to large ly selected households, selecting one household member to participate at random. Table 3: Effects of an unity-wide treatment relative to annual school-based deworming on prevalence of hookworm and Trichuris trichiureNumber positive of Community prevalence Absolute percentage Unadjusted risk ratio p value Adjusted risk ratio* p value total respondents (95% CI) change from baseline (95% CI) (95% CI) (95% CI) Hookworm 12-month assessment School-based deworming 1284 of 7957 16.1% (12.1 to 20-1) -2.4% (-10.9 to 6-1) 1 (ref) 1 (ref) Annual community-wide 984 of 8355 11-8% (9-0 to 14.6) -6-1% (-13-6 to -1.3) 0.73 (0.52 to 1.03) 0-77 (0-65 to 0-91) treatment Biannual community-wide 836 of 8177 10.2% (7.6 to 12-9) -10-4% (-15.5 to -6.0) 0.64 (0.45 to 0.92) 0.04 0.65 (0.53 to 0-78)