Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please help with table 11 and 12 Your information: 1. Your company produces sandwich cookie snack packs. There are three main processes used to make




Please help with table 11 and 12
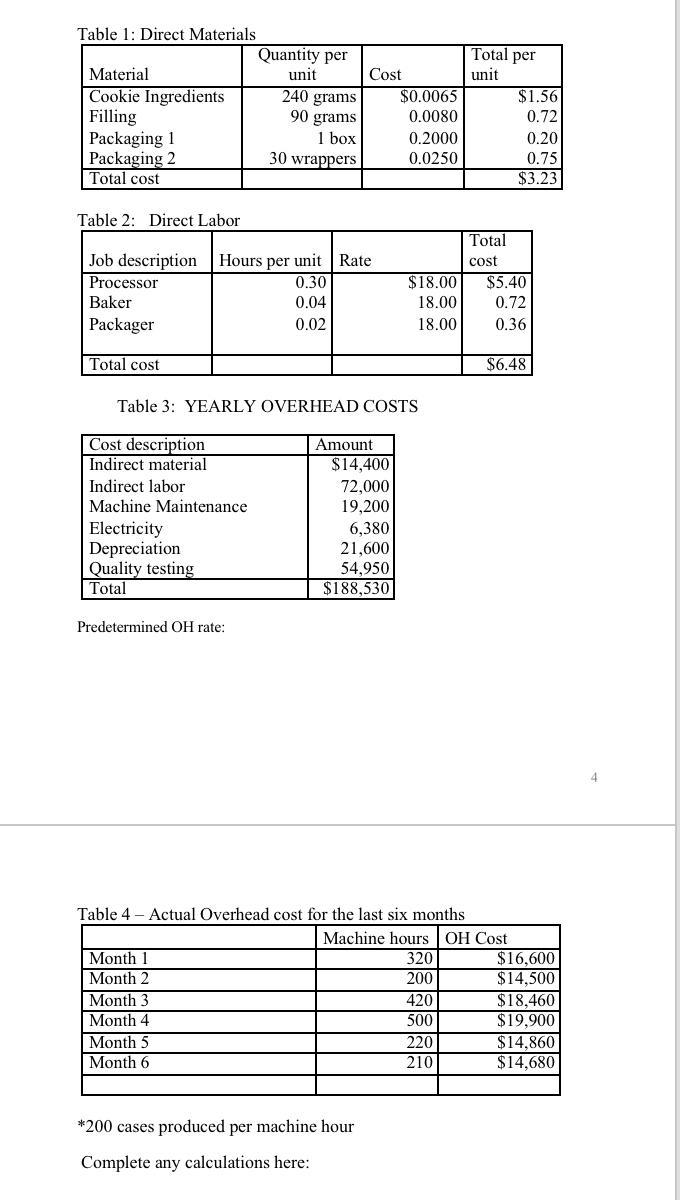
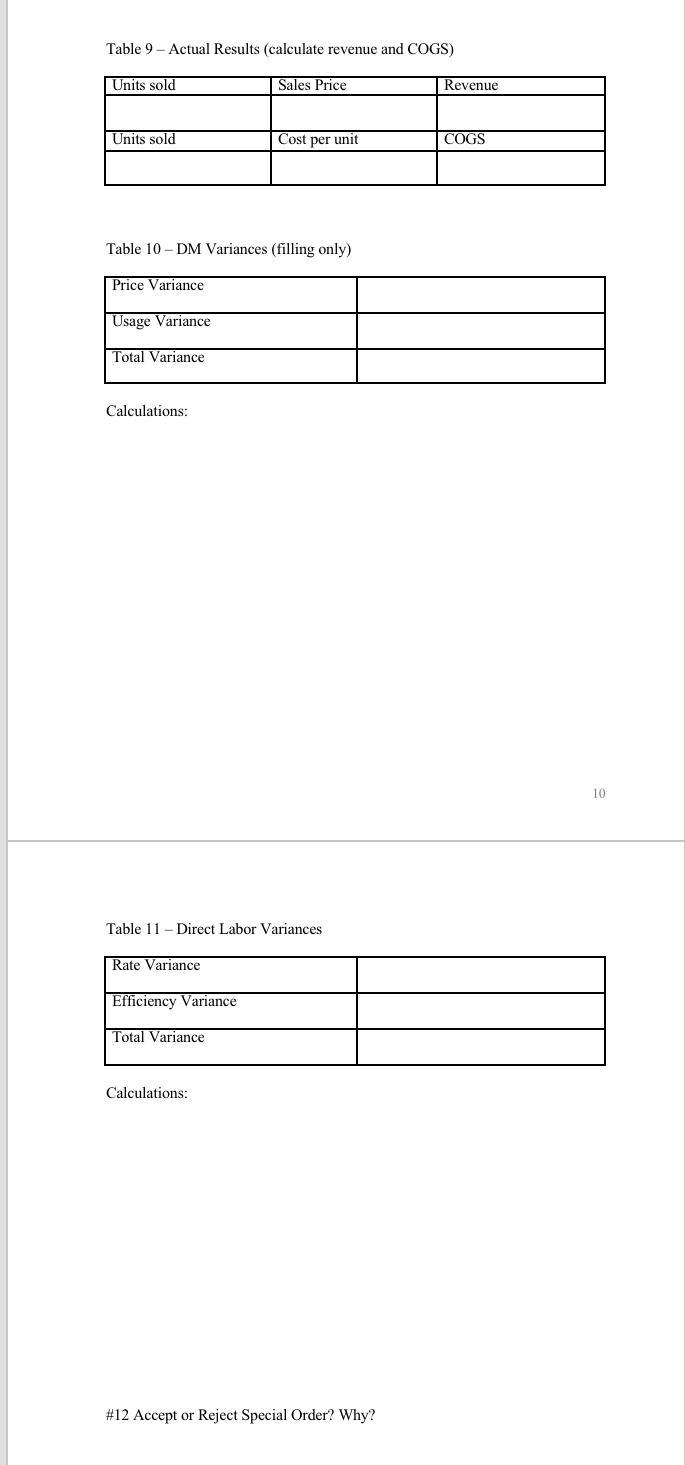
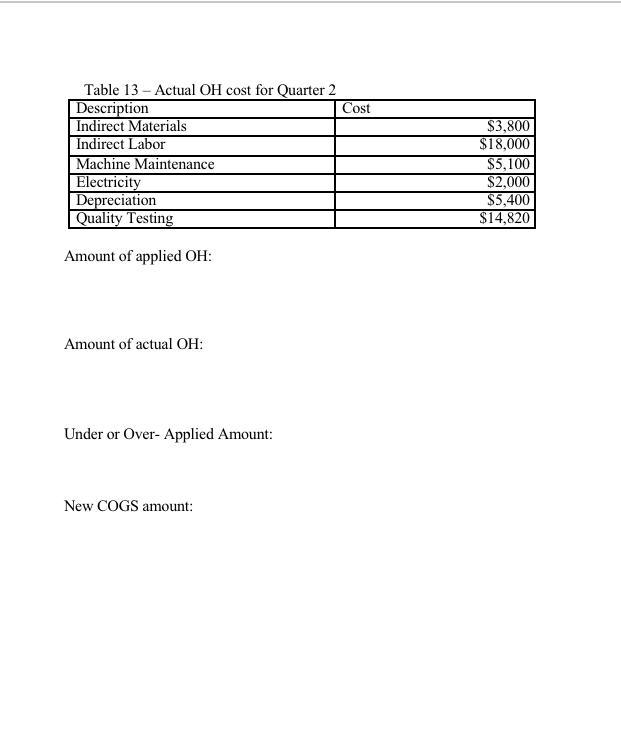
Your information: 1. Your company produces sandwich cookie snack packs. There are three main processes used to make the cookies. The first process preps and mixes the ingredients into the cookie and the filling. The second process shapes, forms and bakes the cookies. The third process packages the cookies. The cookies are sold in cases of 30 cookie packs (1 case is a unit) 2. Information on the direct materials is listed in table 1. Consider this information the standard. Direct labor information given in Table 2. Consider this information the standard. 3. Annual overhead information is given in Table 3. Overhead is allocated based direct labor hours. Estimated annual direct labor hours are 221,800. Calculate a predetermined OH rate (round to two decimal places if needed). Use this rate when you need to apply OH. 4. Table 4 gives you the information for the last six months on the manufacturing overhead cost and machine hours. Using the high/low method of cost estimation and this information, determine the fixed and variable portions of the manufacturing overhead cost. (You will need this information to complete Table 5). Machine hours have been determined as the best cost driver for manufacturing OH. It takes one machine hour to make 200 cases of cookies. 5. Table 5 is where you will list all your production cost (DM, DL, MOH), separated into their fixed and variable components. Note this table wants variable cost per unit and annual fixed cost. 6. Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Relationships a. Selling Price: You sell a case of cookies for $16 b. Breakeven point: Calculate the breakeven point. Be sure to include the fixed component of mixed cost in your fixed costs and the variable component in the variable cost. Show your breakeven in Sales units and in Sales Dollars c. Profit Planning: Determine the number of units you must sell to make an annual pretax profit using 3 assumptions concerning your net income (profit), both in sales units and sales dollars. i. Aggressive Profit ($4,125,000) ii. Conservative Profit ($1,750,000) iii. Average Profit ($3,589,200) 7. Budgeting: a. Create a sales budget using the information for earning an average profit for the year. You will break the budget down into the four quarters for the year. (Sales tend to be consistent each quarter, you can only sale a whole unit so round-up if necessary) Use table 6 to complete the sales budget. b. Create a production budget for each quarter of the year (keep it in quarters; you do not need to break it down by month). You desire to keep 10% of next quarter's sales in ending inventory. Sales for Qtr 1 the following year (year 2) are expected to be 160,000 cases of cookies. There is not any beginning finished goods inventory for quarter one this year. Use table 7 to complete the production budget. 8. Running quarter two = Weighted-average process costing. Table 8 presents the information for the packaging department. Complete the questions under table 8 . 9. Actuals are in for quarter two. You sold 5% less units than you budgeted for (round to a whole unit), but price per unit was $16.50. a. Calculate revenue b. Compute the cost of goods sold (total and per unit) before adjusting for actual OH cost (there was not any beginning finished goods inventory for Q2) 10. Actual filling ingredients usage for quarter one was 15,925,000 grams at a price of $0.0085 per gram. Actual equivalent units of production (cases of cookies) completed through the second process (where the filling is added) was 176,000. Calculate the direct materials variances for the filling (price, usage, and total) and indicate if these variances are favorable or unfavorable. 11. Actual direct labor hours for the quarter were 62,870 at an average rate of $18.50 per hour. For actual production, you expected to use 62,756 direct labor hours. Calculate the direct labor variances (rate, efficiency and total) and indicate if these variances are favorable or unfavorable. 12. For July, you have received a special offer of 5,000 cases of cookies at a total price of $55,000. Your current capacity per month is 80,000 cases. The event organizers ordering these cookies have requested a special summer themed wrapping that will cost $1,800 for you to set-up. Should you accept or reject this offer? Why? 13. Determine over- or under-applied overhead and close to cost of goods sold. Actual OH costs are given in table 13 (look at \#11 for actual DL hours used to apply OH ). Determine the new cost of goods sold amount. Table 2: Direct Labor Table 3: YEARLY OVERHEAD COSTS Predetermined OH rate: Table 4 - Actual Overhead cost for the last six months * 200 cases produced per machine hour Complete any calculations here: Table 5: Variable and Fixed Costs If a cost is mixed, put the fixed amount in the Inxed column and the variabie amount in the variable column. CVP Calculations: Table 6-Sales Budget (Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4) Table 7 - Production Budget Process Costing - Packaging Department Direct materials are added 90% at the beginning of the process and the remaining 10% are added when the cookies are 80% complete with the packaging process. Direct labor and overhead are added evenly throughout the process. Added during Qtr2 : Direct Materials - $126,450 Direct Labor-3150 brs @ \$18.50 per hour Overhead - OH is applied based on predetermined OH rate and actual DL hours 1. Determine the number of units completed during quarter 2 . 2. Compute the equivalent units using the weighted average method. 3. Compute the cost per equivalent unit using the weighted average method 4. Compute the cost of goods transferred to finished goods inventory 5. Compute the ending balance in WIP, Packaging Table 9 - Actual Results (calculate revenue and COGS) Table 10 - DM Variances (filling only) Calculations: Table 11 - Direct Labor Variances Calculations: \#12 Accept or Reject Special Order? Why? Table 12-Actual OH cost for Mnarter? Amount of applied OH : Amount of actual OH : Under or Over- Applied Amount: New COGS amount: Your information: 1. Your company produces sandwich cookie snack packs. There are three main processes used to make the cookies. The first process preps and mixes the ingredients into the cookie and the filling. The second process shapes, forms and bakes the cookies. The third process packages the cookies. The cookies are sold in cases of 30 cookie packs (1 case is a unit) 2. Information on the direct materials is listed in table 1. Consider this information the standard. Direct labor information given in Table 2. Consider this information the standard. 3. Annual overhead information is given in Table 3. Overhead is allocated based direct labor hours. Estimated annual direct labor hours are 221,800. Calculate a predetermined OH rate (round to two decimal places if needed). Use this rate when you need to apply OH. 4. Table 4 gives you the information for the last six months on the manufacturing overhead cost and machine hours. Using the high/low method of cost estimation and this information, determine the fixed and variable portions of the manufacturing overhead cost. (You will need this information to complete Table 5). Machine hours have been determined as the best cost driver for manufacturing OH. It takes one machine hour to make 200 cases of cookies. 5. Table 5 is where you will list all your production cost (DM, DL, MOH), separated into their fixed and variable components. Note this table wants variable cost per unit and annual fixed cost. 6. Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Relationships a. Selling Price: You sell a case of cookies for $16 b. Breakeven point: Calculate the breakeven point. Be sure to include the fixed component of mixed cost in your fixed costs and the variable component in the variable cost. Show your breakeven in Sales units and in Sales Dollars c. Profit Planning: Determine the number of units you must sell to make an annual pretax profit using 3 assumptions concerning your net income (profit), both in sales units and sales dollars. i. Aggressive Profit ($4,125,000) ii. Conservative Profit ($1,750,000) iii. Average Profit ($3,589,200) 7. Budgeting: a. Create a sales budget using the information for earning an average profit for the year. You will break the budget down into the four quarters for the year. (Sales tend to be consistent each quarter, you can only sale a whole unit so round-up if necessary) Use table 6 to complete the sales budget. b. Create a production budget for each quarter of the year (keep it in quarters; you do not need to break it down by month). You desire to keep 10% of next quarter's sales in ending inventory. Sales for Qtr 1 the following year (year 2) are expected to be 160,000 cases of cookies. There is not any beginning finished goods inventory for quarter one this year. Use table 7 to complete the production budget. 8. Running quarter two = Weighted-average process costing. Table 8 presents the information for the packaging department. Complete the questions under table 8 . 9. Actuals are in for quarter two. You sold 5% less units than you budgeted for (round to a whole unit), but price per unit was $16.50. a. Calculate revenue b. Compute the cost of goods sold (total and per unit) before adjusting for actual OH cost (there was not any beginning finished goods inventory for Q2) 10. Actual filling ingredients usage for quarter one was 15,925,000 grams at a price of $0.0085 per gram. Actual equivalent units of production (cases of cookies) completed through the second process (where the filling is added) was 176,000. Calculate the direct materials variances for the filling (price, usage, and total) and indicate if these variances are favorable or unfavorable. 11. Actual direct labor hours for the quarter were 62,870 at an average rate of $18.50 per hour. For actual production, you expected to use 62,756 direct labor hours. Calculate the direct labor variances (rate, efficiency and total) and indicate if these variances are favorable or unfavorable. 12. For July, you have received a special offer of 5,000 cases of cookies at a total price of $55,000. Your current capacity per month is 80,000 cases. The event organizers ordering these cookies have requested a special summer themed wrapping that will cost $1,800 for you to set-up. Should you accept or reject this offer? Why? 13. Determine over- or under-applied overhead and close to cost of goods sold. Actual OH costs are given in table 13 (look at \#11 for actual DL hours used to apply OH ). Determine the new cost of goods sold amount. Table 2: Direct Labor Table 3: YEARLY OVERHEAD COSTS Predetermined OH rate: Table 4 - Actual Overhead cost for the last six months * 200 cases produced per machine hour Complete any calculations here: Table 5: Variable and Fixed Costs If a cost is mixed, put the fixed amount in the Inxed column and the variabie amount in the variable column. CVP Calculations: Table 6-Sales Budget (Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4) Table 7 - Production Budget Process Costing - Packaging Department Direct materials are added 90% at the beginning of the process and the remaining 10% are added when the cookies are 80% complete with the packaging process. Direct labor and overhead are added evenly throughout the process. Added during Qtr2 : Direct Materials - $126,450 Direct Labor-3150 brs @ \$18.50 per hour Overhead - OH is applied based on predetermined OH rate and actual DL hours 1. Determine the number of units completed during quarter 2 . 2. Compute the equivalent units using the weighted average method. 3. Compute the cost per equivalent unit using the weighted average method 4. Compute the cost of goods transferred to finished goods inventory 5. Compute the ending balance in WIP, Packaging Table 9 - Actual Results (calculate revenue and COGS) Table 10 - DM Variances (filling only) Calculations: Table 11 - Direct Labor Variances Calculations: \#12 Accept or Reject Special Order? Why? Table 12-Actual OH cost for Mnarter? Amount of applied OH : Amount of actual OH : Under or Over- Applied Amount: New COGS amountStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


