Question: please i need this asap, you need to choose one. knowledge od area chosen: Human-Computer Interaction Module 02 Activity Specification Mospec cation w e com
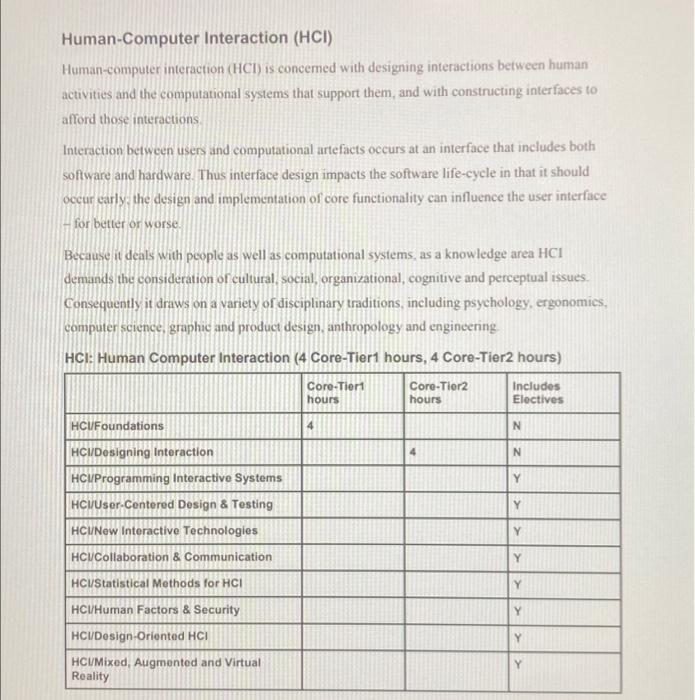



Module 02 Activity Specification Mospec cation w e com tudom - Expectations KnowledgeArea_Graphics and Visualization (GV) SC 37 Knowledge Area_Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) SC Vinderea Information Assurance and Security (LAS) SC 17 Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) Human-computer interaction (HCI) is concerned with designing interactions between human activities and the computational systems that support them, and with constructing interfaces to afford those interactions Interaction between users and computational artefacts occurs at an interface that includes both software and hardware. Thus interface design impacts the software life-cycle in that it should occur varly the design and implementation of core functionality can influence the user interface for better or worse. Because it deals with people as well as computational systems, as a knowledge area HCI demands the consideration of cultural, social, organizational, cognitive and perceptual issues. Consequently it draws on a variety of disciplinary traditions, including psychology, ergonomies. computer science, graphic and product design, anthropology and engineering HCI: Human Computer Interaction (4 Core-Tier1 hours, 4 Core-Tier2 hours) Core-Tieri Core-Tior2 Electives Includes hours hours HCUFoundations 4 N HCI/Designing Interaction N Y Y HC Programming Interactive Systems HCV/User-Centered Design & Testing HCI/New Interactive Technologies HCV Collaboration & Communication Y Y HCUStatistical Methods for HCI Y HCHHuman Factors & Security Y Y HC/Design-Oriented HCI HCI/Mixed, Augmented and Virtual Reality . HCl/Foundations [4 Core-Tier1 hours) Motivation: For end-users, the interface is the system. So design in this domain must be interaction-focused and human-centered Students need a different repertoire of techniques to address this than is provided elsewhere in the curriculum Topics: Contexts for HCI anything with a user interface eg, webpage, business applications mobile applications, and games Processes for user-centered development, es carly focus on users empirical testing, iterative design Different measures for evaluation er utility, efficiency, learnability, user satisfaction Usability heuristics and the principles of usability testing Physical apabilities that informanteraction design, cs, color perception, ergonomics Cognitive models that intiem interaction design e gattention, perception and recognition, movement, und memory gulls of expectation and execution Social models that inform interaction design, eg culture, communication networks and organizations Principles of good design and good designers, engineering tradeoffs Accessibility interfaces for differently-abled populations (eg, blind, motion-impaired) Interfaces for differently-aged population groups (eg. children, 80-) . . 3 Learning Outcomes Discuss why human-centered software development is important (Familiarity Summarize the basic precepts of psychological and social interaction (Familiarity) Develop and use a conceptual vocabulary for analyzing human interaction with software affordance conceptual model feedback and forth Usagel 4 Pelissa ser cealerad deste process that explicitly takes account of the fact that the user is not like the developer of the acquaintances are 5. Create and conduct a simple usability test for an existing software application Assessment HCI/Designing Interaction [4 Core-Tier2 hours) Motivation: CS students need a minimal set of well-established methods and tools to bring to interface construction Topics: . Principles of graphical user interfaces IGUI Elements of visual deaga (layout color, fonts, labeling) Task analyses including qualitative aspects of generating task analytic models Low-fidelity (paper) prototyping Quantitative evaluation techniques, eg kysttoke-level evaluation Help and documentation Handling human system failure User Interface standards Learning Outcomes 1. Foran identified user group, undertake and document an analysis of their needs [Assessment 2 Create a simple application, together with help and documentation, that supports a graphical user interface (Usage! 3. Conducta quantitative evaluation and discussicport the results. (Usage) 4 Discuss at least one national or international user interface design standard (Familiarity HCI/Programming Interactive Systems [Elective] Motivation: To take a user-experience-centered view of software development and then cover approaches and technologies to make that happen Topics: Software Architecture Patterns eg Model-View controller command objects, online, offline (cross reference PL Event Driven and Reactive Programming, where MVC is used in the context of event-driven programming) Interaction Design Patterns, visual hierarchy, navigational distance Event management and user interaction Gicometry management (cross-reference GV Cicometric Modelling) Choosing interaction styles and interaction techniques Presenting information navigation representation, manipulation Interface animation techniques og scene graphs) Widget classes and libraries Modem Gullbranes cg ios Andrund, JavaFXI GUI builders and Ul programming environments (cross- Telerende PBD Mobile Platfonns) Declarating Interface Specification Stylesheets and DOM Data-driven Applications database-backed web pages) Cross-platform design Design for resource-constrained devices te g small mobile devices) Learning Outcomes: Explain the importance of Model-View controller to interface programming (Familiarity] 2 Create an application with a modern graphical user interface (Usage] Identify commonalities and differences in Uls across different platforms. (Familiarity Explain and use GUI programming concepts event handling, constraint-based layout management, ce Familunity HCI/User-Centered Design and Testing [Elective) Motivation: An exploration of techniques to ensure that end-users are fully considered at all stages of the design process, from inception to implementation Topics: Approaches to and characteristics of the design process Functionality and ability requirements (cross-reference to SERequirements Engineering) Techniques for gathering requirements, eg interviews, surveys, ethnographic and contextualquiry Techniques and tools for the analysis and presentation of requirements et porta personas Prototyping techniques and tools es sketching storyboards, low.fidelity prototyping, wiretame Evaluation without users using both qualitative and quantitative techniques, es, walkthroughs, GOMS expert-based analysis, heuristics, guidelines, and standards Evaluation with users, es observation think-aloud, interview, survey, experiment Challenges to effective evaluation et simpling generalization Reporting the results of evaluation Internationalization, designing for csers from other cultures, cross-cultural Learning Outcomes: 1 Explain how user-centered design complements other software process models (Familiarity 2 Use to fillow fidelity prototyping techniques to gather and report user responses Usage 3 Choose appropriate methods to support the development of a specific Ut Assessment 4 Use avanety of techniques to evaluate a given Ul Assessment) 3 Compare the constraints and benefits of different evaluative methods Assessment . HCI/New Interactive Technologies [Elective) Motivation: As technologies evolve new interaction styles are made possible. This knowledge unit should be considered extensible to track emergent technology Topics: Choosing interaction styles and interaction techniques Representing information to users, navigation, representation, manupulation Approaches to design, implementation and evaluation of non-mouse interaction Touch and multi-touch interfaces o Shured, embodied, and large interfices New input modalities (such as sensor and location data) New Windows, eg iPhone, Android Speech recognition and natural language processing (cross reference is Natural Language Processing Wearable and tangible interfaces Pensive interaction and emotion Ubiquitous and content-aware interaction technologies (Uhicom) Bayesian inference is predictive text, guidad points Ambient peripheral display and incrastin
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


