Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Please let me know if you need anything else. Thank You! Problem 9-57 (Algo) Activity-Based Costing and Predetermined Overhead Allocation Rates (LO 9-3, 5, 6)
Please let me know if you need anything else. Thank You!
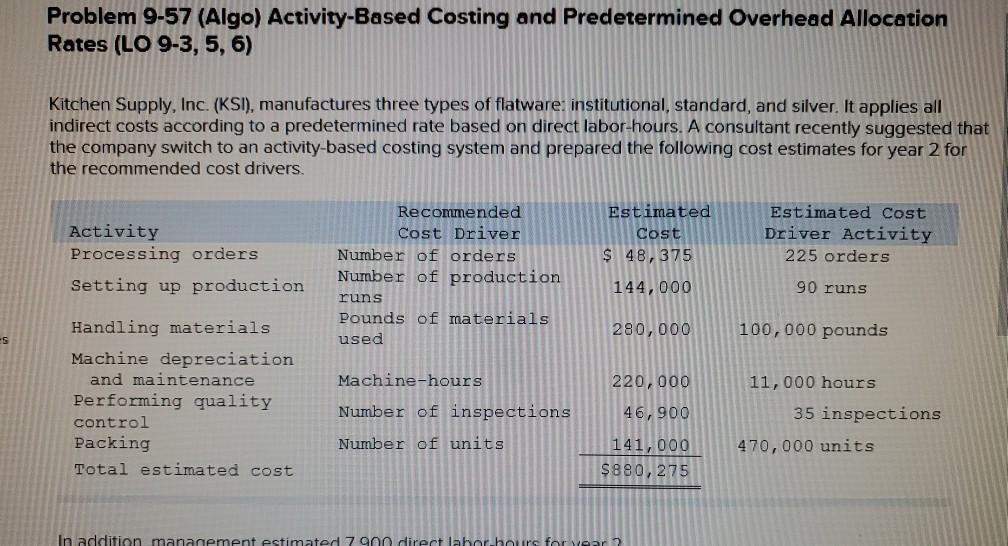
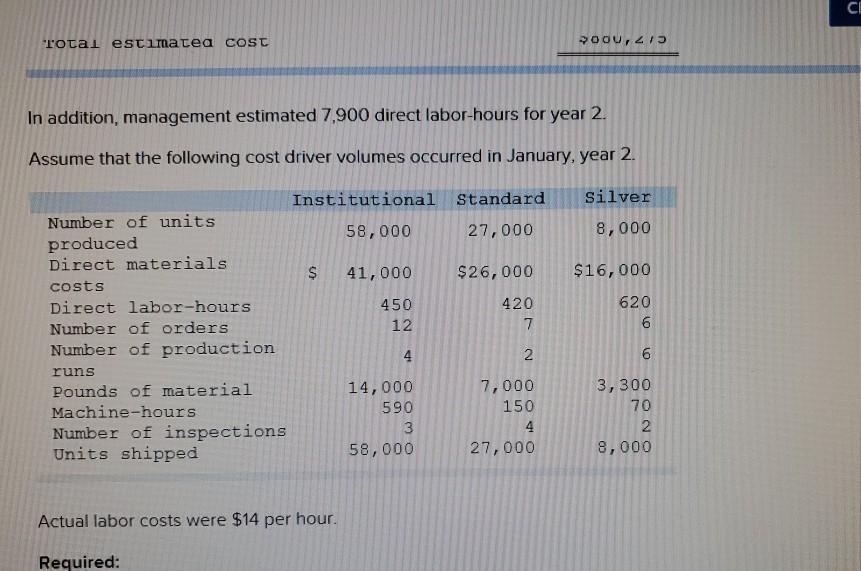
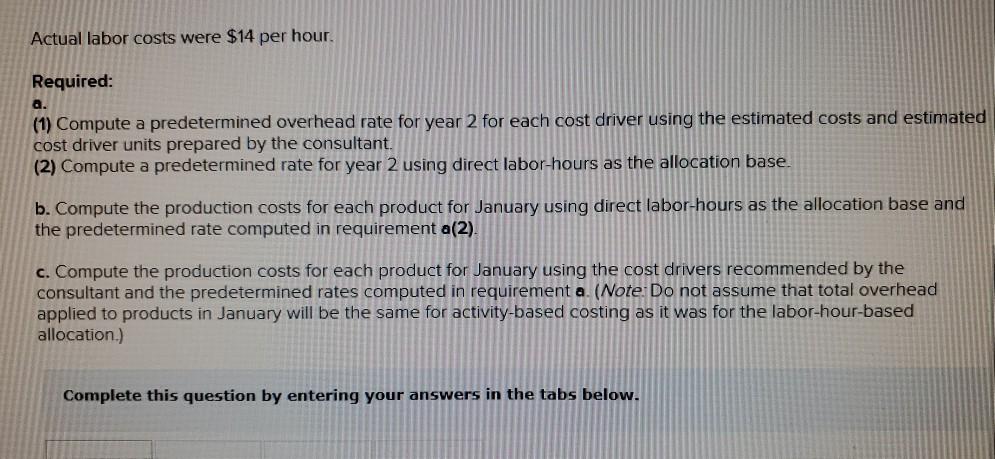
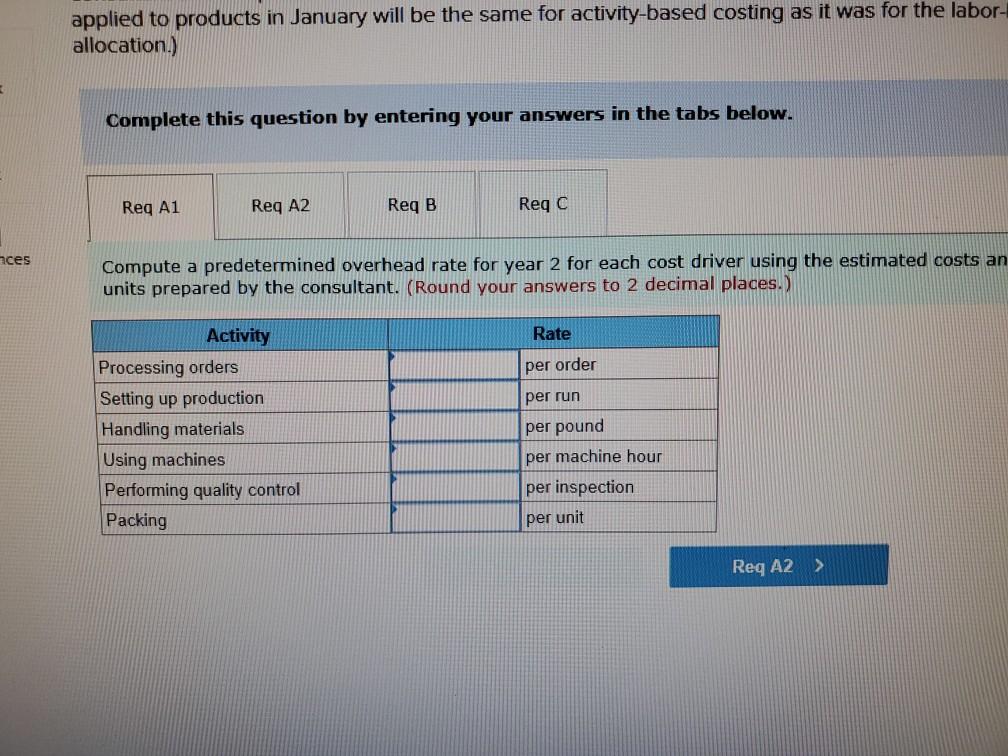
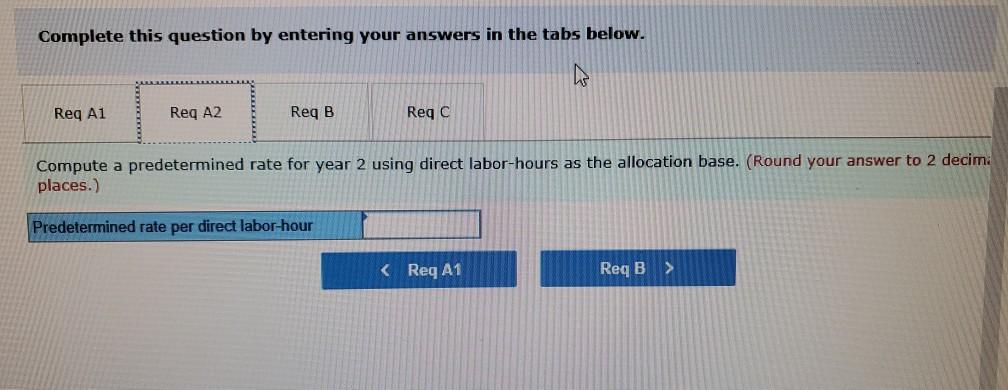
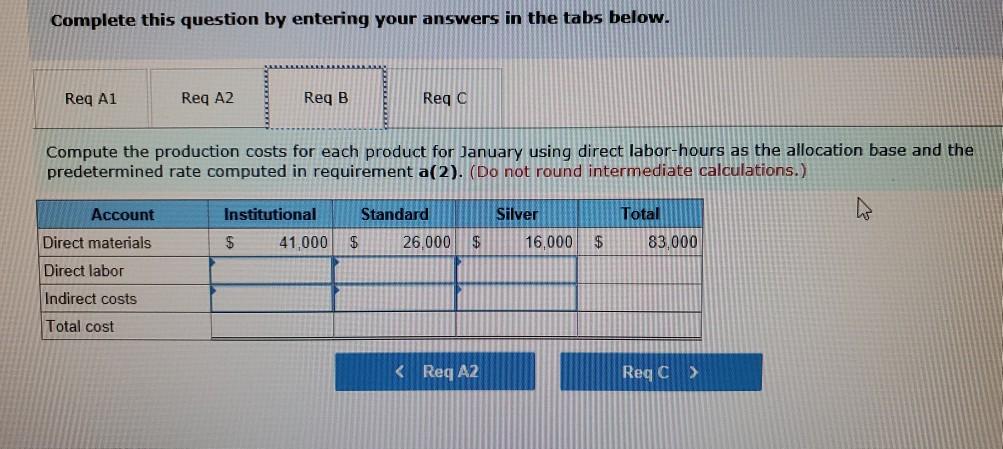
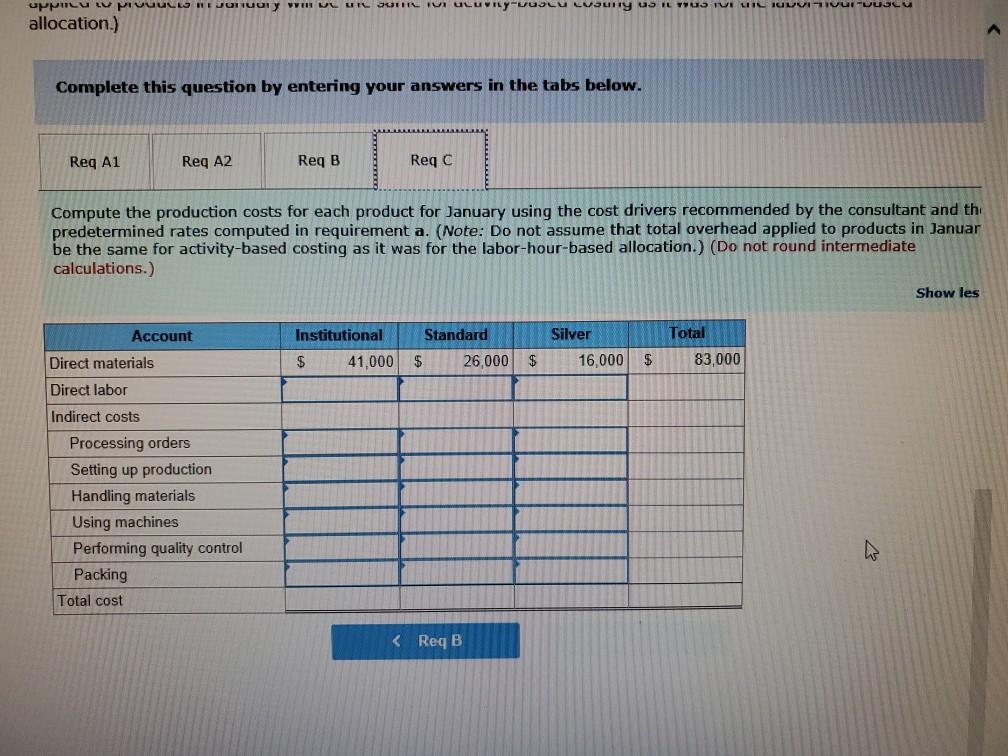
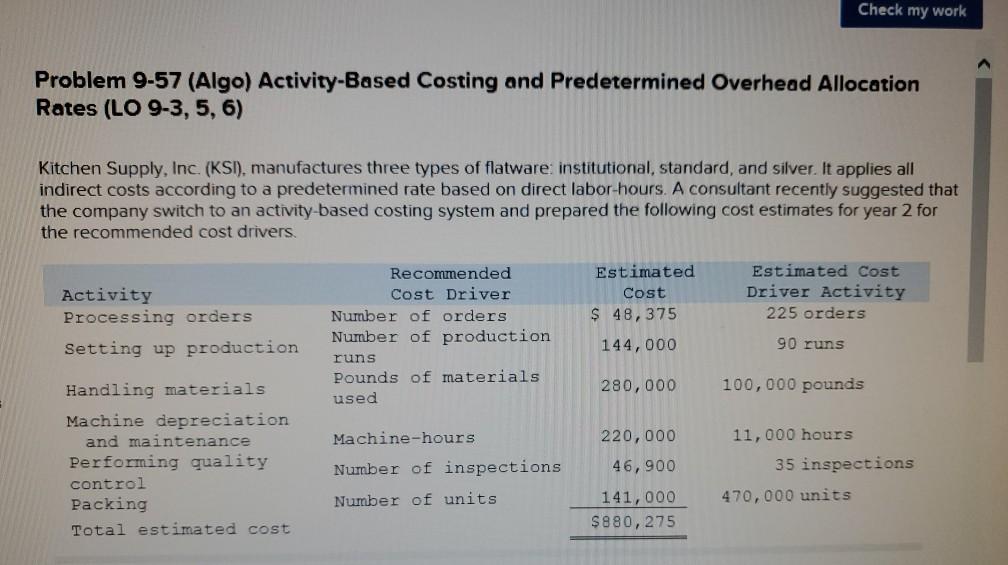
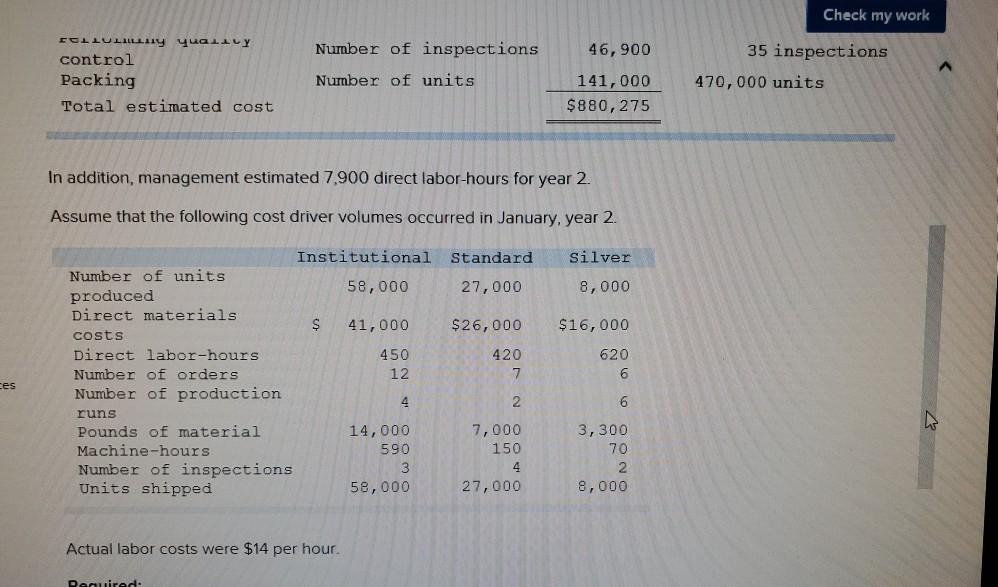
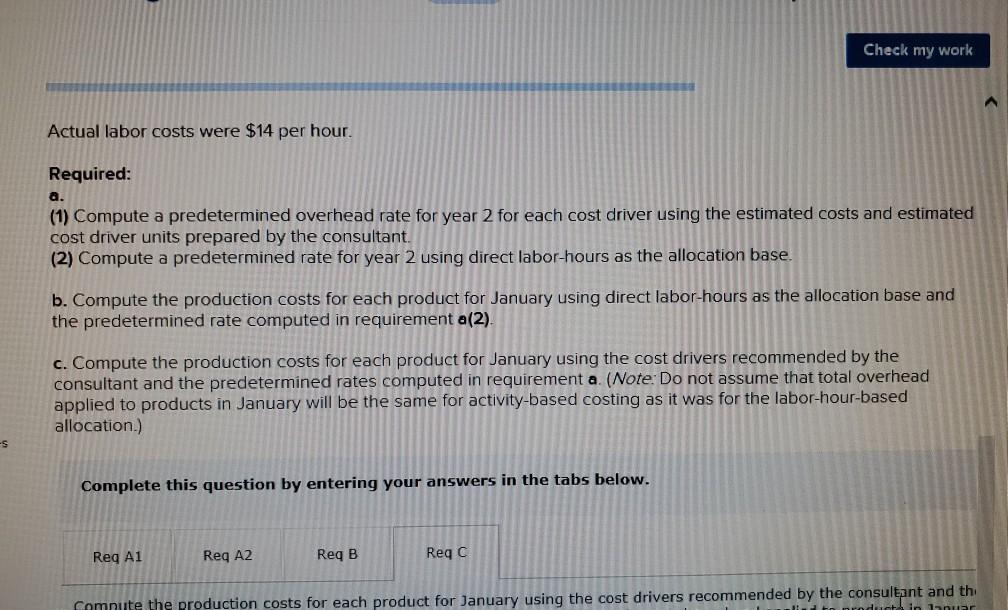
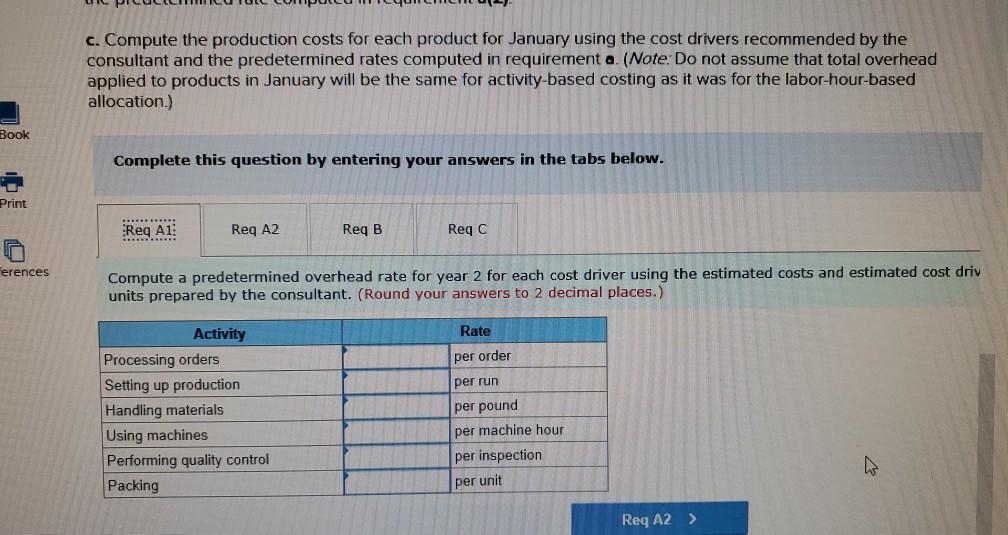
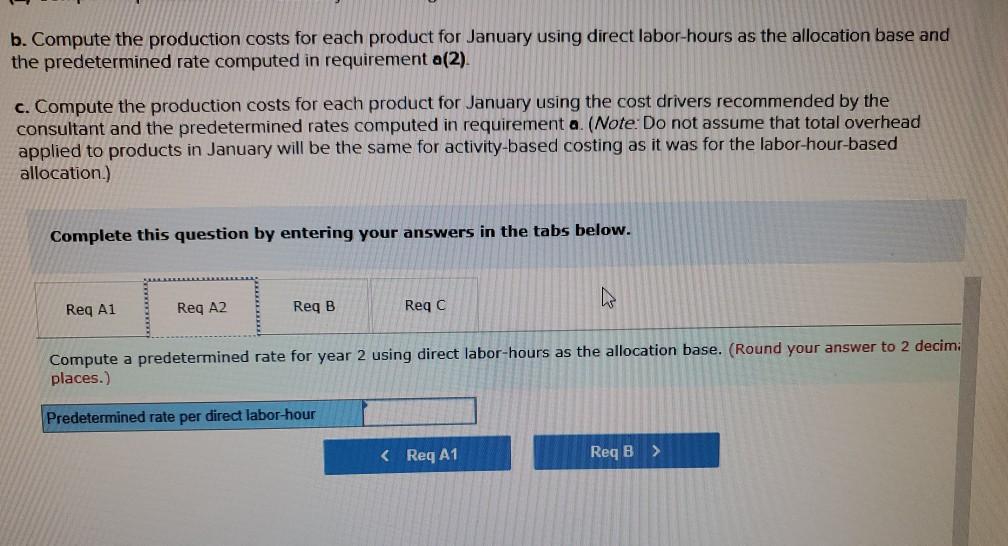
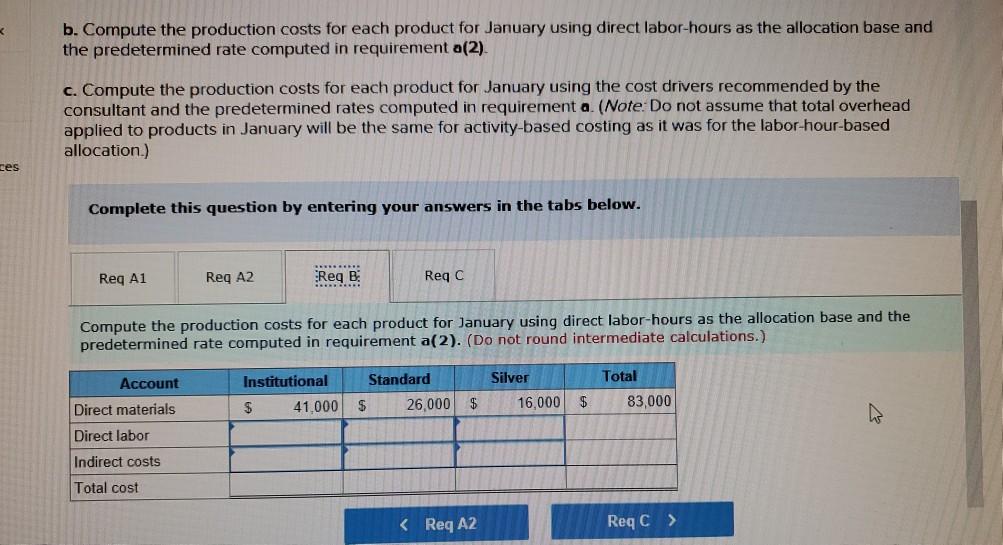
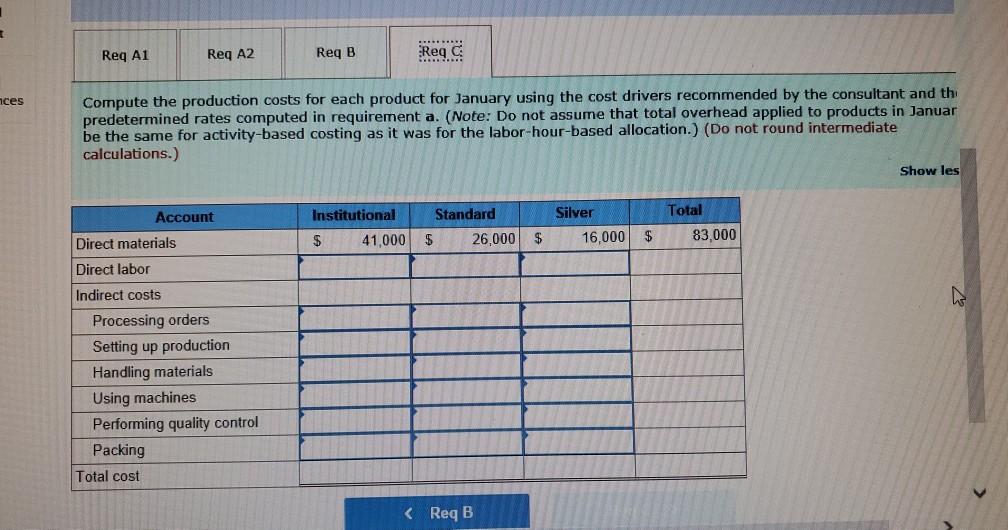
Problem 9-57 (Algo) Activity-Based Costing and Predetermined Overhead Allocation Rates (LO 9-3, 5, 6) Kitchen Supply, Inc. (KSI), manufactures three types of flatware: institutional, standard, and silver. It applies all indirect costs according to a predetermined rate based on direct labor-hours. A consultant recently suggested that the company switch to an activity-based costing system and prepared the following cost estimates for year 2 for the recommended cost drivers. Activity Processing orders Setting up production Estimated Cost $ 48,375 Estimated cost Driver Activity 225 orders Recommended Cost Driver Number of orders Number of production runs Pounds of materials used 144,000 90 runs 280,000 100,000 pounds Machine-hours 220,000 Handling materials Machine depreciation and maintenance Performing quality control Packing Total estimated cost Number of inspections 46,900 11,000 hours 35 inspections 470,000 units Number of units 141,000 $880, 275 In addition management estimated 790 direct labor hours for year 2 CI Total estimatea COST Podu, 2/3 In addition, management estimated 7,900 direct labor-hours for year 2. Assume that the following cost driver volumes occurred in January, year 2. Silver Institutional Standard 58,000 27,000 8,000 $ 41,000 $26,000 $16,000 Number of units produced Direct materials costs Direct labor-hours Number of orders Number of production 620 450 12 420 7 4 N 0 runs 3,300 70 Pounds of material Machine-hours Number of inspections Units shipped 14,000 590 3 58,000 7,000 150 4 27,000 2 8,000 Actual labor costs were $14 per hour. Required: Actual labor costs were $14 per hour. Required: a. (1) Compute a predetermined overhead rate for year 2 for each cost driver using the estimated costs and estimated cost driver units prepared by the consultant (2) Compute a predetermined rate for year 2 using direct labor-hours as the allocation base. b. Compute the production costs for each product for January using direct labor-hours as the allocation base and the predetermined rate computed in requirement a(2) c. Compute the production costs for each product for January using the cost drivers recommended by the consultant and the predetermined rates computed in requirement a. (Note: Do not assume that total overhead applied to products in January will be the same for activity-based costing as it was for the labor-hour-based allocation.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. applied to products in January will be the same for activity-based costing as it was for the labor- allocation.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Reg A1 Reg A2 Req B Reqc nces Compute a predetermined overhead rate for year 2 for each cost driver using the estimated costs an units prepared by the consultant. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Rate per order per run Activity Processing orders Setting up production Handling materials Using machines Performing quality control Packing per pound per machine hour per inspection per unit Reg A2 > Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 Req A2 Req B Reqc Compute a predetermined rate for year 2 using direct labor-hours as the allocation base. (Round your answer to 2 decim. places.) Predetermined rate per direct labor-hour Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 Req A2 Req B Reg C Compute the production costs for each product for January using direct labor-hours as the allocation base and the predetermined rate computed in requirement a(2). (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Account Total Institutional Standard $ 41,000 $ 26,000 Silver 16,000 Direct materials $ $ 83.000 Direct labor Indirect costs Total cost UPLU PUULLNEJURUury RULUR SUR FUI ULUviy-vucu Luully US 03 VELICIOUViivuruus allocation.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Reg A1 Reg A2 Req B Reqc Compute the production costs for each product for January using the cost drivers recommended by the consultant and th predetermined rates computed in requirement a. (Note: Do not assume that total overhead applied to products in Januar be the same for activity-based costing as it was for the labor-hour-based allocation.) (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Show les Total Account Direct materials Institutional Standard $ 41,000 $ 26,000 $ Silver 16,000 $ 83,000 Direct labor Indirect costs Processing orders Setting up production Handling materials Using machines Performing quality control Packing Total cost b. Compute the production costs for each product for January using direct labor-hours as the allocation base and the predetermined rate computed in requirement a(2). c. Compute the production costs for each product for January using the cost drivers recommended by the consultant and the predetermined rates computed in requirement a. (Note: Do not assume that total overhead applied to products in January will be the same for activity-based costing as it was for the labor-hour-based allocation.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req A1 Reg A2 Req B Reqc Compute a predetermined rate for year 2 using direct labor-hours as the allocation base. (Round your answer to 2 decimi places.) Predetermined rate per direct labor-hour b. Compute the production costs for each product for January using direct labor-hours as the allocation base and the predetermined rate computed in requirement (2) c. Compute the production costs for each product for January using the cost drivers recommended by the consultant and the predetermined rates computed in requirement a. (Note: Do not assume that total overhead applied to products in January will be the same for activity-based costing as it was for the labor-hour-based allocation.) ces Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. . Req A1 Reg A2 Req B Reqc HERE Compute the production costs for each product for January using direct labor-hours as the allocation base and the predetermined rate computed in requirement a(2). (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Institutional Total Silver 16,000 Standard $ 26,000 Account Direct materials Direct labor $ 41,000 $ $ 83,000 Indirect costs Total cost Req A1 Req A2 Req B ... Reg ...... nces Compute the production costs for each product for January using the cost drivers recommended by the consultant and th predetermined rates computed in requirement a. (Note: Do not assume that total overhead applied to products in Januar be the same for activity-based costing as it was for the labor-hour-based allocation.) (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Show les Account Silver Institutional $ 41,000 Standard $ 26,000 Total 83,000 $ 16,000 $ Direct materials Direct labor Indirect costs Processing orders Setting up production Handling materials Using machines Performing quality control Packing Total costStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


