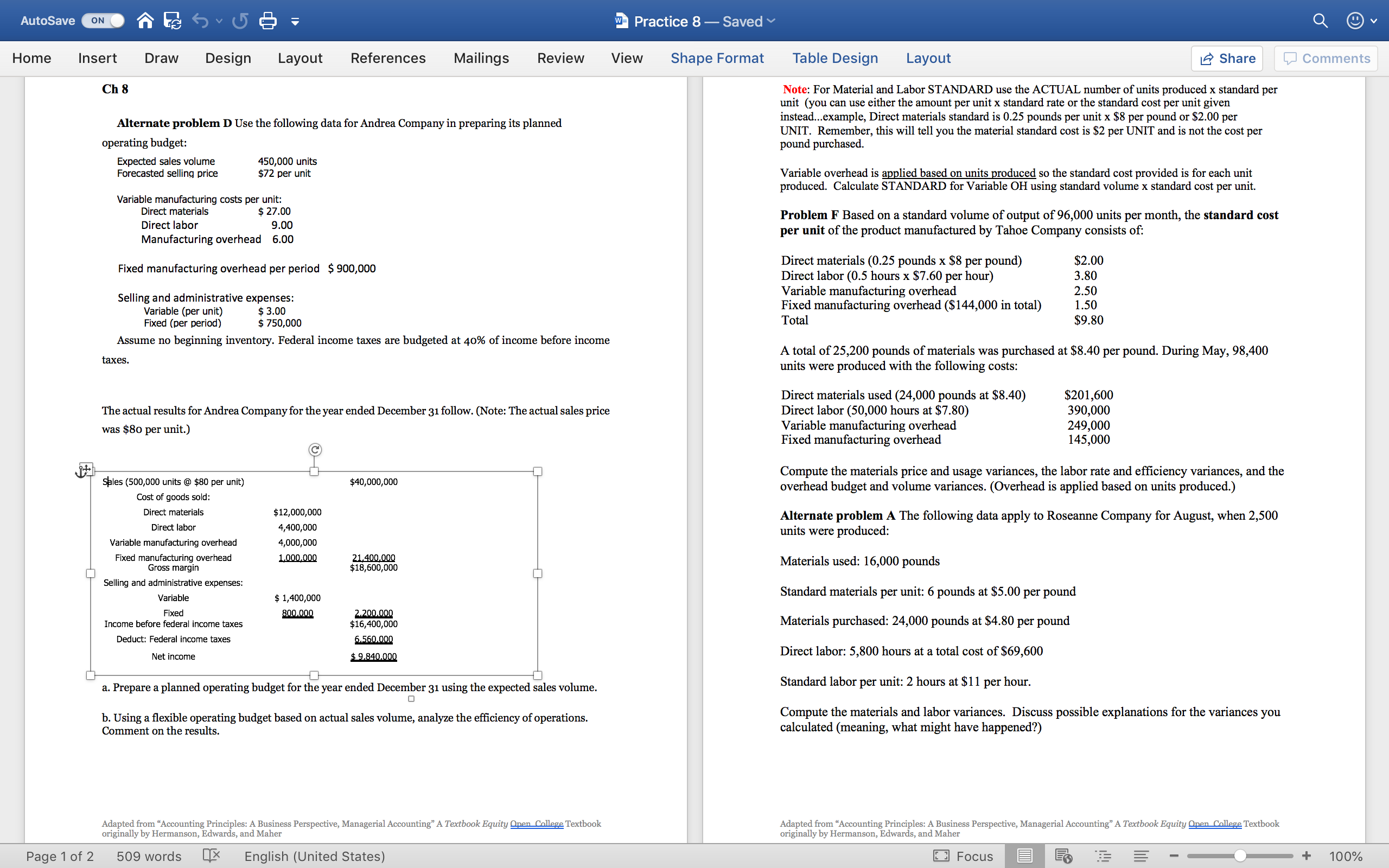
PLEASE ONLY USE EXCEL PLEASE AND SCREENSHOT IT. THANK YOU.
AutoSave ON w Practice 8 - Saved Q Q v Home Insert Draw Design Layout References Mailings Review View Shape Format Table Design Layout Share Comments Ch 8 Note: For Material and Labor STANDARD use the ACTUAL number of units produced x standard per unit (you can use either the amount per unit x standard rate or the standard cost per unit given Alternate problem D Use the following data for Andrea Company in preparing its planned instead...example, Direct materials standard is 0.25 pounds per unit x $8 per pound or $2.00 per UNIT. Remember, this will tell you the material standard cost is $2 per UNIT and is not the cost per operating budget pound purchased. Expected sales volume 450,000 units Forecasted selling price $72 per unit Variable overhead is applied based on units produced so the standard cost provided is for each unit produced. Calculate STANDARD for Variable OH using standard volume x standard cost per unit. Variable manufacturing costs per unit: Direct materials $ 27.00 Direct labor 9.00 Problem F Based on a standard volume of output of 96,000 units per month, the standard cost Manufacturing overhead 6.00 per unit of the product manufactured by Tahoe Company consists of Fixed manufacturing overhead per period $ 900,000 Direct materials (0.25 pounds x $8 per pound) $2.00 Direct labor (0.5 hours x $7.60 per hour) 3.80 Selling and administrative expenses: Variable manufacturing overhead 250 Variable (per unit) $ 3.00 Fixed manufacturing overhead ($144,000 in total) 1.50 Fixed (per period $ 750,000 Tota $9.80 Assume no beginning inventory. Federal income taxes are budgeted at 40% of income before income taxes. A total of 25,200 pounds of materials was purchased at $8.40 per pound. During May, 98,400 units were produced with the following costs Direct materials used (24,000 pounds at $8.40) $201,600 The actual results for Andrea Company for the year ended December 31 follow. (Note: The actual sales price Direct labor (50,000 hours at $7.80) 390,000 was $80 per unit.) Variable manufacturing overhead 249.000 Fixed manufacturing overhead 145,000 Sales (500,000 units @ $80 per unit) $40,000,000 Compute the materials price and usage variances, the labor rate and efficiency variances, and the overhead budget and volume variances. (Overhead is applied based on units produced.) Cost of goods sold: Direct materials $12,000,000 Alternate problem A The following data apply to Roseanne Company for August, when 2,500 Direct labor 4,400,000 Variable manufacturing overhead 4,000,000 units were produced: Fixed manufacturing overhead Gross margin 1000,000 21,400,000 $18,600,000 Materials used: 16,000 pounds Selling and administrative expenses: Variable $ 1,400,000 Standard materials per unit: 6 pounds at $5.00 per pound Fixed 800.000 2.200.000 Income before federal income taxes $16,400,00 Materials purchased: 24,000 pounds at $4.80 per pound Deduct: Federal income taxes 6.560.000 Net income $ 9.840.000 Direct labor: 5,800 hours at a total cost of $69,600 a. Prepare a planned operating budget for the year ended December 31 using the expected sales volume. Standard labor per unit: 2 hours at $11 per hour. b. Using a flexible operating budget based on actual sales volume, analyze the efficiency of operations. Compute the materials and labor variances. Discuss possible explanations for the variances you Comment on the results. calculated (meaning, what might have happened?) Adapted from "Accounting Principles: A Business Perspective, Managerial Accounting" A Textbook Equity Open College Textbook Adapted from "Accounting Principles: A Business Perspective, Managerial Accounting" A Textbook Equity Open College Textbook originally by Hermanson, Edwards, and Maher originally by Hermanson, Edwards, and Maher Page 1 of 2 509 words LX English (United States) Focus + 100%