please please help me

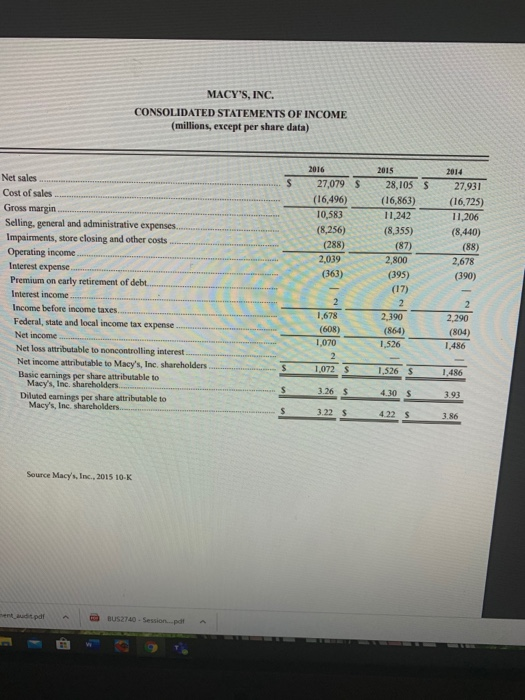
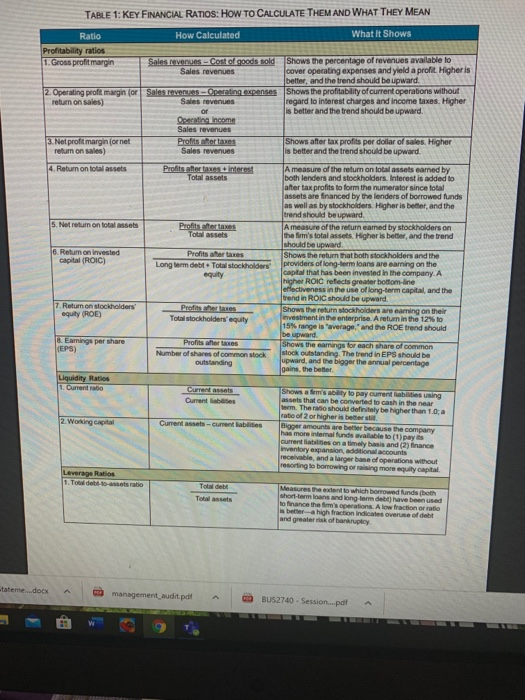
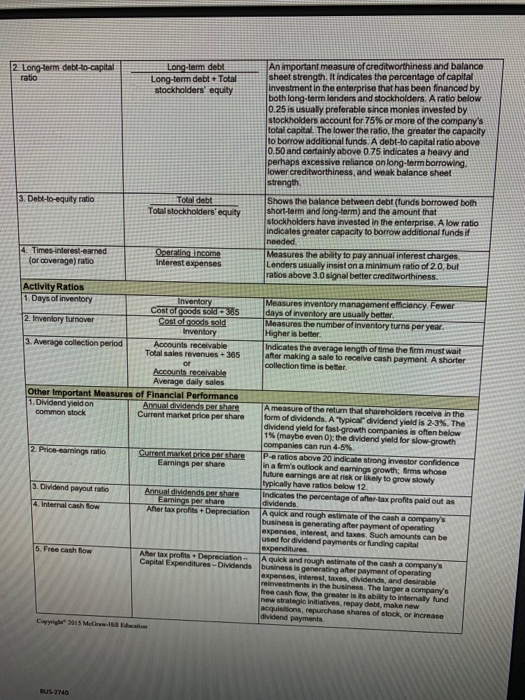
Financial Statement Analysis Assignment Name: Using the financial ratios provided in the Key Financial Ratios file and the financial statement information for Macy's, Inc., calculate the following ratios for Macy's for the years 2015 and 2016. 2016 Financial Ratio 1. Gross profit margin. 2. Operating profit margin. 3. Net profit margin. 4. Times interest earned coverage. 5. Return on shareholder's equity. 6. Return on assets. 7. Debt-to-equity ratio. 8. Days of inventory. 9. Inventory turnover ratio. 10. Average collection period. 1-Based on these ratios, did Macys financial performance improve, weaken, or remain about the same from 2015 to 2016? 2-Explain your answer. MACY'S, INC. CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME (millions, except per share data) 2016 S 27,079 (16,496) 10,583 (8,256) 2015 28,105 $ (16,863) 11,242 (8,355) 2014 27,931 (16,725) 11,206 (8,440) (88) 2,678 (390) (288) 2.039 (87) 2,800 ........... Net sales. Cost of sales Gross margin...... Selling, general and administrative expenses........... Impairments, store closing and other costs ................... Operating income ...... Interest expense Premium on early retirement of debt..... .................... Interest income ............................ Income before income taxes......................................................... Federal, state and local income tax expense.................................... Net income Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interest .................................. Net income attributable to Macy's, Inc. shareholders........................ Basic earnings per share attributable to Macy's, Inc. shareholders. Diluted eamings per share attributable to Macy's, Inc. shareholders... $ 2.290 1.486 1,486 s 3.268 4.30 $ 393 3.22 S Source Macy's, Inc., 2015 10-K entdit.pdf BUS2740 - Session.pdf TABLE 1: KEY FINANCIAL RATIOS: HOW TO CALCULATE THEM AND WHAT THEY MEAN How Calculated What It Shows Ratio Profitability ratios 1. Gross profit margin Sales.e u - Cost of goods sold Sales revenues Shows the percentage of revenues available to cover operating expenses and yield a profit. Higher is better, and the trend should be upward. Shows the profitability of current operations without regard to interest charges and income taxes. Higher lis better and the trend should be upward. Operating expenses 2. Operating profit margin for Sales revenues return on sales) Operating income Sales revenues Profits afer taxes 3. Net profit margin lornet return on sales) Shows after tax profits per dollar of sales. Higher is better and the trend should be upward. 4. Return on total assets Profits after 5. Net return on total assets Profits ter taxes Total assets 16. Return on invested capital (ROIC) Profits for taxes Long term debt. Tot i stockholders Ameasure of the return on total assets earned by both lenders and stockholders. Interest is added to after tax profits to form the numerator since total assets are financed by the lenders of borrowed funds as well as by stockholders. Higher is better, and the trend should be upward. Ameasure of the returneamed by stockholders on the firm's total assets. Higher is better, and the trend should be upward. Shows the return that both stockholders and the providers of long-term loans are eaming on the capital that has been invested in the company. A higher ROIC refects greater bottom line rectiveness in the use of long-term capital and the trend in ROIC should be upward Shows the return stockholders are earning on their investment in the enterprise. A return in the 12% to 15% range is "average, and the ROE trend should be upward. shows the comings for each share of common stock outstanding. The trend in EPS should be lupward, and the bigger the annual percentage gains the better 7. Return on stockholders' equity ( ROE) Profiteres Total stockholderseguity Emmings per (EPS) Profits where Number of shares of common stock outstanding Currentes et abilities Shows m y to pay current abilities using assets that can be converted to cash in the near term. The radio should definitely be higher than 1.0,a ratio of 2 or higher is better til Bigger amounts are better because the company has more internal funds available to (1) pays current liabilities on a timely basis and (2) Finance Inventory expansion, additional accounts receivable, and a larger base of operations without resorting to borrowing raising more equity capital Measures the extent to which borrowed and both short-term loans and long term de have been used to finance the fm's operations. A low fraction or ratio is beter a high fraction indicates overuse of debt and greater risk of bankruptcy tateme...docx management audit pdt BUS2740 - Session.pdf 2. Long-term debt-to-capital Long-tam deb Long-term debt Total stockholders' equity An important measure of creditworthiness and balance sheet strength. It indicates the percentage of capital investment in the enterprise that has been financed by both long-term lenders and stockholders. A ratio below 0.25 is usually preferable since monies invested by stockholders account for 75% or more of the company's total capital. The lower the ratio, the greater the capacity to borrow additional funds. A debt-to capital ratio above 0.50 and certainly above 0.75 indicates a heavy and perhaps excessive reliance on long-term borrowing. lower creditworthiness, and weak balance sheet strength 3. Debt-to-equity ratio Total debt Total stockholders' equity Shows the balance between debt (funds borrowed both short-term and long-term) and the amount that stockholders have invested in the enterprise. A low ratio indicates greater capacity to borrow additional funds if nended Measures the ability to pay annual interest charges Lenders usually insist on a minimum ratio of 20, but ratios above 3.0 signal better creditworthiness. 4. Times interest-earned for coverage) ratio Operating income Interest expenses Activity Ratios 1. Days of inventory 2. Inventory turnover Inventory Cost of goods sold +385 Cost of goods sold Inventory Accounts receivable Total sales revenues + 365 3. Average collection period Measures inventory management efficiency. Fewer days of inventory are usually better. Measures the number of inventory turns per year. Higher is better. Indicates the average length of time the firm must wait after making a sale to receive cash payment. A shorter collection time is better Accounts receivable Average daily sales Other Important Measures of Financial Performance 1. Olidend yieldon Annual dividends pertshare common stock Current market price per share 2. Price samnings ratio Current market pricepershare Earnings per share 3. Dividend payout ratio 4. Internal Cashow Annual dividends per share Earnings per share Alertax profits + Depreciation A measure of the return that shareholders receive in the form of dividends. A typical dividend yield is 2-3%. The dividend yield for fast-growth companies is often below 1% (maybe even Oy the dividend yield for slow-growth companies can run 4-5% P-e ratios above 20 Indicata strong investor confidence in a firm's outlook and earnings growth; firms whose future earnings are at risk or likely to grow slowly typically have ratios below 12 Indicates the percentage of a r-tax profits paid out as dividends. A quick and rough estimate of the cash a company's business is generating after payment of operating expenses, Interest, and taxes. Such amounts can be used for dividend payments or funding capital expenditures A quick and rough estimate of the cash a company's business is generating after payment of operating expenses, interest, taxes, dividends, and desirable reinvestments in the business. The larger a company's free cash flow, the greater is its ability to internal fund new strategic initiatives, repay debt, make new acquisitions, repurchase shares of stock, or increase dividend payments Ater tax profits. Depreciation - Capital Expenditures-Dividends Copyright 2015 M BUS-2740